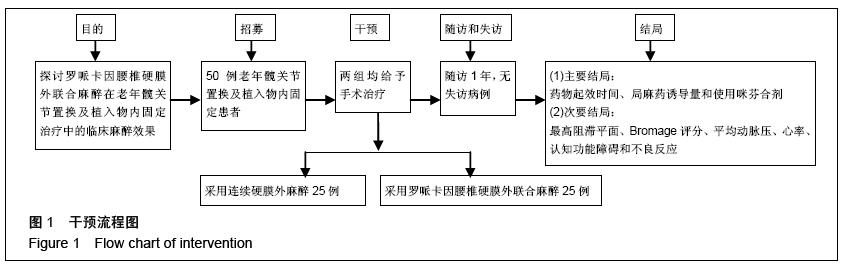
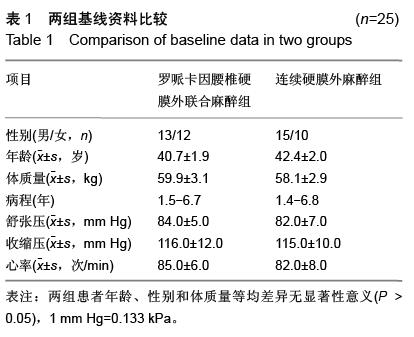
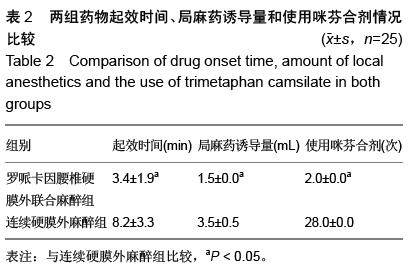
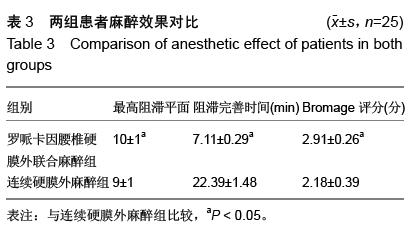
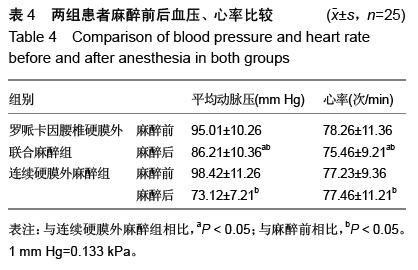
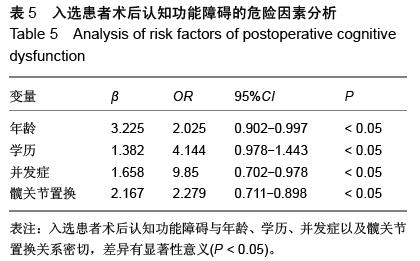
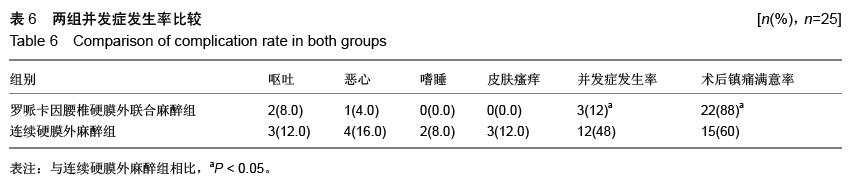
| [1] 李永乐,王颖,武广义,等.股神经阻滞联合帕瑞昔布静注在老年膝关节置换后的镇痛效果研究[J].中国医药导报, 2012, 9(14):105-106, 111.
[2] 谢伟.罗哌卡因与布比卡因用于腰硬联合麻醉剖宫产的临床效果对比[J].中国医药导刊,2011,13(10):1764-1765.
[3] 周红梅,祝胜美.静脉注射帕瑞昔布联合股神经阻滞用于老年病人膝关节置换后镇痛及膝关节功能康复的效果[J].中华麻醉学杂志,2011,31(8):929-931.
[4] 李文江.不同麻醉方式应用于剖宫产术的效果观察[J].实用临床医药杂志,2012,16(5):57-58, 65.
[5] 王冬娜,方洪亮,杨林.罗哌卡因与布比卡因用于腰硬联合麻醉的对比临床观察[J].中国临床研究,2010,23(6):485-486.
[6] 郑彬,傅文婷,曾彦茹,等.老年患者蛛网膜下腔注射左旋布比卡因、罗哌卡因和布比卡因运动阻滞效能的比较[J].实用医学杂志,2011,27(5):859-861.
[7] Salazar F, Do ate M, Boget T, et al. Intraoperative warming and post-operative cognitive dysfunction after total knee replacement. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2011;55(2):216-222.
[8] Norkien I, Samalaviius R, Misiūrien I, et al. Incidence and risk factors for early postoperative cognitive decline after coronary artery bypass grafting. Medicina (Kaunas). 2010;46(7):460-464.
[9] Rrtgen D, Kloos J, Fries M, et al. Comparison of early cognitive function and recovery after desflurane or sevoflurane anaesthesia in the elderly: a double-blinded randomized controlled trial. Br J Anaesth. 2010;104(2):167-174.
[10] Bjrkelund KB, Hommel A, Thorngren KG, et al. Reducing delirium in elderly patients with hip fracture: a multi-factorial intervention study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2010;54(6):678-688.
[11] Evered L, Scott DA, Silbert B, et al. Postoperative cognitive dysfunction is independent of type of surgery and anesthetic. Anesth Analg. 2011;112(5):1179-1185.
[12] Jildenstl PK, Hallén JL, Rawal N, et al. Effect of auditory evoked potential-guided anaesthesia on consumption of anaesthetics and early postoperative cognitive dysfunction: a randomised controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2011;28(3):213-219.
[13] Deo H, West G, Butcher C, et al. The prevalence of cognitive dysfunction after conventional and computer-assisted total knee replacement. Knee. 2011;18(2):117-120.
[14] 黄宇光,徐仲煌,罗爱伦.外周区域阻滞与术后镇痛的新观点和新方法[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2011,17(18): 275-277.
[15] 万明涛.老年人髋关节置换应用腰-硬联合麻醉与全身麻醉的效果对照[J].健康之路,2014,13(8):182-183.
[16] 彭加英,蒋涛.腰麻-硬膜外联合麻醉在老年髋关节置换中的临床应用[J].医学理论与实践,2011,13(13):131-132.
[17] 梁多芳,张宜金,刘庆,等.地佐辛用于剖宫产术后静脉镇痛300例临床效果评价[J].现代生物医学进展, 2013,13(23): 4499-4502.
[18] Yang JN, Zhang YA, Ye H, et al. The optimal compatibility dosage of sufentanil-morphine combination with epidural postoperative analgesia. Prog Modern Biomed. 2013;13(1):107-111.
[19] Wang SC, Wan L, Ding GN, et al. The clinical research on spinal anesthesia with different dose of isobaric ropivacaine in caesarean section. J Clin Exp Med. 2013; 12(14):1135-1139.
[20] Wu CS, Sun DG. Effect evaluation on clonidine added to ropivacaine for epidural anesthesia of cesarean section. Guoji Yiyao Weisheng Daobao. 2012;18(4): 479-481.
[21] Qu XL, Li J, Zhang W, et al. Comparative study of different concentration of ropivacaine combined with butophanol on epidural anesthesia for cesarean section. Xibu Yixue. 2013;25(1):111-113.
[22] 曹亲亲,郭献阳,陈丽梅,等.不同麻醉方式应用于老年患者髋部手术时的血流动力学变化比较[J].温州医学院学报, 2011,11(1):665-667.
[23] 吴礼平,程文高,曹启旺,等.腰硬联合麻醉复合全身麻醉在老年患者髋关节置换中的麻醉效果[J].湖北民族学院学报(医学版),2012,29(4):46-47.
[24] 邓一午,文春艳.小剂量布比卡因腰硬联合麻醉与罗哌卡因硬膜外麻醉对老年人麻醉效果比较[J].中国医学工程, 2014,22(3):52-53.
[25] Shigeru T, Atsushi S, Yumiko I, et al. A local anesthetic, ropivacaine, suppresses activated microglia via a nerve growth factor-dependent mechanism and astrocytes via a nerve growth factor-independent mechanism in neuropathic pain. Mol Pain. 2011;7(1):2.
[26] 单海华,朱常花,谢红,等.超声引导下罗哌卡因连续股神经阻滞用于20例全膝关节置换后康复镇痛的疗效分析[J].重庆医学,2012,41(13):1312-1314.
[27] 陆慧红,李桂凤,白浪,等.全膝关节置换后局部浸润的持续镇痛效果[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,(4):529-534.
[28] 李蕊.罗哌卡因腰-硬联合麻醉在高龄患者髋部及下肢骨科手术中的应用[J].中华实用诊断与治疗杂志,2013, 27(1): 72-73.
[29] 赵文宝,万磊,李彦平,等.应用不同比重罗哌卡因单侧腰麻对下肢手术麻醉效果的比较性观察[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2014,13(11):934-937.
[30] 周雁,王薇,王东信,等.右美托咪定对老年单侧膝关节置换后谵妄发生率的影响[J].中国医药导报,2014,11(14): 77-81.
[31] 王诚,李琦,王宇冬,等.罗哌卡因腰椎硬膜外联合麻醉组在老年下肢骨关节置换中的应用[J].中国老年学杂志,2012, 32(19):4318-4319.
[32] 敬勇君,姬桂荣,张原,等.0.5%罗哌卡因在80岁以上高龄患者下肢骨科手术腰-硬联合麻醉中的应用[J].中国医药导报,2010,7(4):63-65.
[33] Bharti N, Praveen R, Bala I. A dose-response study of caudal dexmedetomidine with ropivacaine in pediatric day care patients undergoing lower abdominal and perineal surgeries:a randomized controlled trial. Paediatr Anaesth. 2014;24(11):1158-1163.
[34] 王玺,余湘元,朱建华,等.不同麻醉方法对老年患者人工髋关节置换手术后认知功能的影响[J].医学临床研究,2014, 31(1):115-117.
[35] 孙立,田晓滨,陈涛,等.局部浸润镇痛在老年全髋关节置换后多模式镇痛中的作用及安全性[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2014,8(2):151-155.
[36] 欧阳丽珍.低浓度罗哌卡因复合舒芬太尼用于高龄患者术后硬膜外镇痛[J].中国医药指南,2014,(34):183-184.
[37] Kim BG, Kang H. The effect of preemptive perianal ropivacaine and ropivacaine with dexmedetomidine on pain after hemorrhoidectomy: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Indian J Surg. 2014;76(1):49-55.
[38] Manuar MB, Majumdar S, Das A, et al. Pain relief after arthroscopic knee surgery: a comparison of intra-articular ropivacaine, fentanyl, and dexmedetomidine: a prospective,double-blinded, randomized controlled study. Saudi J Anaesth. 2014; 8(2):233-237.
[39] Kang H. The effect of dexmedetomidine added to preemptive ropivacaine infiltration on post-operative pain after inguinal herniorrhaphy: a prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur Surg. 2012;44(4):274-280.
[40] 王春爱,赵振文,王承祥,等.局部浸润罗哌卡因联合静脉镇痛对全膝关节置换后镇痛及早期康复的影响[J].临床骨科杂志,2014,17(3):274-276. |
.jpg)