| [1] Ji JF, Ji SJ, Sun R, et al. Forced running exercise attenuates hippocampal neurogenesis impairment and the neurocognitive deficits induced by whole-brain irradiation via the BDNF-mediated pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014; 443(2): 646-651. [2] Blackmore DG, Golmohammadi MG, Large B, et al. Exercise increases neural stem cell number in a growth hormone-dependent manner, augmenting the regenerative response in aged mice. Stem Cells. 2009; 27(8): 2044-2052. [3] Wu CW, Chang YT, Yu L, et al. Exercise enhances the proliferation of neural stem cells and neurite growth and survival of neuronal progenitor cells in dentate gyrus of middle-aged mice. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2008; 105(5): 1585-1594. [4] Tapia-Rojas C, Aranguiz F, Varela-Nallar L, et al. Voluntary running attenuates memory loss, decreases neuropathological changes and induces neurogenesis in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol. 2016;26(1): 62-74. [5] Karim A, Salleh R, Khan MK. SMARTbot: A Behavioral Analysis Framework Augmented with Machine Learning to Identify Mobile Botnet Applications. PLoS One. 2016; 11(3): e0150077. [6] 孙涛, 曾贵荣, 杨韬,等.神经行为学评价方法研究进展[J].中国医师杂志, 2014,16(10):1427-1429. [7] Pietropaolo S, Feldon J, Alleva E, et al. The role of voluntary exercise in enriched rearing: a behavioral analysis. Behav Neurosci.2006;120(4): 787-803. [8] Kiyota T, Zhang G, Morrison CM, et al. AAV2/1 CD74 Gene Transfer Reduces β-amyloidosis and Improves Learning and Memory in a Mouse Model of Alzheimer's Disease. Mol Ther.2015;23(11): 1712-1721. [9] Kanninen K, Heikkinen R, Malm T, et al. Intrahippocampal injection of a lentiviral vector expressing Nrf2 improves spatial learning in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2009;106(38):16505-16510. [10] Lok K, Zhao H, Zhang C, et al. Effects of accelerated senescence on learning and memory, locomotion and anxiety-like behavior in APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol Sci. 2013;335(1-2):145-154. [11] He Y, Zhu J, Huang F, et al Age-dependent loss of cholinergic neurons in learning and memory-related brain regions and impaired learning in SAMP8 mice with trigeminal nerve damage. Neural Regen Res. 2014; 9(22): 1985-1994. [12] 李腾飞,孙秀萍,石哲,等.不同品系小鼠在三种常见抑郁检测方法中的行为学表现[J].中国比较医学杂志, 2011, 21(8): 20-23. [13] 高翠英,崔秀玉.BALB/c和ICR小鼠的学习记忆能力等行为学研究[J].中国实验动物学报, 2007, 15(5): 372-375. [14] Fernandes C, Liu L, Paya-Cano JL, et al. Behavioral characterization of wild derived male mice (Mus musculus musculus) of the PWD/Ph inbred strain: high exploration compared to C57BL/6J. Behav Genet.2004; 4(6): 621-630. [15] Yu JL, Ma L, Ma L, et al. Voluntary wheel running enhances cell proliferation and expression levels of BDNF, IGF1 and WNT4 in dentate gyrus of adult mice. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2014; 66(5): 559-568. [16] Wong-Goodrich SJ, Pfau ML, Flores CT, et al. Voluntary running prevents progressive memory decline and increases adult hippocampal neurogenesis and growth factor expression after whole-brain irradiation. Cancer Res. 2010;70(22): 9329-9338. [17] Kapgal V, Prem N, Hegde P, et al. Long term exposure to combination paradigm of environmental enrichment, physical exercise and diet reverses the spatial memory deficits and restores hippocampal neurogenesis in ventral subicular lesioned rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2016;130: 61-70. [18] Itoh T, Imano M, Nishida S, et al. Exercise inhibits neuronal apoptosis and improves cerebral function following rat traumatic brain injury. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2011;118(9): 1263-1272. [19] Nam SM, Kim JW, Yoo DY, et al. Effects of treadmill exercise on neural stem cells, cell proliferation, and neuroblast differentiation in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus in cyclooxygenase-2 knockout mice. Neurochem Res. 2013; 38(12): 2559-2569. [20] Van Dam D, Lenders G, De Deyn PP. Effect of Morris water maze diameter on visual-spatial learning in different mouse strains. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2006; 85(2): 164-172. [21] O'Leary TP, Savoie V, Brown RE. Learning, memory and search strategies of inbred mouse strains with different visual abilities in the Barnes maze. Behav Brain Res,2011,216(2): 531-42. [22] Yoshida M1, Goto K, Watanabe S. Task-dependent strain difference of spatial learning in C57BL/6N and BALB/c mice. Physiol Behav.2001; 73(1-2): 37-42. [23] 薛丹,徐淑萍,刘进修,等.水迷宫实验中三种品系小鼠学习记忆能力的比较[J].中国实验动物学报,2010, 18(2): 149-152. [24] Patil SS, Sunyer B, Höger H, et al. Evaluation of spatial memory of C57BL/6J and CD1 mice in the Barnes maze, the Multiple T-maze and in the Morris water maze. Behav Brain Res. 2009; 198(1): 58-68. [25] Thifault S, Lalonde R, Sanon N, et al. Comparisons between C57BL/6J and A/J mice in motor activity and coordination, hole-poking, and spatial learning. Brain Res Bull. 2002;58(2): 213-218. [26] Stavnezer AJ, Hyde LA, Bimonte HA, et al. Differential learning strategies in spatial and nonspatial versions of the Morris water maze in the C57BL/6J inbred mouse strain. Behav Brain Res.2002;133(2): 261-270. |
.jpg)
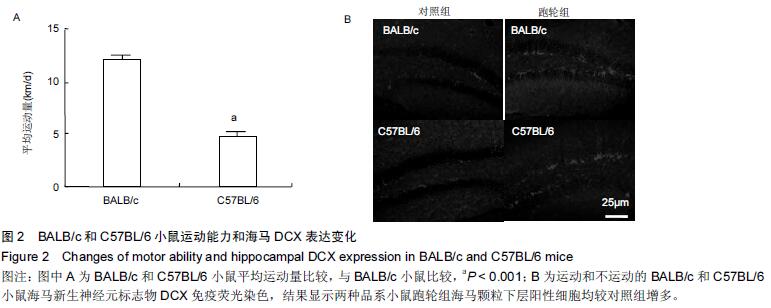
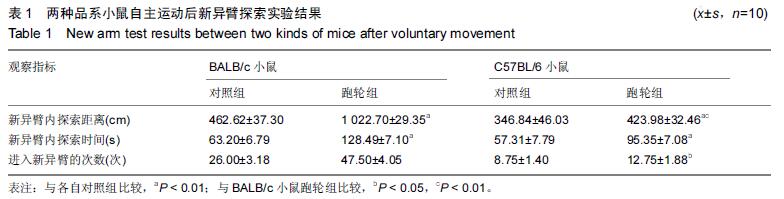
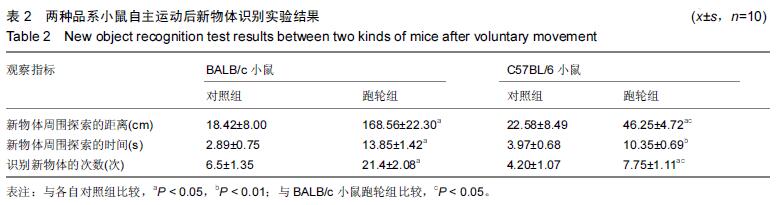
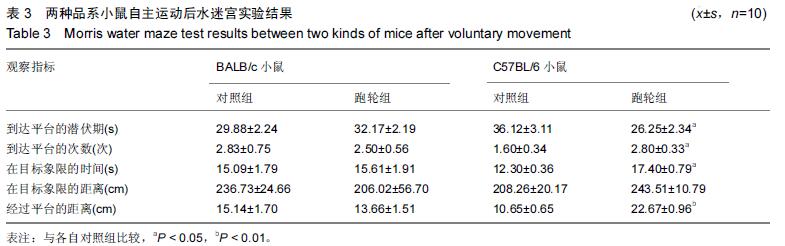
.jpg)
.jpg)