| [1] Garfin SR,Yuan HA, Reiley MA. New technologies in spine: kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for the treatment of painful osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(14):1511-1515.
[2] Bozkurt M, Kahilogullari G, Ozdemir M, et al. Comparative analysis of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. Asian Spine J.2014;8(1):27-34.
[3] Yu CW, Hsieh MK, Chen LH, et al. Percutaneous balloon kyphoplasty for the treatment of vertebral compression fractures. BMC Surg. 2014;14:3.
[4] Lo YP, Chen WJ, Chen LH, et al. New vertebral fracture after vertebroplasty. J Trauma. 2008;65(6): 1439-1445.
[5] Seo DH, Oh SH, Yoon KW, et al. Risk Factors of New Adjacent Compression Fracture after Percutaneous Vertebroplasty: Effectiveness of Bisphosphonate in Osteoporotic or Osteopenic Elderly Patients. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2014;10(2):86-91.
[6] Zhai W, Jia Y, Wang J, et al. The clinical effect of percutaneous kyphoplasty for the treatment of multiple osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures and the prevention of new vertebral fractures. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(8):13473-13481.
[7] Mudano AS, Bian J, Cope JU, ,et al. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty are associated with an increased risk of secondary vertebral compression fractures: a population-based cohort study. Osteoporos Int. 2009; 20(5):819-826.
[8] Lin EP, Ekholm S, Hiwatashi A,et al. Vertebroplasty: cement leakage into the disc increases the risk of new fracture of adjacent vertebral body. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25(2):175-180.
[9] Lindsay R, Silverman SL, Cooper C, et al. Risk of new vertebral fracture in the year following a fracture. JAMA. 2001;285(3):320-323.
[10] Takahara K, Kamimura M, Moriya H, et al. Risk factors of adjacent vertebral collapse after percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral fracture in postmenopausal women. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2016;17:12.
[11] Staples MP, Howe BM, Ringler MD, et al. New vertebral fractures after vertebroplasty: 2-year results from a randomised controlled trial. Arch Osteoporos. 2015;10:229.
[12] Villarraga ML, Bellezza AJ, Harrigan TP, et al. The biomechanical effects of kyphoplasty on treated and adjacent nontreated vertebral bodies. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18(1): 84-91.
[13] Barrey C, Jund J, Noseda O. Sagittal balance of the pelvis-spine complex and lumbar degenerative diseases. A comparative study about 85 cases. Eur Spine J. 2007;16(9): 1459-1467.
[14] Diamond TH, Bryant C, Browne L, et al. Clinical outcomes after acute osteoporotic vertebral fractures: a 2-year non-randomised trial comparing percutaneous vertebroplasty with conservative therapy. Med J Aust. 2006;184(3):113-117.
[15] Rousing R, Hansen KL, Andersen MO, et al. Twelve-months follow-up in forty-nine patients with acute/semiacute osteoporotic vertebral fractures treated conservatively or with percutaneous vertebroplasty: a clinical randomized study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(5):478-482.
[16] Balkarli H, Demirtas H, Kilic M, et al. Treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures with percutaneous vertebroplasty under local anesthesia: clinical and radiological results. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(9): 16287-16293.
[17] 方秀统,于方,付胜良,等.经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗老年人骨质疏松性脊柱压缩骨折的疗效分析[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2013,93(33):2654-2658.
[18] Luo J, Adams MA, Dolan P. Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty Can Restore Normal Spine Mechanics following Osteoporotic Vertebral Fracture. J Osteoporos. 2010;2010:729257.
[19] Korovessis P, Zacharatos S, Repantis T, et al. Evolution of bone mineral density after percutaneous kyphoplasty in fresh osteoporotic vertebral body fractures and adjacent vertebrae along with sagittal spine alignment. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2008;21(4): 293-298.
[20] Kolb JP, Kueny RA, Puschel K,et al. Does the cement stiffness affect fatigue fracture strength of vertebrae after cement augmentation in osteoporotic patients? Eur Spine J. 2013;22(7):1650-1656.
[21] Uppin AA, Hirsch JA, Centenera LV, et al. Occurrence of new vertebral body fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporosis. Radiology. 2003;226(1): 119-124.
[22] Melton LJ 3rd, Atkinson EJ, Cooper C, et al. Vertebral fractures predict subsequent fractures. Osteoporos Int. 1999;10(3):214-222.
[23] Lee KA, Hong SJ, Lee S, et al. Analysis of adjacent fracture after percutaneous vertebroplasty: does intradiscal cement leakage really increase the risk of adjacent vertebral fracture? Skeletal Radiol. 2011; 40(12):1537-1542.
[24] Movrin I, Vengust R, Komadina R. Adjacent vertebral fractures after percutaneous vertebral augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a comparison of balloon kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130(9): 1157- 1166.
[25] Pradhan BB, Bae HW, Kropf MA, et al. Kyphoplasty reduction of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: correction of local kyphosis versus overall sagittal alignment. Spine. 2006;31(4): 435-441.
[26] 欧阳超,陈志明,马华松,等.椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松椎体压缩骨折术后非手术椎体新发骨折的相关因素分析[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(3):222-227.
[27] Zou J, Mei X, Zhu X,et al. The long-term incidence of subsequent vertebral body fracture after vertebral augmentation therapy: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Pain Phys. 2012;15(4):E515-522.
[28] Chen LX, Li YL, Ning GZ,et al. Comparative efficacy and tolerability of three treatments in old people with osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a network meta-analysis and systematic review. PLoS One. 2015; 10(4):e0123153.
[29] Mac-Thiong J, Roussouly P, Berthonnaud E, et al. Sagittal paramefers of global spinal balance: normative values from a prospective cohort of seven hundred nine Caucasian asympomatic adults. Spine. 2010; 35(22): E1193-1198.
[30] Hu P, Yu M, Sun Z, et al. Analysis of Global Sagittal Postural Patterns in Asymptomatic Chinese Adults. Asian Spine J. 2016;10(2):282-288.
[31] La Maida GA, Zottarelli L, Mineo GV,et al. Sagittal balance in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: radiographic study of spino-pelvic compensation after surgery. Eur Spine J. 2013;22 Suppl 6: S859-867.
[32] 刘辉,希腊本大,郑召民,等.腰椎间盘退变与脊柱-骨盆矢状面平衡的相关性[J].中华医学杂志, 2013,93(15): 1123-1128.
[33] 袁宁,田伟,袁强,等.Ⅰ度或Ⅱ度腰椎滑脱手术对患者脊柱矢状面形态的影响[J]. 山东医药, 2014,54(44):10-12.
[34] Bruno AG, Anderson DE, D'Agostino J, et al. The effect of thoracic kyphosis and sagittal plane alignment on vertebral compressive loading. J Bone Miner Res. 2012; 27(10): 2144-2151.
[35] Briggs AM, Wrigley TV, van Dieen JH, et al. The effect of osteoporotic vertebral fracture on predicted spinal loads in vivo. Eur Spine J. 2006;15(12):1785-1795.
[36] Greig AM, Briggs AM, Bennell KL, et al. Trunk muscle activity is modified in osteoporotic vertebral fracture and thoracic kyphosis with potential consequences for vertebral health. PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e109515.
[37] Xu JX, Yang SD, Wang BL, et al. Correlative analyses of isolated upper lumbar disc herniation and adjacent wedge-shaped vertebrae. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015; 8(1):1150-1155.
[38] Movrin I, Vengust R, Komadina R. Adjacent vertebral fractures after percutaneous vertebral augmentation of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: a comparison of balloon kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2010;130(9): 1157-1166.
[39] 张相伟,孙建民,崔新刚,等. 骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折患者脊柱矢状面的失平衡[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(26):4224-4228.
[40] Bansal S, Katzman WB, Giangregorio LM. Exercise for improving age-related hyperkyphotic posture: a systematic review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014; 95(1):129-140. |
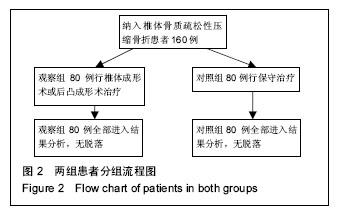
.jpg)
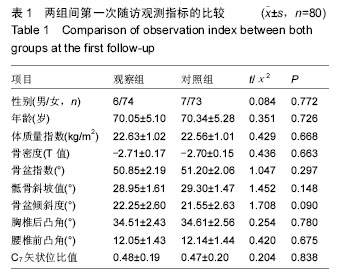
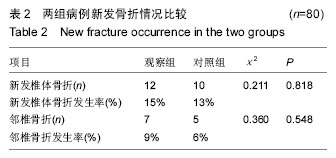
.jpg)
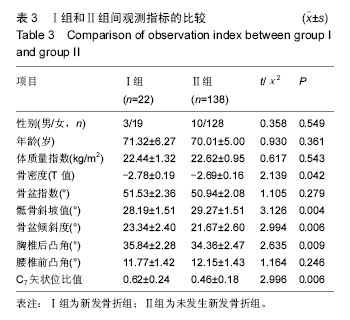
.jpg)