中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (42): 6278-6283.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.42.007
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
一氧化氮及一氧化氮合酶抑制剂对髓核细胞线粒体功能的影响
周建国1,杨 操2,熊蠡茗2
- 1赣州市人民医院骨科,江西省赣州市 341000;2华中科技大学同济医学院附属协和医院骨科,湖北省武汉市 430022
Effects of nitric oxide and nitric oxide synthase inhibitors on mitochondrial function of nucleus pulposus cells
Zhou Jian-guo1, Yang Cao2, Xiong Li-ming2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, People’s Hospital of Ganzhou, Ganzhou 341000, Jiangxi Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Union Hospital Affiliated to Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan 430022, Hubei Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
髓核:是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨板与纤维环之间。由纵横交错的纤维网状结构即软骨细胞和蛋白多糖黏液样基质构成的弹性胶冻物质。婴幼儿时期的髓核含水量为80%-90%,即使到了老年,其含水量也在70%上下。
线粒体:是一种存在于大多数细胞中的由两层膜包被的细胞器,是细胞中制造能量的结构,是细胞进行有氧呼吸的主要场所,被称为“power house”。其直径在0.5-1.0 μm。
文题释义:
髓核:是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨板与纤维环之间。由纵横交错的纤维网状结构即软骨细胞和蛋白多糖黏液样基质构成的弹性胶冻物质。婴幼儿时期的髓核含水量为80%-90%,即使到了老年,其含水量也在70%上下。
线粒体:是一种存在于大多数细胞中的由两层膜包被的细胞器,是细胞中制造能量的结构,是细胞进行有氧呼吸的主要场所,被称为“power house”。其直径在0.5-1.0 μm。
.jpg) 文题释义:
髓核:是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨板与纤维环之间。由纵横交错的纤维网状结构即软骨细胞和蛋白多糖黏液样基质构成的弹性胶冻物质。婴幼儿时期的髓核含水量为80%-90%,即使到了老年,其含水量也在70%上下。
线粒体:是一种存在于大多数细胞中的由两层膜包被的细胞器,是细胞中制造能量的结构,是细胞进行有氧呼吸的主要场所,被称为“power house”。其直径在0.5-1.0 μm。
文题释义:
髓核:是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨板与纤维环之间。由纵横交错的纤维网状结构即软骨细胞和蛋白多糖黏液样基质构成的弹性胶冻物质。婴幼儿时期的髓核含水量为80%-90%,即使到了老年,其含水量也在70%上下。
线粒体:是一种存在于大多数细胞中的由两层膜包被的细胞器,是细胞中制造能量的结构,是细胞进行有氧呼吸的主要场所,被称为“power house”。其直径在0.5-1.0 μm。摘要
背景:一氧化氮可通过诱发炎性细胞因子的释放,进而干扰细胞线粒体功能,加速椎间盘损伤及退变,是压力等外界因子导致椎间盘退变的重要炎性细胞递质。
目的:分析一氧化氮及一氧化氮合酶抑制剂烟酰胺对兔髓核细胞线粒体功能的影响及其与髓核细胞生物学行为的相关性。
方法:将体外培养的兔腰椎间盘髓核细胞分为6组,正常空白对照组、10 μmol/L 硝普钠组、100 μmol/L硝普钠组、200 μmol/L硝普钠组、0.05 g/L烟酰胺组(100 μmol/L硝普钠+0.05 g/L烟酰胺)、0.5 g/L烟酰胺组(加入100 μmol/L硝普钠和0.5 g/L烟酰胺干预),向各组培养基内加入不同剂量的一氧化氮供体硝普钠及烟酰胺进行干预。干预3 d后检测髓核细胞增殖活力、细胞内ATP浓度、细胞内活性氧水平、细胞内一氧化氮合酶活性以及髓核细胞线粒体膜电位。
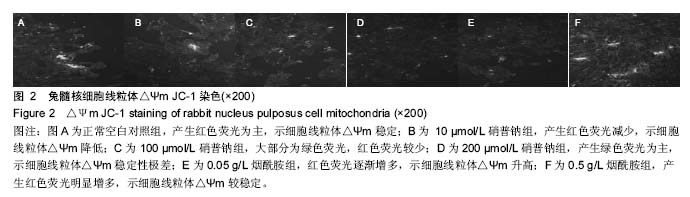
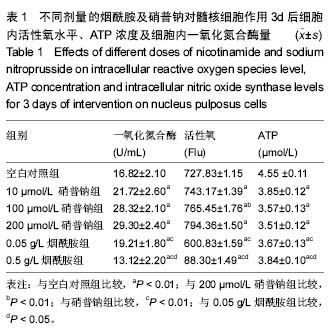
结果与结论:①兔髓核细胞经不同浓度的硝普钠干预3 d后,细胞内一氧化氮合酶量随硝普钠浓度加大而增加、ATP浓度则随着减小,与正常对照组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01);②硝普钠组可提高髓核细胞内活性氧水平, 烟酰胺组呈剂量依赖性改善因硝普钠干预下的细胞内活性氧水平(P < 0.01);③硝普钠组可引起髓核细胞膜电位下降,烟酰胺组可减轻因硝普钠引起的膜电位下降(P < 0.01);④与硝普钠组比较烟酰胺组也呈剂量依赖性促进髓核细胞增殖(P < 0.01)及改善髓核细胞的增殖活力,2组之间差异有显著性意义(P < 0.01);⑤结果说明,过量一氧化氮可损伤兔髓核细胞线粒体功能而导致细胞能量代谢障碍,烟酰胺能够通过抑制一氧化氮的合成以及保护椎间盘细胞线粒体功能和改善细胞能量代谢,有助于预防椎间盘退变。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-6651-2701(周建国)
中图分类号:

.jpg) 文题释义:
髓核:是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨板与纤维环之间。由纵横交错的纤维网状结构即软骨细胞和蛋白多糖黏液样基质构成的弹性胶冻物质。婴幼儿时期的髓核含水量为80%-90%,即使到了老年,其含水量也在70%上下。
线粒体:是一种存在于大多数细胞中的由两层膜包被的细胞器,是细胞中制造能量的结构,是细胞进行有氧呼吸的主要场所,被称为“power house”。其直径在0.5-1.0 μm。
文题释义:
髓核:是乳白色半透明胶状体,富于弹性,为椎间盘结构的一部分,位于两软骨板与纤维环之间。由纵横交错的纤维网状结构即软骨细胞和蛋白多糖黏液样基质构成的弹性胶冻物质。婴幼儿时期的髓核含水量为80%-90%,即使到了老年,其含水量也在70%上下。
线粒体:是一种存在于大多数细胞中的由两层膜包被的细胞器,是细胞中制造能量的结构,是细胞进行有氧呼吸的主要场所,被称为“power house”。其直径在0.5-1.0 μm。