| [1] Jansen PL.Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.Neth J Med. 2004;62(7):217.
[2] Fan JG,Zhong L,Tiay L,et al.Effects of ursodeoxycholic aciand/or low-calorie diet on steatohepatitis in ratswith obesity anhyperlipidemia. World J Gastroenterol. 2005; 11(15):234.
[3] 南月敏,王蕾,李良宵,等.非酒精性脂肪肝动物模型研究进展[J].河北医科大学学报,2007,28(1):67.
[4] 徐磊,徐承富,石巧娟,等.小鼠非酒精性脂肪性肝病模型的建立和评价[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2007,15(9): 693-694.
[5] 王舒然,麻微微,赵丹,等.高脂饮食诱导肥胖与肥胖抵抗动物模型建立[J].中国公共卫生,2007,23(7):774-775.
[6] 史燕如,常艳,辛鹏,等.沉默信息调节因子2相关酶1及脂肪酸合成酶在非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠模型中的表达及意义[J].中国现代医学杂志,2015,25(32):9-13.
[7] 韩然,于燕妮,杨丹.高糖饮食致大鼠非酒精性脂肪肝模型的建立[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2015,24(11):1354- 1356,1360.
[8] 杨梅,张航,赵琦,等.祛脂愈肝颗粒对非酒精性脂肪肝模型大鼠Th17细胞表达的影响[J].贵州医药,2015,39(7): 592-594.
[9] 唐外娇,姚育法,殷锦锦,等.护肝清脂片对非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠肝脏蛋白质合成及胆汁代谢的影响[J].中药材, 2014, 37(8):1452-1454.
[10] 聂山文,赵文霞,石艳芬,等.高脂饲料联合四环素腹腔注射复制非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠模型的实验研究[J].中国中西医结合急救杂志,2013,20(6):374-375.
[11] 楼琦,石巧娟,郭红刚,等.非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠脂质代谢及病理变化的动态观察[J].中国比较医学杂志,2012,22(3): 5-11.
[12] 刘庆丰,李中东,施孝金,等.高脂血症非酒精性脂肪肝大鼠模型的建立[J].时珍国医国药,2013,24(1):171-172.
[13] 魏香兰,方如塘,冀爱云,等.高脂资料中胆固醇含量对大鼠非酒精性脂肪肝动物模型建立的影响[J].西北药学杂志, 2012,27(3):233-236.
[14] 王敏,闫曙光.非酒精性脂肪肝动物模型的建立与思考[J].陕西中医,2012,33(9):1248-1250.
[15] 麻微微,赵丹,苏畅,等.饮食诱导肥胖易感和肥胖抵抗小鼠HSL和LPL基因表达的研究[J].卫生研究,2007,36(3): 320-322.
[16] 王羚,董梁,夏国园,等.高脂高糖低蛋白构建大鼠非酒精性脂肪肝模型的实验研究[J].职业与健康,2015,31(2): 190-192.
[17] 杨玉琴,冯洁,柏熊,等.东方田鼠非酒精性脂肪肝模型的建立[J].中国实验动物学报,2013,21(2):34-38.
[18] 李晓飞,胡义扬,冯琴.超营养饮食方法诱导的非酒精性脂肪肝动物模型研究进展[J].肝脏,2012,17(12):897-899.
[19] 郑全喜,王昆,刘超.非酒精性脂肪性肝病动物模型的研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2013,19(2):357-360.
[20] Cheah WL,Lee PY,Chang CT,et al.Prevalence of ultrasound diagnosed nonalcoholic fatty liver disease among rural indigenous community of Sarawak and its association with biochemical and anthropometric measures. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2013;44(2):309-317.
[21] Thoma C,Day CP,Trenell MI.Lifestyle interventions for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in adults:a system-atic review. Hepatology. 2012;56(1):255-266.
[22] McCarthy EM,Rinella ME.The role of diet and nutrient composition in nonalcoholic Fatty liver disease. Acad Nutr Diet. 2012;112(3):401-409.
[23] 王宇,郑锦锋.非酒精性脂肪肝营养干预的研究进展[J].医学研究生学报,2014,27(1):99-101.
[24] Cong WN, Tao RY, Tian JY, et al. The establishment of a novel non-alcoholic steatohepatitis model accompanied with obesity and insulin resistance in mice. Life Sci. 2008;82(19-20):983-990.
[25] Pathil A, Mueller J, Warth A, et al. Ursodeoxycholyl lysophosphatidylethanolamide improves steatosis and inflammation in murine models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 2012;55(5):1369-1378.
[26] Xu Q, Wang J, Chen F, et al. Protective role of magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the associated molecular mechanisms. Int J Mol Med. 2016. [Epub ahead of print]
[27] Piña-Zentella RM, Rosado JL, Gallegos-Corona MA, et al. Lycopene Improves Diet-Mediated Recuperation in Rat Model of Nonalcoholic Fatty LiverDisease.J Med Food. 2016. [Epub ahead of print]
[28] Lee SK, Yoon DW, Lee SW, et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among sasang constitutional types: a population-based study in Korea. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015;15:399.
[29] Zhang L, Zhang Z, Li Y, et al. Cholesterol induces lipoprotein lipase expression in a tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri chinensis)model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15970.
[30] Yang N, Zhang Y, Guo J. Preventive effect of total glycosides from Ligustri Lucidi Fructus against nonalcoholic fatty liver in mice. Z Naturforsch C. 2015;70(9-10):237-241.
[31] Bhatt BD, Lukose T, Siegel AB, et al. Increased risk of colorectal polyps in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease undergoingliver transplant evaluation. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2015;6(5):459-468.
[32] Ryu JE, Jo W, Choi HJ, et al. Evaluation of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in C57BL/6J Mice by Using MRI and Histopathologic Analyses. Comp Med. 2015;65(5):409-415. |
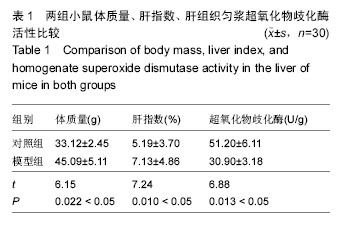
.jpg)
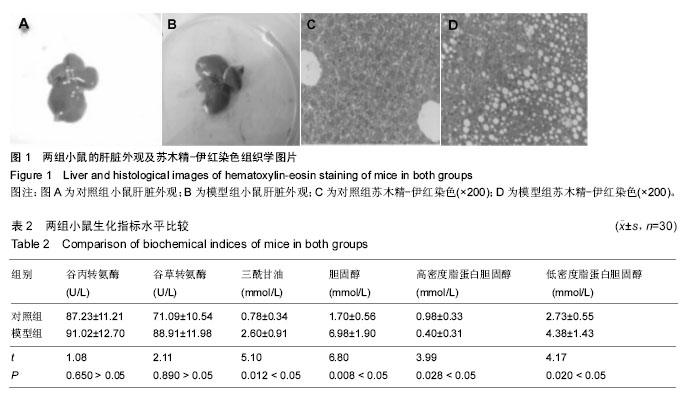
.jpg)