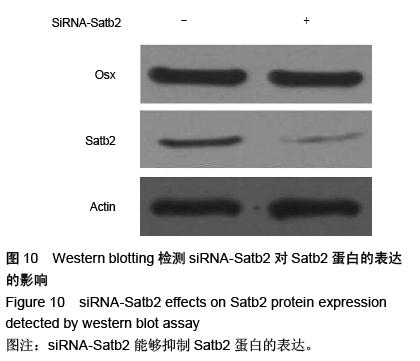
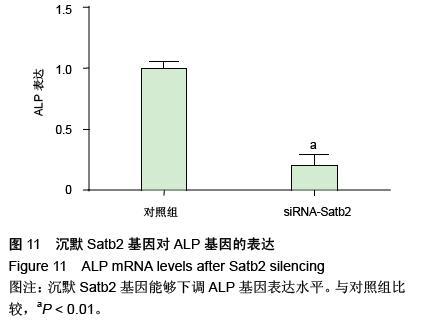
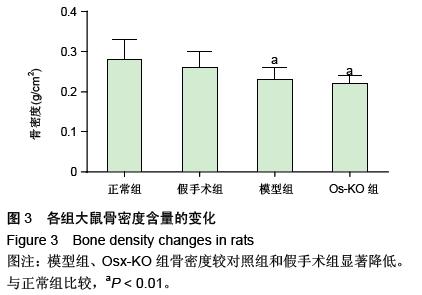
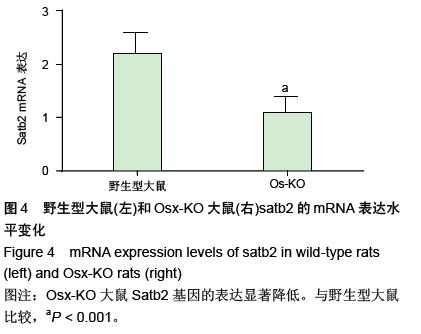
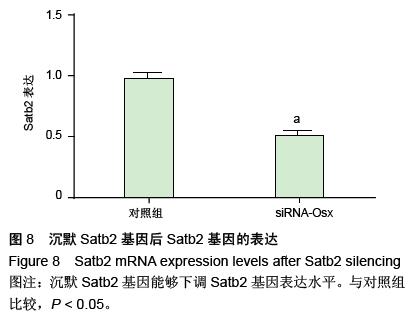
| [1] Dhinsa BS, Adesida AB.Current clinical therapies for cartilage repair, their limitation and the role of stem cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther.2012;7(2): 143-148.[2] Xu L, Meng F, Ni M, et al. N-cadherin regulates osteogenesis and migration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Biol Rep.2012;40(3): 2533-2539.[3] Shi Y, Xia YY, Wang L, et al. Neural cell adhesion molecule modulates mesenchymal stromal cell migration via activation of MAPK / ERK signaling. Exp Cell Res.2012; 318(17):2257-2267.[4] Deng J, Zou ZM, Zhou TL, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells can be mobilized into peripheral blood by G-CSF in vivo and integrate into traumatically injured cerebral tissue. Neurol Sci. 2011;32(4): 641-651.[5] Tang JM,Wang JN,Zhang L,et al.VEGF/SDF-1 promotes cardiac stem cell mobilization and myocardial repair in the infarcted heart. Cardiovasc Res.2011;91(3): 402-411.[6] Yu Q,Chen L,You Y,et al.Erythropoietin combined with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor enhances MMP-2 expression in mesenchymal stem cells and promotes cell migration. Mol Med Rep.2011;4(1): 31-36.[7] Neuss S, Schneider RK, Tietze L, et al.Secretion of fibrinolytic enzymes facilitates human mesenchymal stem cell invasion into fibrin clots. Cells Tissues Organs.2010;191(1): 36-46.[8] Liu H, Xue W, Ge G, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning advances CXCR4 and CXCR7 expression by activating HIF-1α in MSCs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2010;401(4): 509-515.[9] Chaturvedi P, Gilkes DM, Wong CC. Hypoxia-inducible factor dependent breast cancer-mesenchymal stem cell bidirectional signaling promotes metastasis. J Clin Invest.2013;123(1):189-205.[10] Lee SH, Lee YJ, Song CH, et al. Role of FAK phosphorylation in hypoxia-induced hMSCS migration: involvement of VEGF as well as MAPKS and eNOS pathways. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.2010;298(4): C847-C856.[11] Yu J, Li M, Qu Z, et al.SDF-1/CXCR4-mediated migration of transplanted bone marrow stromal cells toward areas of heart myocardial infarction through activation of PI3K / Akt. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2010;55(5): 496-505.[12] Dong F, Harvey J, Finan A, et al. Myocardial CXCR4 expression is required for mesenchymal stem cell mediated repair following acute myocardial infarction. Circulation.2012;126(3):314-324.[13] Sullivan GJ, Hay DC, Park IH, et al. Generation of functional human hepatic endoderm from human induced pluripotent stem cells.Hepatology.2010; 51(1):329-335.[14] 覃基政,韩晓东.骨髓间充质干细胞体外培养及其归巢机制[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 14(20): 7555-7559.[15] Picinich SC, Glod JW, Banerjee D. Protein kinase C zeta regulates interleukin -8 -mediated stromal-derived factor-1 expression and migration of human mesenchymal stromal cells. Exp Cell Res.2010;316(4): 593-602.[16] Lee SH, Lee YJ, Han HJ.Role of hypoxia-induced fibronectin integrin beta1 expression in embryonic stem cell proliferation and migration:Involvement of PI3K/Akt and FAK. J Cell Physiol.2011;226(2): 484-493.[17] Liu X, Duan B, Cheng Z, et al. SDF-1/CXCR4 axis modulates bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell apoptosis, migration and cytokine secretion.Protein Cell.2011;2(10):845-854.[18] Fischer-Valuck BW, Barrilleaux BL, PhinneyDG, et al. Migratory response of mesenchymal stem cells to macrophage migration inhibitory factor and its antagonist as a function of colony forming efficiency. Biotechnol Lett.2010;32(1):19-27. [19] LiM, Yu J, LiY, et al. CXCR4 positive bone mesenchymal stem cellsmigrate to human endothelial cell stimulated by ox-LDL via SDF-1alpha/CXCR4 signaling axis. ExpMol Patho. 2010;88(2): 250-255.[20] Thibeault S,Rautureau Y,Oubaha M,et al. S-nitrosylation of B-catenin by eNOS-derived NO promotesVEGF-induced endothelial cell permeability. Molecular Cell. 2010;39(3): 468-476.[21] Neuss S, Schneider RK, Tietze L, etal. Secretion of fibrinolytic enzymes facilitates humanmesenchymal stem cell invasion into fibrin clots. Cells Tissues Organs.2010; 191(1): 36-46.[22] Bassi EJ,Aita CA,Camara NO.Immune regulatory properties of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells: where do we stand?. World J Stem Cells.2011;3(1): 1-8.[23] Lange C, Brunswig-Spickenheier B, Cappallo-Obermann H, et al. Radiation rescue: mesenchymal stromal cells protect from lethal irradiation. PLoS One.2011;6(1): e14486.[24] Ankrum J, Karp JM. Mesenchymal stem cell therapy: Two steps forward, one step back. Trends Mol Med. 2010;16(5): 203-209.[25] Maijenburg MW, Gilissen C, Melief SM, et al. Nuclear receptors Nur77 and Nurr1 modulate mesenchymal stromal cell migration. Stem Cells and Development. 2012; 21(2): 228-238.[26] Hu SL, Lu PG, Zhang LJ, et al.In vivo magnetic resonance imaging tracking of SPIO-labeled human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(3):1005-1012.[27] 邱裕生,张银刚.骨组织再生策略的思考及膜性负压假说[J]. 西安交通大学学报:医学版,2011,32(6):659-663.[28] Nauth A, Schemitsch EH. Stem cells for the repair and regeneration of bone[J]. Indian J Orthop.2012;46:19-21.[29] 封卫兵,谢明,刘艳萍,等.骨损伤刺激对骨髓间充质干细胞增殖的影响[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(25):4-6.[30] 侯长举,朱振安,赵鑫,等.骨折大鼠血清对不同来源间充质干细胞的趋化作用[J].国际骨科学杂志,2011,32(4): 250-252.[31] 段小军,杨柳,周跃,等.增强型绿色荧光蛋白标记技术对骨折后骨髓间充质干细胞的迁移示踪[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2006,20(2):102-106.[32] 黎润光,邵景范,魏明发,等.牵引应力对体外骨髓间充质干细胞形态、排列及迁移的影响[J]. 生物医学工程与临床, 2011,15(1):1-4.[33] 廖新根,殷明,李士勇,等.SDF-1/CXCR4 轴在骨再生修复中的研究进展[J]. 生命科学,2010,22(10):1069-1073.[34] Kumar S, Wan C, Ramaswamy G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells expressing osteogenic and angiogenic factors synergistically enhance bone formation in a mouse model of segmental bone defect. Mol Ther.2011; 18:1026-34.[35] 范东艳,刘然, 徐福春,等.CXCL12/CXCR4生物学轴对骨髓间充质干细胞修复脊髓损伤的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(36):6651-6656.[36] 徐世红,谢兴文.骨髓间充质干细胞的相关迁移机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(19):3573-3576.[37] Tang JM,Wang JN,Zhang L,et al.VEGF/SDF-1 promotes cardiac stem cell mobilization and myocardial repair in the infarcted heart.Cardiovasc Res. 2011;91(3):402-411.[38] 徐丽,周健.趋化因子在骨缺损修复中的研究进展[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2011,21(10):636-638.[39] Kitaori T,Ito H,Schwarz EM,et al.Stromal cell-derived factor 1/CXCR4 signaling is critical for the recruitment of mesenchy-mal stem cells to the fracture site during skeletal repair in a mouse model.Arthritis Rheum.2009; 60(3): 813-823.[40] 石长贵,蔡筑韵,鲍哲明,等.骨骼生长因子促进骨折愈合的研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版, 2010,4(8): 126-128. |
.jpg)
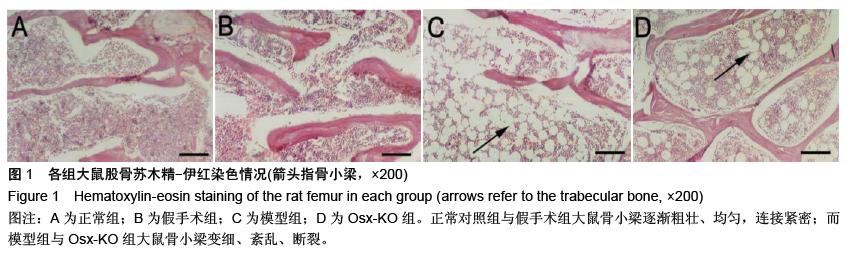
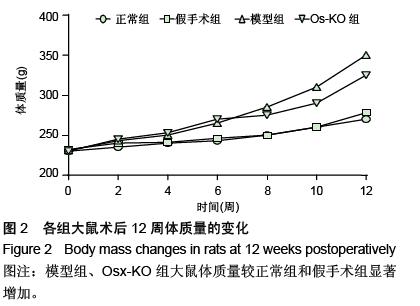
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)