| [1] Sun W, Zhang K, Liu G, et al. Sox9 gene transfer enhanced regenerative effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on the degenerated intervertebral disc in a rabbit model. PLoS One. 2014; 9(4):e93570. [2] March L, Smith EU, Hoy DG, et al. Burden of disability due to musculoskeletal (MSK) disorders. Best Practice Res Clin Rheumatol. 2014;28(3):353-366. [3] Weinstein JN, Lurie JD, Tosteson TD, et al. Surgical versus nonoperative treatment for lumbar disc herniation: four-year results for the Spine Patient Outcomes Research Trial (SPORT). Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2008;33(25):2789-2800. [4] Depalma MJ, Ketchum JM, Saullo TR, et al. Is the history of a surgical discectomy related to the source of chronic low back pain? Pain Physician. 2012; 15(1): E53-E58. [5] Guterl CC, See EY, Blanquer SB, et al. Challenges and strategies in the repair of ruptured annulus fibrosus. Eur Cell Mater. 2013;25:1-21. [6] Jankowitz BT, Atteberry DS, Gerszten PC, et al. Effect of fibrin glue on the prevention of persistent cerebral spinal fluid leakage after incidental durotomy during lumbar spinal surgery. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(8): 1169-1174. [7] Long RG, Burki A, Zysset P, et al. Mechanical restoration and failure analyses of a hydrogel and scaffold composite strategy for annulus fibrosus repair. Acta Biomater. 2016;30:116-125. [8] 陈靖,石松生,张国良,等.生物型人工硬脑膜修补硬脑膜缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(51):8914-8919. [9] Gui K, Ren W, Yu Y, et al. Inhibitory effects of platelet-rich plasma on intervertebral disc degeneration: a preclinical study in a rabbit model. Med Sci Monitor. 2015;21:1368-1375. [10] 周葳,徐义春,王其友,等.两种手术入路消融术建立兔椎间盘退变模型的比较研究[J].中华实验外科杂志, 2014, 31(3):669-671. [11] 刘海飞,张晗,乔光曦,等.应用纤维结合素建立新型兔腰椎间盘退变模型[J].中华外科杂志, 2013,51(4):362- 366. [12] 王彦强,吕鹏飞,张光武,等.人脐带间充质干细胞移植修复兔退变椎间盘的初步研究[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2014, (6):523-526. [13] Masuda K, Imai Y, Okuma M, et al. Osteogenic protein-1 injection into a degenerated disc induces the restoration of disc height and structural changes in the rabbit anular puncture model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(7):742-754. [14] 白亦光,韩小伟,张旭乾,等.纤维环穿刺抽吸法和纤维环切开法建立兔椎间盘退变模型的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,(7):690-694. [15] Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, et al. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine. 2001;26(17): 1873-1878. [16] Urrutia J, Besa P, Campos M, et al. The Pfirrmann classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration: an independent inter-and intra-observer agreement assessment. Eur Spine J. 2016. [17] 贺庆,李兵,卓祥龙,等.经皮纤维环穿刺与经肌间隙纤维环刀刺建立兔椎间盘退变模型[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(13):2059-2064. [18] Keorochana G, Johnson JS, Taghavi CE, et al. The effect of needle size inducing degeneration in the rat caudal disc: evaluation using radiograph, magnetic resonance imaging, histology, and immunohistochemistry. Spine J. 2010;10(11):1014-1023. [19] 崔运能,李绍林,周荣平,等.CT引导下经皮纤维环穿刺建立兔腰椎间盘退变模型[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2014, 4(3):234-243. [20] Huang B, Zhuang Y, Li CQ, et al. Regeneration of the intervertebral disc with nucleus pulposus cell-seeded collagen II/hyaluronan/chondroitin-6-sulfate tri-copolymer constructs in a rabbit disc degeneration model. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2011;36(26):2252-2259. [21] 王海莹,张旭,丁文元,等.椎间盘退变动物模型的研究进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2015,25(3):279-282. [22] 顾韬,张超,何勍,等.不同类型椎间盘退变动物模型的评价与比较[J].脊柱外科杂志,2015,(2):115-120. [23] 陈靖,石松生,张国良,等.生物型人工硬脑膜修补硬脑膜缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(51):8914-8919. [24] Long R G, Burki A, Zysset P, et al. Mechanical restoration and failure analyses of a hydrogel and scaffold composite strategy for annulus fibrosus repair. Acta Biomater. 2016;30:116-125. [25] Pirvu T, Blanquer SB, Benneker LM, et al. A combined biomaterial and cellular approach for annulus fibrosus rupture repair. Biomaterials. 2015;42:11-19. [26] Ledet EH, Jeshuran W, Glennon JC, et al. Small intestinal submucosa for anular defect closure: long-term response in an in vivo sheep model. Spine. 2009;34(14):1457-1463. [27] Jin L, Feng G, Reames DL, et al. The effects of simulated microgravity on intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J. 2013;13(3):235-242. [28] Marinelli NL, Haughton VM, Munoz A, et al. T2 relaxation times of intervertebral disc tissue correlated with water content and proteoglycan content. Spine. 2009;34(5):520-524. [29] Mwale F, Ciobanu I, Giannitsios D, et al. Effect of oxygen levels on proteoglycan synthesis by intervertebral disc cells. Spine. 2011;36(2):E131-E138. [30] Roughley PJ. Biology of intervertebral disc aging and degeneration: involvement of the extracellular matrix. Spine. 2004;29(23):2691-2699. [31] Samartzis D, Borthakur A, Belfer I, et al. Novel diagnostic and prognostic methods for disc degeneration and low back pain. Spine J. 2015;15(9): 1919-1932. [32] Sharifi S, Bulstra SK, Grijpma DW, et al. Treatment of the degenerated intervertebral disc; closure, repair and regeneration of the annulus fibrosus. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;9(10):1120-1132. |
.jpg)
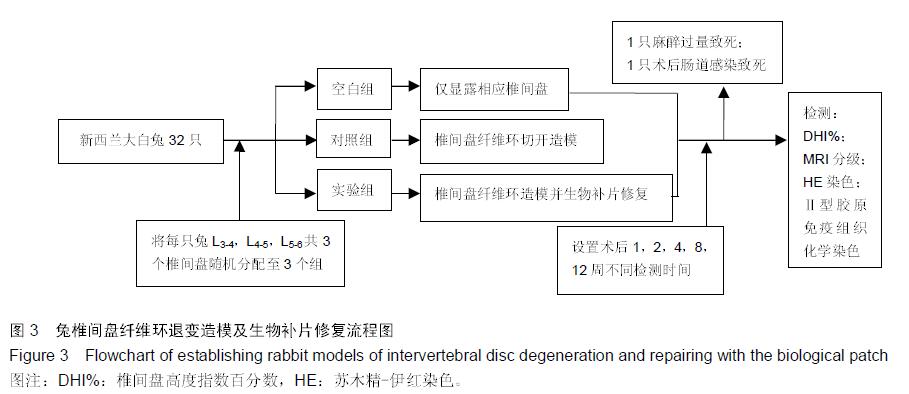
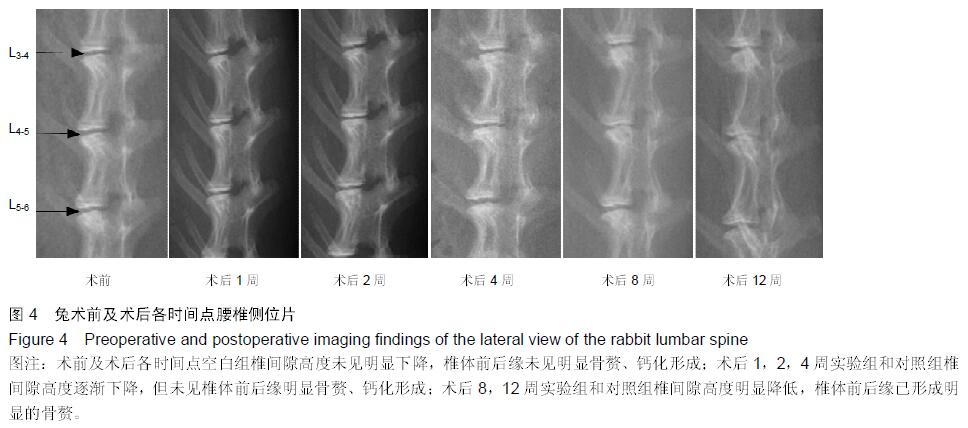
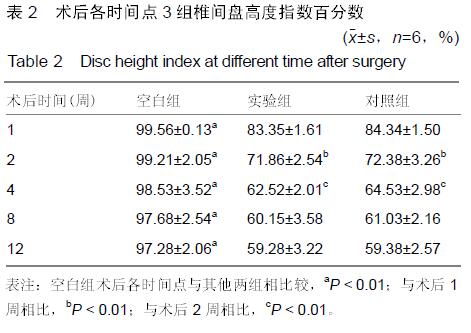
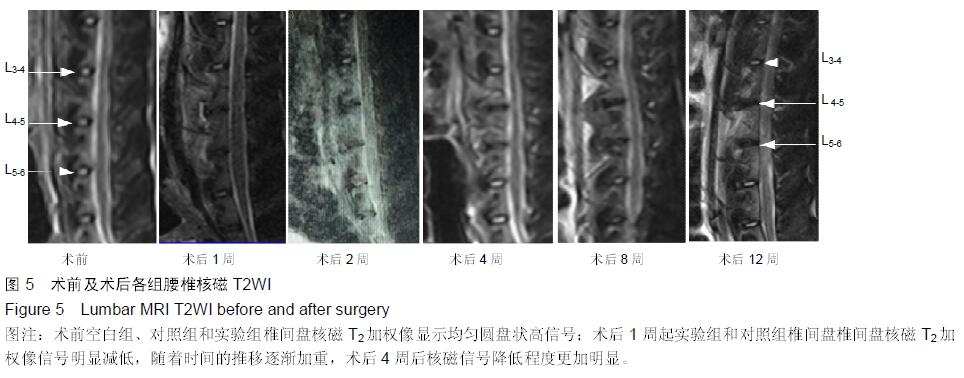

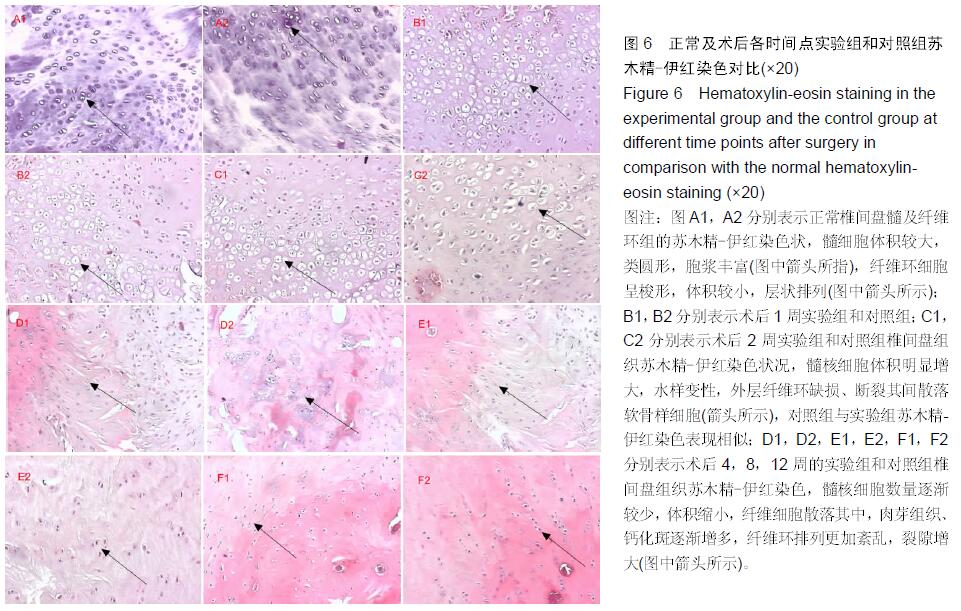
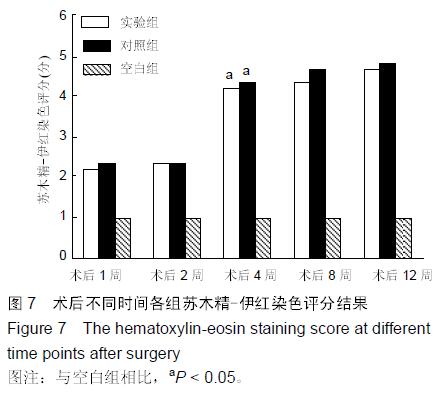
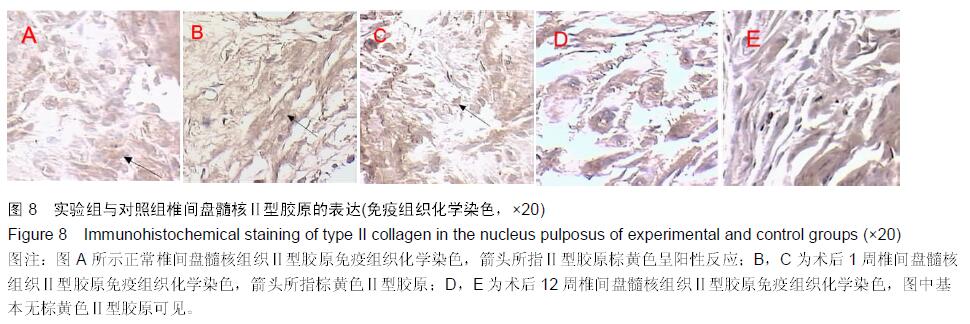
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)