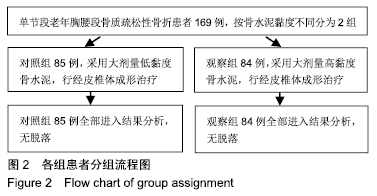
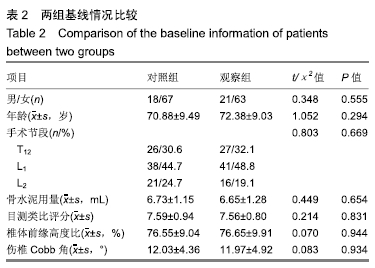
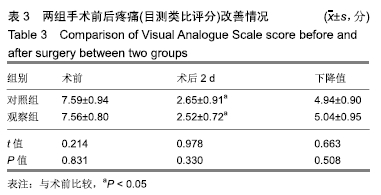
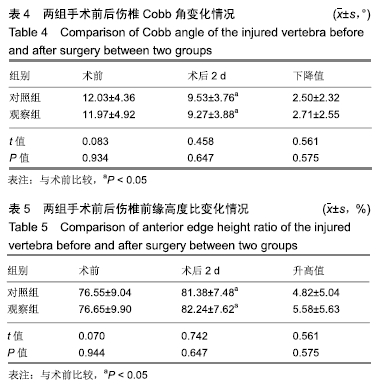
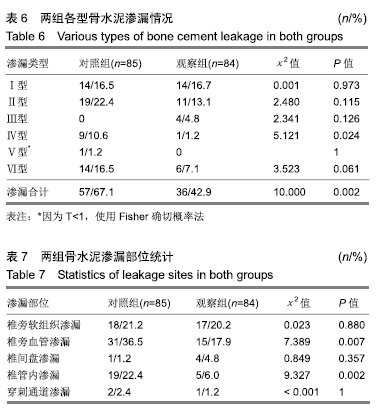
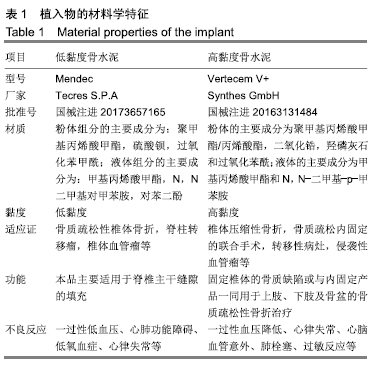
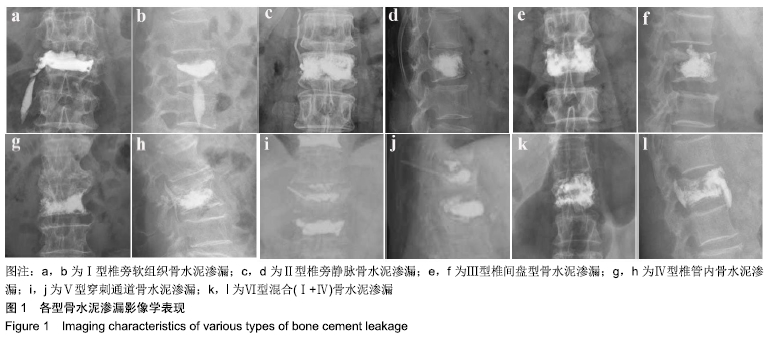
[1] YI X, LU H, TIAN F, et al. Recompression in new levels after percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty compared with conservative treatment. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2014;134(1): 21-30.
[2] GALIBERT P, DERAMOND H, ROSAT P, et al. Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vertebroplasty.Neurochirurgie.1987;33(2):166-168.
[3] HATZANTONIS C, CZYZ M, PYZIK R, et al. Intracardiac bone cement embolism as a complication of vertebroplasty: management strategy. Eur Spine J.2017;26(12):3199-3205.
[4] FU Z, HU X, WU Y, et al. Is There a Dose-Response Relationship of Cement Volume With Cement Leakage and Pain Relief After Vertebroplasty?Dose Response. 2016;14(4):1559325816682867.
[5] RODER C, BOSZCZYK B, PERLER G, et al. Cement volume is the most important modifiable predictor for pain relief in BKP: results from SWISSspine, a nationwide registry.Eur Spine J. 2013;22(10):2241-2248.
[6] MARTINCIC D, BROJAN M, KOSEL F, et al. Minimum cement volume for vertebroplasty.Int Orthop. 2015;39(4):727-733.
[7] GSTÖTTNER M, ANGERER A, ROSIEK R, et al. Quantitative volumetry of cement leakage in viscosity-controlled vertebroplasty.J Spinal Disord Tech.2012;25(5):E150-154.
[8] YEOM JS,KIM WJ,CHOY WS,et al.Leakage of cement in percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic compression fractures.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2003;85(1):83-89.
[9] 铁镔,何仕诚,滕皋军,等.经皮椎体成形术后骨水泥渗漏的CT评价[J].中华医学杂志, 2012,92(5):299-302.
[10] 马远征,王以朋,刘强,等.中国老年骨质疏松症诊疗指南(2018)[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2018,24(12):1541-1567.
[11] SEBAALY A, NABHANE L, ISSA EL KHOURY F, et al. Vertebral Augmentation: State of the Art.Asian Spine J. 2016;10(2): 370-376.
[12] TSAI YW, HSIAO FY, WEN YW, et al. Clinical outcomes of vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty for patients with vertebral compression fractures: a nationwide cohort study.J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2013;14(1):41-47.
[13] PHILLIPS FM, PFEIFER BA, LIEBERMAN IH, et al. Minimally invasive treatments of osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty.Instr Course Lect. 2003;52:559-567.
[14] 印平,马远征,马迅,等.骨质疏松性椎体压缩性骨折的治疗指南[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2015,21(6):643-648.
[15] NIEUWENHUIJSE MJ, VAN ERKEL AR, DIJKSTRA PD. Cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: identification of risk factors.Spine J. 2011; 11(9):839-848.
[16] PAPANASTASSIOU ID, FILIS A, GEROCHRISTOU MA, et al. Controversial issues in kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty in osteoporotic vertebral fractures.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014: 934206.
[17] ZHU SY, ZHONG ZM, WU Q, et al. Risk factors for bone cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty: a retrospective study of four hundred and eighty five patients.Int Orthop. 2016;40(6): 1205-1210.
[18] 郑召民.经皮椎体成形术和经皮椎体后凸成形术灾难性并发症—骨水泥渗漏及其预防[J].中华医学杂志,2006,86(43):3027-3030.
[19] DING J, ZHANG Q, ZHU J, et al. Risk factors for predicting cement leakage following percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures.Eur Spine J. 2016; 25(11):3411-3417.
[20] JENSEN ME, DION JE. Percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic compression fractures.Neuroimaging Clin N Am.2000;10(3):547-568.
[21] SONG YH, HAHN HH, HOFFMANN E, et al. Effect of humic substances on the precipitation of calcium phosphate.J Environ Sci(China).2006;18(5):852-857.
[22] 吴耀,王峰,周建强,等.经皮椎体成形术和经皮椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体骨折的临床疗效分析[J].中国骨伤, 2014,27(5): 385-389.
[23] SEMAAN H, OBRI T, BAZERBASHI M, et al.Clinical outcome and subsequent sequelae of cement extravasation after percutaneous kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty: a comparative review.Acta Radiol. 2018;59(7):861-868.
[24] TAYLOR RS, TAYLOR RJ, FRITZELL P. Balloon kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for vertebral compression fractures: a comparative systematic review of efficacy and safety.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(23):2747-2755.
[25] SARACEN A, KOTWICA Z. Complications of percutaneous vertebroplasty: An analysis of 1100 procedures performed in 616 patients.Medicine(Baltimore).2016;95(24):e3850.
[26] 江晓兵,莫凌,梁德,等.骨水泥在椎体骨折线内弥散情况对椎体成形术治疗效果的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(2):144-149.
[27] LIANG D, YE LQ, JIANG XB, et al. Biomechanical effects of cement distribution in the fractured area on osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: a three-dimensional finite element analysis. J Surg Res.2015;195(1):246-256.
[28] ZHONG BY, HE SC, ZHU HD, et al. Nomogram for Predicting Intradiscal Cement Leakage Following Percutaneous Vertebroplasty in Patients with Osteoporotic Related Vertebral Compression Fractures. Pain Physician.2017;20(4):E513-E520.
[29] TOME-BERMEJO F, PINERA AR, DURAN-ALVAREZ C, et al. Identification of Risk Factors for the Occurrence of Cement Leakage During Percutaneous Vertebroplasty for Painful Osteoporotic or Malignant Vertebral Fracture. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2014;39(11):E693-E700.
|