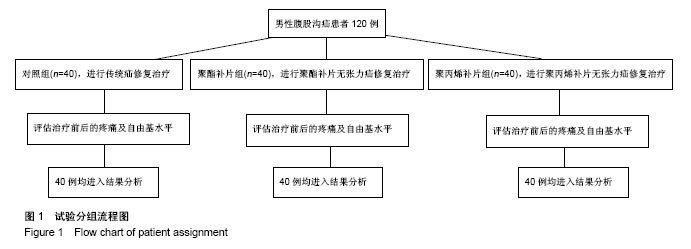
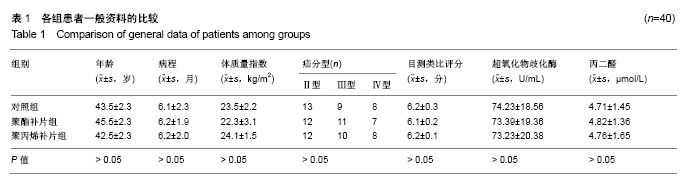
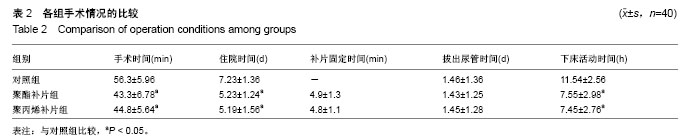
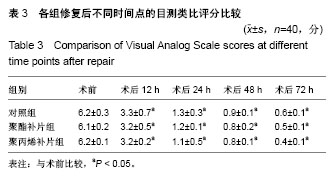
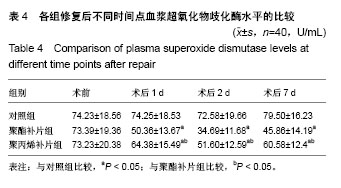
| [1] Rafiq MK, Sultan B, Malik MA, et al. Efficacy of local anaesthesia in repair of inguinal hernia. J Ayub Med Coll Abbottabad. 2016;28(4):755-757.[2] Shekhani HN, Rohatgi S, Hanna T, et al. Amyand's hernia: a case report. J Radiol Case Rep. 2016;10(12):7-11. [3] Raghavendran M, Kumar KG, Prasad S, et al. Post Incisional Hernia Meshplasty Vesicocutaneous Fistula-A Rare Complication. Urol Case Rep. 2017;13:149-151. [4] Brescia A, Tomassini F, Berardi G, et al. A new fixation-free 3D multilamellar preperitoneal implant for open inguinal hernia repair.Can J Surg. 2017;60(1):66-68.[5] Patel LY, Lapin B, Gitelis ME, et al. Long-term patterns and predictors of pain following laparoscopic inguinal hernia repair: a patient-centered analysis. Surg Endosc. 2017;31(5):2109-2121. [6] Tabbara M, Genser L, Bossi M, et al. Inguinal hernia repair using self-adhering sutureless mesh: adhesix™: a 3-year follow-up with low chronic pain and recurrence rate. Am Surg. 2016;82(2):112-116.[7] Bjerring AW, Lier ME, Roed SM, et al. Assessment of caesarean section and inguinal hernia repair as proxy indicators of total number of surgeries.Lancet. 2015;385 Suppl 2:S21. [8] 黄江龙,郑宗珩,叶小龙,等.新型纳米仿生补片修复兔腹壁疝模型的试验研究[J].中华普通外科学文献(电子版),2017,11(2):85-88.[9] 杜中伟.无张力疝修复对疝气患者治疗的临床效果体会[J].中国保健营养,2017,27(13):137-138.[10] 周先锋,马聪,王琦,等.轻量型和标准型聚丙烯补片修补腹股沟无张力疝的效果比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(21):3156-3162.[11] 贺家勇,杨晨晨,李义亮,等.腹腔镜下腹股沟疝前间隙修补、无张力疝修补与传统疝修补临床疗效比较[J].新疆医科大学学报, 2015,38(9):1146-1150, 1154. [12] Prusa AM, Kristo I, Rieder E, et al. Tension-Free Inlay Repair of Large Hiatal Hernias Using Dual-Sided Composite PTFE/ePTFE Meshes in Laparoscopic Surgery for Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2017. doi: 10.1089/lap.2016.0371. [13] Zulu HG, Mewa Kinoo S, Singh B. Comparison of Lichtenstein inguinal hernia repair with the tension-free Desarda technique: a clinical audit and review of the literature. Trop Doct. 2016; 46(3):125-129. [14] Xu H, Chen M, Xu Q, et al. Application of tension-free hernioplasty with hernia meshes of different materials and the postoperative effects on the reproductive function of male rats. Mol Med Rep. 2014;9(5):1968-1974. [15] Shin D, Lipshultz LI, Goldstein M, et al. Herniorrhaphy with polypropylene mesh causing inguinal vasal obstruction: a preventable cause of obstructive azoospermia.Ann Surg. 2005;241(4):553-558.[16] 刘晓瑞.皮肤衰老和氧自由基理论[J].生物学教学,2004,29(6): 4-5.[17] 毕敏,王德生,童绥君,等.局部亚低温对急性脑梗死氧自由基及炎症反应的干预作用[J].中华全科医师杂志,2011,10(7):507-509.[18] 中华医学会外科学分会疝和腹壁外科学组.成人腹股沟疝诊疗指南(2014年版)[J].中国实用外科杂志,2014,34(6):481-483.[19] 程玉前.复丝聚酯补片疝环充填式无张力修补老年性腹股沟斜疝48例临床分析[J].世界最新医学信息文摘(连续型电子期刊), 2015,15(15):71-74.[20] 彭志飚.聚丙烯充填式网塞补片无张力修补腹股沟疝的临床疗效探讨[J].临床医学工程,2017,24(1):93-94. [21] 贡红飞.腹腔镜完全腹膜外腹股沟疝修补(TEP)与开放式无张力腹股沟疝修补(Millikan)术后生活质量对比研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2016.[22] Schweitzer-Chaput B, Kurtén T, Klussmann M. Corrigendum: acid-mediated formation of radicals or baeyer-villiger oxidation from criegee adducts. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017;56(25):7024. [23] 李娜.硝苯地平片联合阿司匹林对妊娠期高血压患者氧自由基及血管内皮细胞功能的影响[J].中国临床实用医学,2017,8(2): 55-57. [24] 向羿,徐瑜,郭纯.替罗非班对冠心病不稳定型心绞痛患者疗效、氧自由基及炎性反应机制研究分析[J].吉林医学,2017,38(2): 287-290.[25] 樊岫珊.羟基自由基诱导DNA损伤机理研究进展[J].生物学杂志, 2017,34(1):80-84.[26] Ueda T, Inden M, Shirai K, et al. The effects of Brazilian green propolis that contains flavonols against mutant copper-zinc superoxide dismutase-mediated toxicity. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1): 2882. [27] Ekoue DN, Bera S, Ansong E, et al. Allele specific interaction between glutathione peroxidase 1 and manganese superoxide dismutase affects the levels of Bcl-2, Sirt3 and E-Cadherin. Free Radic Res. 2017:51(6):582-590. [28] Dragun Z, Filipovi? Mariji? V, Krasni?i N, et al. Malondialdehyde concentrations in the intestine and gills of Vardar chub (Squalius vardarensis Karaman) as indicator of lipid peroxidation. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9305-x. [29] Chatziralli IP, Theodossiadis G, Dimitriadis P, et al. The Effect of Vitamin E on Oxidative Stress Indicated by Serum Malondialdehyde in Insulin-dependent Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Retinopathy. Open Ophthalmol J. 2017;11:51-58. [30] 谢秋巧,黄湘,李菊满,等.龙胆木水提物对四氯化碳致小鼠肝损伤的保护作用研究[J].西医科大学学报,2017,34(2):181-184.[31] 张玥,朱晓冉,蔡玥,等. 灯盏花素对动脉粥样硬化大鼠氧化应激和炎症反应的影响[J].贵州医科大学学报,2017,42(1):71-75. [32] 胡浩.丁苯酞软胶囊对改善血管性痴呆患者认知功能的疗效及作用机制分析[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2017,20(1):98-99.[33] Zhang XF, Huang FH, Zhang GL, et al. Novel biomolecule lycopene-reduced graphene oxide-silver nanoparticle enhances apoptotic potential of trichostatin A in human ovarian cancer cells (SKOV3). Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12: 7551-7575. [34] Naidoo DB, Phulukdaree A, Anand K, et al. Centella asiatica Fraction-3 Suppresses the Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 Anti-Oxidant Pathway and Enhances Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated Cell Death in Cancerous Lung A549 Cells. J Med Food. 2017;20(10):959-968.[35] Pooja M, Pradeep ANR, Hungund SP, et al. Oxidative stress and cytotoxicity elicited lipid peroxidation in hemocytes of Bombyx mori larva infested with dipteran parasitoid, Exorista bombycis. Acta Parasitol. 2017;62(4):717-727. [36] Yuan YG, Gurunathan S. Combination of graphene oxide-silver nanoparticle nanocomposites and cisplatin enhances apoptosis and autophagy in human cervical cancer cells. Int J Nanomedicine. 2017;12:6537-6558. [37] Gan F, Hu Z, Zhou Y, Huang K. Overexpression and Low Expression of Selenoprotein S Impact Ochratoxin A-Induced Porcine Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis in Vitro. J Agric Food Chem. 2017;65(32):6972-6981. [38] Adebayo JO, Adewole KE, Krettli AU. Cysteine-stabilised peptide extract of Morinda lucida (Benth) leaf exhibits antimalarial activity and augments antioxidant defense system in P. berghei-infected mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2017; 207:118-128. [39] Kim J, Chen CH, Yang J, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2*2 knock-in mice show increased reactive oxygen species production in response to cisplatin treatment. J Biomed Sci. 2017;24(1):33. [40] Vipin AV, Raksha RK, Nawneet KK, et al. Protective effects of phenolics rich extract of ginger against Aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;91:415-424. |
.jpg)
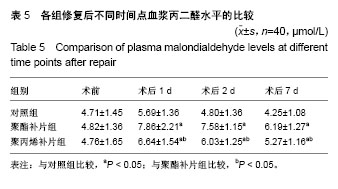
.jpg)