| [1] Dorai Z, Morgan H, Coimbra C. Titanium cage reconstruction after cervical corpectomy. Neurosurg Spine. 2003;99:3-7.
[2] Thalgott JS, Xiongsheng C, Giuffre JM. Single stage anterior cervical reconstruction with titanium mesh cages, local bone graft,and anterior plating.Spine. 2003;3:294-300.
[3] Sevki K, Mehmet T, Ufuk T, et al. Results of surgical treatment for degenerative cervical myelopathy: anterior cervical corpectomy and stabilization. Spine. 2004;29:2493-2500.
[4] 宋科冉,袁文,王新伟.椎体次全切除与椎间隙减压治疗多节段颈椎病的疗效比较[J].脊柱外科杂志,2011, 9(2): 102-107.
[5] Song KJ, Choi BW, Jeon TS, et al. Adjacent segment degenerative disease: is it due to disease progression or a fusion associated phenomenon? Comparison between segments adjacent to the fused and non-fused segments. Eur Spine J. 2011;20:1940-1945.
[6] Hilibrand AS, Carlson GD, Palumbo MA, et al. Radiculopathy and myelopathy at segments adjacent to the site of a previous anterior cervical arthrodesis. Bone Joint Surg Am. 1999;81:519-528.
[7] Dohler JR, Kahn MR, Hughes SP. Instability of the cervical spine after anterior interbody fusion. A study on its incidence and clinical significance in 21 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1985;104: 247-250.
[8] Katsuura A, Hukuda S, Saruhashi Y, et al. Kyphotic malalignment after anterior cervical fusion is one of the factors promoting the degenerative process in adjacent intervertebral levels. Eur Spine J. 2001;10: 320-324.
[9] Baba H,Furusawa N,Imura S,et al. Late rasiographic findings after anterior cervical fusion for spongylotic myeloradiculopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993;18: 2167-2173.
[10] Goffin J, van Loon J, Van Calenbergh F, et al. Long-term results after anterior cervical fusion and osteosynthetic stabilization for fractures and/or dislocations of the cervical spine. Spinal Disord. 1995;8:500-508.
[11] Kaplan EL, Meier P. Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. Am Stat Assoc. 1958;53: 457-481.
[12] McGrory BJ, Klassen RA. Arthrodesis of the cervical spine for fractures and dislocations in children and adolescents. A long-term follow-up study. Bone Joint Surg Am. 1994;76:1606-1616.
[13] Komura S, Miyamoto K, Hosoe H, et al. Lower incidence of adjacent segment degeneration after anterior cervical fusion found with those fusing C5-6 and C6-7 than those leaving C5-6 or C6-7 as an adjacent level. Spinal Disord Tech. 2012;25:23-29.
[14] Song JS, Choi BW, Song KJ. Risk factors for the development of adjacent segment disease following anterior cervical arthrodesis for degenerative cervical disease:Comparison between fusion methods. J Clin Neurosci. 2014;21(5):794-798.
[15] Park JB, Watthanaaphisit T, Riew KD. Timing of development of adjacent-level ossification after anterior cervical arthrodesis with plates. Spine. 2007;7(6):633-636.
[16] 王辉,丁文元,申勇,等.颈椎后纵韧带骨化症间接减压术后轴性症状分析[J].中华外科杂志,2012,50(7):601-606.
[17] lshibara A. Roetgenographic studies on the normal pattern of the cervical curvature. Nihon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi. 1968;42: 1033-1044.
[18] Wu JC,Liu L,Hang WC,et al. The Incidence of adiacent segment disease requriring surgery after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion:estimation using an eleven-year comprehensive nationwide database in Taiwan. Neurosurgery. 2011;2011VN.
[19] Lee JC, Lee SH, Peters C, et al. Adjacent segment pathology requiring reoperation after anterior cervical arthrodesis: the influence of smoking, sex, and number of operated levels. Spine. 2015;40(10):E571-577.
[20] Goffin J, Geusens E, Vantomme N, et al. Long-term follow-up after interbody fusion of the cervical spine. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2004;17(2):79-85.
[21] 马志兵,冯虎,袁锋,等.颈椎前路减压固定融合术后钢板固定位置对相邻节段退变的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2010, 20(3):201-204.
[22] Chen Y,Chen D,Guo Y,et al. Subsidence of titanium mesh cage: a study based on 300 cases. Spinal Disord Tech. 2008;21(7):489-492.
[23] Van Jonbergen HP,Spruit M,Anderson PG,et al. Anterior cervical interbody fusion with a titanium box cage: early radiological assessment of fusion and subsidence. Spine J. 2005;5(6):645-649.
[24] 王志海.120例脊髓型颈椎病前路手术并发症临床观察[J].现代诊断与治疗,2013,24(10):2346-2347.
[25] 谢宁,贾连顺,孙建国,等.颈椎不稳对颈椎病早期发病的影响[J].第二军医大学学报,2000,21(7):10-11.
[26] Lee JH,Kim JS,Lee JH,et al.Comparison of cervical kinematics between patients with cervical artificial disc replacement and anterior cervical discectomy and fusion for cervical disc hernia tion. Spine J. 2014; 14(7):1199-1204.
[27] Aghayev K, Doulgeris JJ, Gonzalez-Blohm SA, et al. Biomechanical comparison of a two-level anterior discectomy and a one-level corpectomy, combined with fusion and anterior plate reconstruction in the cervical spine. Clin Biomech. 2014;29(1):21-25.
[28] Elsawaf A, Mastronardi L, Roperto R, et al. Effect of cervical dynamics on adjacent segment degeneration after anterior cervical fusion with cages. Neurosurg Rev. 2009;32(2):215-224.
[29] Eck JC,Humphreys SC,Lim TH,et al. Biomechanical study on the effect of cervical spine fusion on adjacent-level intradiscal pressure and segmental motion. Spine. 2002;27(22):2431-2434.
[30] 杨晋才,海涌,裴葆,等.颈前路融合节段数对上位邻近节段影响的生物力学研究[J].中华外科杂志,2014,9,52(9):692-696.
[31] Katsuura A,Hukuda S,Saruhashi Y,et al. Kyphotic malalignment after anterior cervical fusion is one of the factors promoting the degenerative process in adjacent intervertebral levels. Eur Spine. 2001;10 :320–324.
[32] Lee SE, Jahng TA, Kim HJ. Correlation between cervical lordosis and adjacent segment pathology after anterior cervical spinal surgery. Eur Spine J. 2015; 24(12): 1-11. |
.jpg)
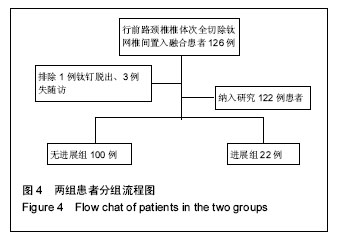
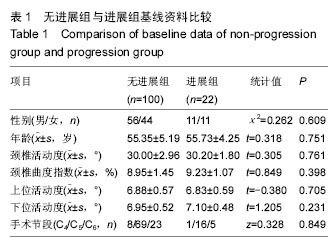
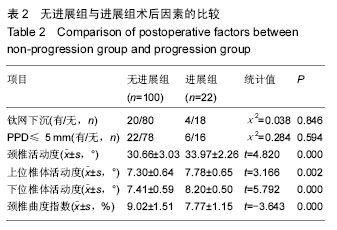
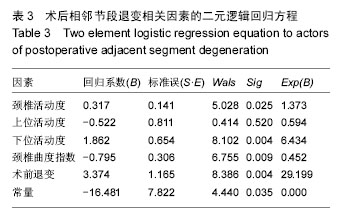
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)