中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (49): 8026-8031.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.49.027
• 运动医学动物模型 Animal models of sports medicine • 上一篇 下一篇
原花青素对大负荷运动模型大鼠脾细胞自由基代谢及凋亡蛋白的影响
李 园1,刘文杰2,杨 宁1,闵 柱1
- 1南京师范大学体育科学学院,江苏省南京市 210000;2成都体育学院研究生院,四川省成都市 610041
Effects of proanthocyanidins on free radical metabolism and apoptosis-related protein expression in rat splenocytes after heavy-load exercise
Li Yuan1, Liu Wen-jie2, Yang Ning1, Min Zhu1
- 1Sport Science College of Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210000, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Graduate School of Chengdu Sport University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
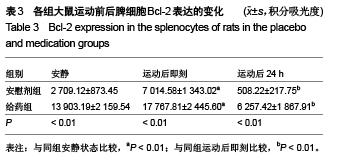
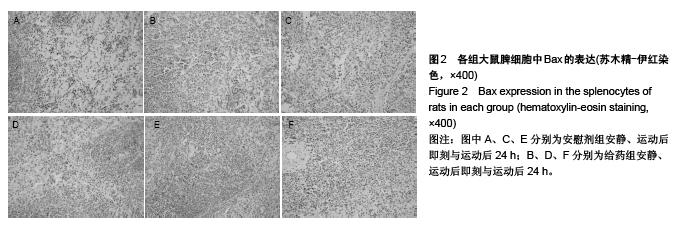
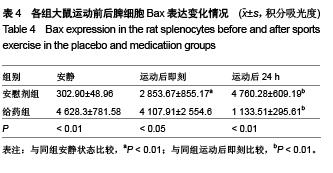
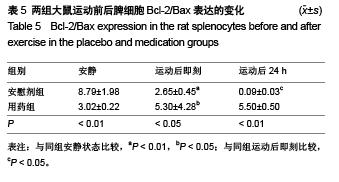
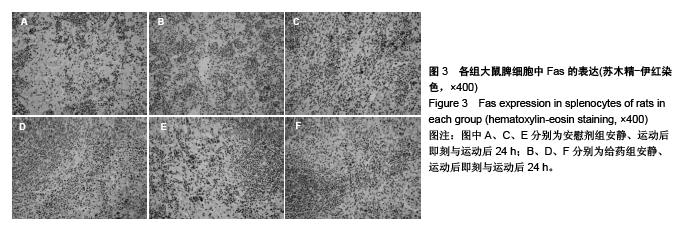
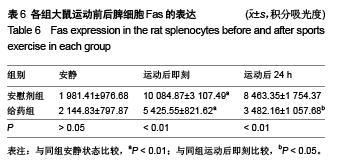
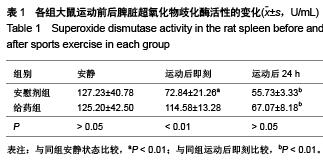
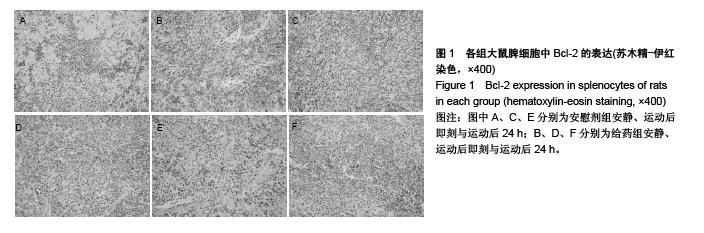
背景:研究发现,原花青素可以抑制细胞缺氧、复氧损伤过程中的细胞凋亡现象。 目的:观察原花青素对大负荷运动模型大鼠脾细胞自由基代谢及细胞凋亡相关蛋白Bcl-2、Fas、Bax表达的影响。 方法:将48只SD大鼠随机均分为安慰剂组和用药组,给药组灌胃给予原花青素水溶液15 mL/(kg•d),安慰剂组灌胃给予等量蒸馏水,连续给药2周。给药2周后,两组各均分为3个亚组,运动后即刻及运动后24 h组进行一次坡度为-10°、20 m/min的大负荷跑台运动,分别于运动后即刻、运动后24 h处死大鼠,安静组直接处死大鼠,检测脾细胞Bcl-2、Bax、Fas蛋白的表达,以及脾脏组织匀浆液超氧化物歧化酶、丙二醛水平。 结果与结论:①超氧化物歧化酶活性:两组组内比较,运动后24 h组<运动后即刻组<安静组;给药组运动后即刻、24 h的酶活性高于安慰剂组对应时相。②丙二醛水平:安慰剂组运动后即刻及24 h的水平均高于安静状态,给药组运动后即刻及24 h的含量均低于安静状态,给药组运动后即刻、24 h的丙二醛水平均低于安慰剂组对应时相(P < 0.01)。③Bcl-2:两组均于运动后即刻升高,于运动后24 h下降,并且给药组运动即刻及24 h的表达高于安慰剂组对应时相(P < 0.01)。④Bax:安慰剂组运动后即刻及24 h的表达高于安静状态(P < 0.01),给药组运动后即刻及24 h的表达低于安静状态(P < 0.01),并且给药组安静、运动后即刻及24 h的表达高于安慰剂组对应时相(P < 0.05,P < 0.01)。⑤Fas:两组组内比较,安静组<运动后24 h组<运动后即刻组;给药组运动即刻及24 h的表达低于安慰剂组对应时相(P < 0.01)。表明原花青素有助于减轻大负荷运动引起的脾脏脂质过氧化损伤,有效减缓自由基引起的运动性疲劳,有效降低脾细胞凋亡程度。
中图分类号:
.jpg)