| [1] Afonso V,Champy R,Mitrovic D,et al. Reactive oxygen species and superoxide dismutases: role in joint deseases. Joint Bone Spine.2007;74(4):324-329.
[2] Que LL,Wang HX,Cao BS,et al. The regulation and functions of transcription factor Nrf2 in cancer chemoprevention and chemoresistance. J Chin Pharm Sci.2011;20(1): 5-19.
[3] Phillips J, Moore-Medlin T, Sonavane K,et al.Curcumininhibits UV radiation-induced skin cancer in SKH-1 mice.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.2013;148(5):797-803.
[4] 孙宗建,何琨,张东,等.姜黄素预先给药对兔呼吸机相关性肺损伤时Nrf2蛋白表达的影响.中华麻醉学杂志,2014,34(2):237-240.
[5] Shishodia S,Singh T,Chaturvedi MM. Modulation oftranscriptionfactors bycurcumin. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2007; 595:127-148.
[6] 梁莉,阙琳玲,曹宝山,等. Nrf2在姜黄素保护UVB所致细胞氧化损伤中的作用[J].中华放射医学与防护杂志,2014,34(8): 583-587.
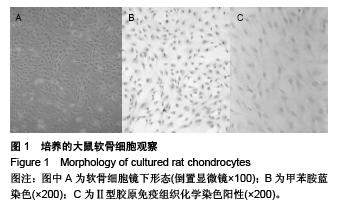
[7] 宋永周,崔慧先,吕哲,等.大鼠关节软骨细胞的培养[J].河北医科大学学报,2008,29(4):534-537.
[8] 宋永周,刘会玲,崔慧先,等.抗骨增生胶囊含药血清对软骨细胞增殖凋亡及基质金属蛋白酶分泌的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(24):4642-4646.
[9] 郑海燕,洪远,陈高.Nrf2-ARE在大鼠创伤性脑损伤模型中的表达及意义[J].中华神经外科杂志,2013,29(1):80-84.
[10] Tetik S,Ahmad S,Alturfan AA,et al.Determination of oxidant stress in plasma of rheumatoid arthritis and primary osteoarthritis patients.Indian J Biochem Biophys.2012;47(6): 353-358.
[11] Scott JL,Gabrielides C,Davidson RK,et al. Superoxide dismutase downregulation in osteoarthritis progression and end-stage disease. Ann Rheum Dis.2010;69(8):1502-1510.
[12] Olszewska-Sonina DM,Matewski D,Drewa G,et al.Oxidative equilibriuminthe prophylaxis of degenerativejoint changes: an analy-sis of pre-and postoperative activity of antioxidant enzymes in patients with hip and knee osteoarthritls.Med Sci Monit.2010;16(5):CR238-245.
[13] 张建武,闵冬雨,周云,等. 番茄红素对H2O2致乳鼠心肌细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2014,20(12): 160-164.
[14] He HB, Xu J, Xu YQ, et al. Cardioprotective effects of saponins from Panax japonicus on acute myocardial ischemia against oxidative stress-triggered damage and cardiac cell death in rats. J Ethnopharmacol.2012;140(1):73.
[15] McMahon M, Thomas N, Hoh K,et al. Dimerization of substrate adaptors can facilitate cullin-mediated ubiquitylation of proteins by a “tethering” mechanism: a two-site interaction model for the Nrf2-Keapl complex.J Biol Chem.2006;281: 24756-24768.
[16] Johnson JA, Johnson DA, Kraft AD, et al. The Nrf2-ARE pathway:an indicator and modulator of oxidative stress in neurodegeneration. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2008;1147:61-69.
[17] Rahman I. Antioxidant therapeutic advances in COPD. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2008;2(6):351-374. |
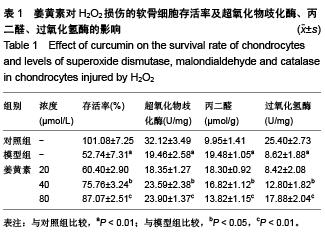
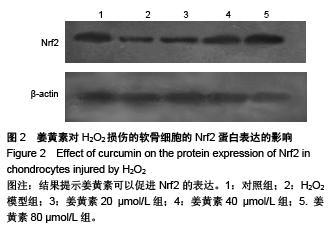
.jpg)
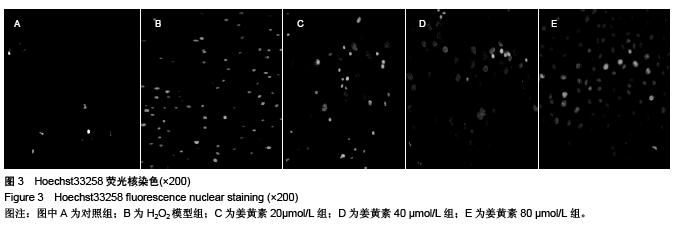
.jpg)