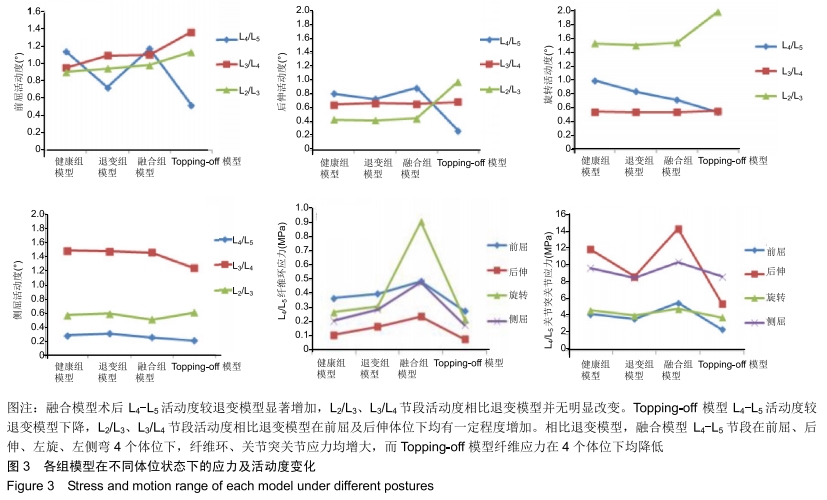
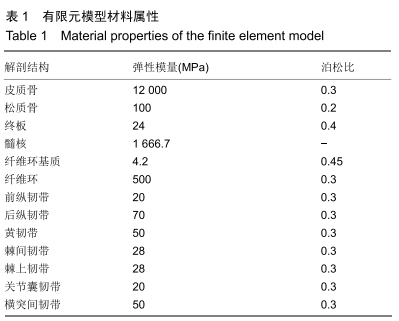
[1] MANNION AF, LEIVSETH G, BROX JI, et al. ISSLS Prize winner: Long-term follow-up suggests spinal fusion is associated with increased adjacent segment disc degeneration but without influence on clinical outcome: results of a combined follow-up from 4 randomized controlled trials. Spine. 2014; 39(17):1373-1383.
[2] 慕春黎,王朋. PLIF术后邻近节段退变的危险因素分析[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2019,34(1):87-89.
[3] CHEN XL, GUAN L, LIU YZ, et al. Interspinous dynamic stabilization adjacent to fusion versus double-segment fusion for treatment of lumbar degenerative disease with a minimum follow-up of three years. Int Orthop. 2016;40(6):1275-1283.
[4] FAIZAN A, SAIRYO K, GOEL VK, et al. Biomechanical rationale of ossification of the secondary ossification center on apophyseal bony ring fracture: a biomechanical study. Clin Biomech. 2007;22(10):1063-1067.
[5] SYLVESTRE PL, VILLEMURE I, AUBIN CE, et al. Finite element modeling of the growth plate in a detailed spine model. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2007;45(10):977-988.
[6] KUMARESAN S, YOGANANDAN N, PINTAR FA, et al. Contribution of disc degeneration to osteophyte formation in the cervical spine:: a biomechanical investigation. J Orthop Res. 2001; 19(5):977-984.
[7] POLIKEIT A, NOLTE LP, FERGUSON SJ, et al. The effect of cement augmentation on the load transfer in an osteoporotic functional spinal unit. Spine. 2003;28(10):991-996.
[8] BYUN DH, SHIN DA, KIM JM, et al. Finite Element Analysis of the Biomechanical. Korean J Spine. 2012;9(3):131-136.
[9] KULDUK A, ALTUN NS, SENKOYLU A, et al. Biomechanical comparison of effects of the Dynesys and Coflex dynamic stabilization systems on range of motion and loading characteristics in the lumbar spine: a finite element study. Int J Med Robot. 2015;11(4): 400-405.
[10] FAN W, GUO LX. A comparison of the influence of three different lumbar interbody fusion approaches on stress in the pedicle screw fixation system: Finite element static and vibration analyses. Int J Numer Method Biomed Eng. 2019; 35(3):3162.
[11] HETH JA, HITCHON PW, GOEL VK, et al. A biomechanical comparison between anterior and transverse interbody fusion cages. Spine. 2001; 26(12):261-267.
[12] LU S, WANG Z, FAU N, et al. Establishment and biomechanical analysis of three-dimensional nonlinear finite element model of three-pieces segment arch. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2013; 31(1):74-79.
[13] DONG F. The contributions of facet joint to the stiffness of the lumbar spine. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 1993;31(7):417-420.
[14] YAMAMOTO I, PANJABI MM, CRISCO T, et al. Three-dimensional movements of the whole lumbar spine and lumbosacral joint. Spine. 1989;14(11):1256-1260.
[15] SOBOTTKE, R, BRUST KS, KAULHAUSEN T, et al. Interspinous implants (X Stop, Wallis, Diam) for the treatment of LSS: is there a correlation between radiological parameters and clinical outcome? Eur Spine J. 2009;18(10):1494-1503.
[16] GALA RJ, RUSSO GS, WHANG PG, et al. Interspinous implants to treat spinal stenosis. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2017; 10(2):182-188.
[17] LANDI A. Interspinous posterior devices: What is the real surgical indication? World J Clin Cases. 2014;2(9):402-408.
[18] LIANG J, DONG Y, ZHAO H. Risk factors for predicting symptomatic adjacent segment degeneration requiring surgery in patients after posterior lumbar fusion. J Orthop Surg Res. 2014; 9:97.
[19] 曹宗锐,郑博,屈博,等. ISObar+TTL动态固定系统治疗双节段腰椎椎间盘突出症:8年随访[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(32): 5110-5116.
[20] PFIRRMANN WA, METZDORF A, ZANETTI M, et al. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine. 2001; 26(17):1873-1878.
[21] LI D, HAI Y, MENG X, et al. Topping-off surgery vs posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar disease: a comparative study of clinical efficacy and adjacent segment degeneration. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):197.
[22] ZHU Z, LIU C, WANG K, et al. Topping-off technique prevents aggravation of degeneration of adjacent segment fusion revealed by retrospective and finite element biomechanical analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:10.
[23] NIU CC, CHEN YLF, HUEI L. Beneficial effects of hyperbaric oxygen on human degenerated intervertebral disk cells via suppression of IL-1beta and p38 MAPK signal. J Orthop Res. 2011; 29(1):14-19.
[24] MURAKAMI H, YOON TS, ATTALLAH-WASIF ES, et al. Quantitative differences in intervertebral disc-matrix composition with age-related degeneration. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2010; 48(5):469-474.
[25] HIRSCH C. Studies on the pathology of low back pain. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1959; 41-B(2):237-243.
[26] TENCER AF, MAYER TG. Soft tissue strain and facet face interaction in the lumbar intervertebral joint--Part II: Calculated results and comparison with experimental data. J Biomech Eng. 1983; 105(3):210-215.
[27] 曹亮亮,徐建广,连小峰,等. Topping-off术后上位相邻节段的MRI表现及近期疗效[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(17): 1552-1557.
[28] KOZANEK M, WANG S, PASSIAS PG, et al. Range of motion and orientation of the lumbar facet joints in vivo. Spine, 2009; 34(19):689-696.
[29] JONES-QUAIDOO SM, DJURASOVIC M, OWENS RK 2ND, et al. Superior articulating facet violation: percutaneous versus open techniques. J Neurosurg Spine. 2013;18(6): 593-597.
|