| [1] Valentini P,Abensur D.Maxillary sinus floor elevation for implant placement with demineralized freeze-dried bone and bovine bone (bio-oss):a clinical study of 20 patients.Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1997;17(3):232-241.
[2] Lin FH,Liao CJ,Chen KS,et al.Preparation of a biphasic porous bioceramic by heating bovine cancellous bone with Na4P2O7•10H2O addition.Biomaterials. 1999;20: 475-484.
[3] 郭朝邦,金海波,杨筠,等.煅烧牛松质骨制备β-TCP/HAP/ Ca2P2O7多孔陶瓷反应机制研究[J].稀有金属材料与工程,2010,39(6):1071-1074.
[4] 丁云飞,张学斌,凤仪,等.牛骨原生物陶瓷的制备及其性能研究[J].合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2010,33(6):804-807.
[5] 李彦林,郭洪涛,韩睿,等.双相陶瓷样生物骨修复节段性骨缺损实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2009,23(5): 607-611.
[6] Gao J,Knaack D,Goldberg VM,et al.Osteochondral defect repair by demineralized cortical bone matrix.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2004;(427 Suppl):62-66.
[7] 陈建明,李彦林,金耀峰,等.兔骨髓基质干细胞在不同脱钙骨基质材料上的增殖[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2009,13(51):10021-10025.
[8] Edward JB,Benfer RA,Morris JS.the effects of dry ashing on the composition of human and animal bone.Biol Trace Elem Res.1990;25(3):219-231.
[9] 修晓光,李彦林,李雅娜,等.双相陶瓷生物骨的制备和细胞相容性研究[J].昆明医学院学报, 2005,26(2):59-62.
[10] Lu M,Rabie AB.The effect of demineralized intramembranous bone matrix and basic fibroblast growth factor on the healing of allogeneic intramembranous bone grafts in the rabbit.Arch Oral Biol.2002;47(12):831-841.
[11] 孙世荃.同种异体骨的制备方法及其成骨效果[J].中华外科杂志,1996,34(7):473-475.
[12] Hashizume H,Tamaki T,Oura H,et a1.Changes in the extracellular matrix on the surface of sintered bovine bone implanted in the femur of a rabbit:an immunohistochemical study.J Orthop Sci. 1998;3(1): 42-53.
[13] 陈伟,周密,左剑,等. FTIR 光谱方法对比分析少年和老年软骨成分含量[J].光谱学与光谱分析, 2007,27(4):683-685.
[14] Wegrzyn J,Roux JP,Farlay D,et al.The role of bone intrinsic properties measured by infrared spectroscopy in whole lumbar vertebra mechanics: Organic rather than inorganic bone matrix? Bone.2013;56(2):229-233.
[15] Lin SY,Li MJ,Che WT.FT-IR and Raman vibrational microspectroscopies used for spectral biodiagnosis of human tissues.Spectroscopy.2007;21:1-30.
[16] Gopi D,Indira J,Prakash VC,et al.spectroscopic characterization of porous nanohydroxyapatite synthesized by a novel amino acid soft solution freezing method.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc.2009;74(1):282-284.
[17] Markovic S,Veselinovic L,Lukic MJ,et al.synthetical bone-like and biological hydroxyapatites: a comparative study of crystal structure and morphology.Biomed Mater.2011;6(4):045005.
[18] Gibson IR,Bonfield W.novel synthesis and characterization of an ab-type carbonate-substituted hydroxyapatite.J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;59(4): 697-708.
[19] Gauthier O,Bouler JM,Aguado E,et al.elaboration conditions influence physicochemical properties and in vivo bioactivity of macroporous biphasic calcium phosphate ceramics.J Mater Sci Mater Med.1999; 10(4):199-204.
[20] Katthagen BD.Bone regeneration with bone substitutes.1st ed.Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press,1983.
[21] Zyman ZZ,Tkachenko MV,Polevodin DV.preparation and characterization of biphasic calcium phosphate ceramics of desired composition.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2008;19(8):2819-2825.
[22] 沈娟,左奕,王学江,等.生物磷灰石中羟基的存在形式及晶体结构[J].化学进展,2009,21(6):1357-1363.
[23] 翟倩倩,赵士贵,王孝海,等.仿生纳米含硅羟基磷灰石的合成与表征[J].无机材料学报,2013,28(1):58-62.
[24] 陆裕朴,晋少汀,葛宝丰.实用骨科学[M].北京:人民军医出版社,1991:63-72.
[25] Lin FH,Liao CJ,Chen KS,et al.preparation of high-temperature stabilized beta-tricalcium phosphate by heating deficient hydroxyapatite with na4p2o7 x 10h2o addition.Biomaterials. 1998;19(11-12): 1101-1107.
[26] Raynaud S,Champion E,Bernache-Assollant D.calcium phosphate apatites w-ith variable ca/p atomic ratio ii.calcination and sintering. Biomaterials. 2002;23(4):1073-1080.
[27] Guo H,Su J,Wei J,et al.Biocompatibility and osteogenicity of degradable Ca-deficient hydroxyapatite scaffolds from calcium phosphate cement for bone tissue engineering.Act Biomaterialia. 2009;5:268-278.
[28] Hollister SJ.Porous scaffold design for tissue enginerring. Nat Mater.2005;4(7):518-524.
[29] 孙璐薇.微波烧结含CO32-的多孔β-TCP/HA双相生物陶瓷材料及其性能研究[D].成都:四川大学,2004.
[30] Nade s,Armstrong L,Mccartney E,et al.Osteogenesis after bone and bone marrow transplantation.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1983;181(12):255-263.
[31] Lowmunkong R,Sohmura T,Suzuki Y,et al.fabrication of freeform bone-filling calcium phosphate ceramics by gypsum 3d printing method.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2009;90(2):531-539.
[32] Doi Y,Shibutani T,Moriwaki Y,et al.sintered carbonate apatites as bioresorbable bone substitutes.J Biomed Mater Res.1998;39(4):603-610.
[33] Reddy S,Wasnik S,Guha A,et al.Evaluation of nano-biphasic calcium phosphate ceramics for bone tissue engineering applications: in vitro and preliminary in vivo studies.J Biomater Appl.2013;27(5):565-575.
[34] Holmes RE.Bone regeneration within a coralline hydroxyapatite implant.Plast Reconstr Surg. 1979;63: 626-633.
[35] Komlev VS,Mastrogiacomo M,Pereira RC,et al. biodegradation of porous calcium phosphate scaffolds in an ectopic bone formation model studied by x-ray computed microtomograph.Eur Cell Mater. 2010;19: 136-146. |
 文题释义:
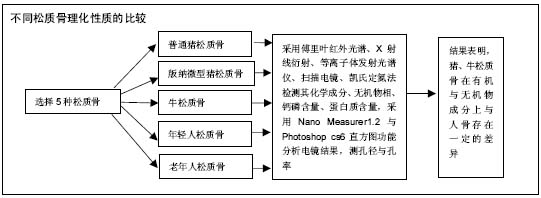
异种松质骨:作为天然骨组织工程支架来源,虽其抗原性强,但其来源广、成本低、便于加工且经过特定处理,如脱蛋白、煅烧、脱脂、冻干等,可减低或消除免疫原性,在作为骨缺损修复材料上有着巨大潜能。
牛、猪松质骨:与人松质骨在理化性质上存在着一定的差异,在选择天然衍生骨材料来源时应该考虑到其中存在的差异性,如在脱钙多孔支架的天然骨原料选择上,猪松质骨中蛋白质的量比牛骨中含量高,提示二者胶原含量的差异应引起研究者的注意。微型猪的Ca/P最高,这可能说明其中含有更多的杂质,或是其羟基磷灰石中含钙量更接近化学成分的羟基磷灰石,在选择天然衍生骨修复材料时,材料的Ca/P对支架材料机械性能与可能对间充质干细胞的成骨性影响亦应该得到重视。
文题释义:
异种松质骨:作为天然骨组织工程支架来源,虽其抗原性强,但其来源广、成本低、便于加工且经过特定处理,如脱蛋白、煅烧、脱脂、冻干等,可减低或消除免疫原性,在作为骨缺损修复材料上有着巨大潜能。
牛、猪松质骨:与人松质骨在理化性质上存在着一定的差异,在选择天然衍生骨材料来源时应该考虑到其中存在的差异性,如在脱钙多孔支架的天然骨原料选择上,猪松质骨中蛋白质的量比牛骨中含量高,提示二者胶原含量的差异应引起研究者的注意。微型猪的Ca/P最高,这可能说明其中含有更多的杂质,或是其羟基磷灰石中含钙量更接近化学成分的羟基磷灰石,在选择天然衍生骨修复材料时,材料的Ca/P对支架材料机械性能与可能对间充质干细胞的成骨性影响亦应该得到重视。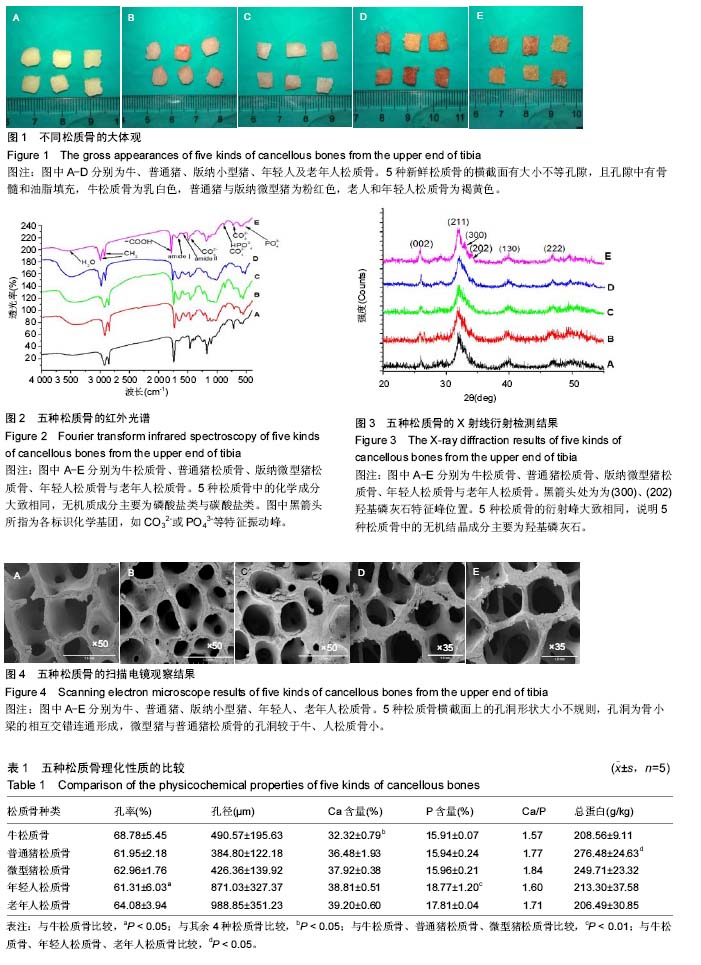
 文题释义:
异种松质骨:作为天然骨组织工程支架来源,虽其抗原性强,但其来源广、成本低、便于加工且经过特定处理,如脱蛋白、煅烧、脱脂、冻干等,可减低或消除免疫原性,在作为骨缺损修复材料上有着巨大潜能。
牛、猪松质骨:与人松质骨在理化性质上存在着一定的差异,在选择天然衍生骨材料来源时应该考虑到其中存在的差异性,如在脱钙多孔支架的天然骨原料选择上,猪松质骨中蛋白质的量比牛骨中含量高,提示二者胶原含量的差异应引起研究者的注意。微型猪的Ca/P最高,这可能说明其中含有更多的杂质,或是其羟基磷灰石中含钙量更接近化学成分的羟基磷灰石,在选择天然衍生骨修复材料时,材料的Ca/P对支架材料机械性能与可能对间充质干细胞的成骨性影响亦应该得到重视。
文题释义:
异种松质骨:作为天然骨组织工程支架来源,虽其抗原性强,但其来源广、成本低、便于加工且经过特定处理,如脱蛋白、煅烧、脱脂、冻干等,可减低或消除免疫原性,在作为骨缺损修复材料上有着巨大潜能。
牛、猪松质骨:与人松质骨在理化性质上存在着一定的差异,在选择天然衍生骨材料来源时应该考虑到其中存在的差异性,如在脱钙多孔支架的天然骨原料选择上,猪松质骨中蛋白质的量比牛骨中含量高,提示二者胶原含量的差异应引起研究者的注意。微型猪的Ca/P最高,这可能说明其中含有更多的杂质,或是其羟基磷灰石中含钙量更接近化学成分的羟基磷灰石,在选择天然衍生骨修复材料时,材料的Ca/P对支架材料机械性能与可能对间充质干细胞的成骨性影响亦应该得到重视。