| [1] 侯喜君,王春华,廉红星,等. β-磷酸三钙煅烧骨负载抗生素治疗慢性骨髓炎的实验研究[J]中国组织工程研究,2012,16(51): 9518-9522.[2] Winters R,Tatum SA 3rd. Chronic nonbacterial osteomyelitis. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2014;22(4):332-335.[3] Conterno LO, da Silva Filho CR. Antibiotics for treating chronic osteomyelitis in adults.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;(3): CD004439.[4] Jae JJ, Ho SL, Young RC, et al. Surgical treatment of non -diabetic chronic osteomyelitis involving the foot and ankle. Foot & AnkleInter.2012;33(2):128-132.[5] 易远历,杨茂伟,王凯,等.VSD联合骨移植替代材料植入治疗跟骨慢性骨髓炎疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013, 28(12): 1210-1211.[6] Roderick MR, Ramanan AV. Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis. Adv Exp Med Biol.2013;764:99-107.[7] Marais LC, Ferreira N. Bone transport through an induced membrane in the management of tibial bone defects resulting from chronic osteomyelitis. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2015;10(1):27-33.[8] Spellberg B, Lipsky BA. Systemic antibiotic therapy for chronic osteomyelitis in adults. Clin Infect Dis. 2012;54(3): 393-407. [9] Panteli M,Puttaswamaiah R,Lowenberg DW,et al.Malignant Transformationbin Chronic Osteomyelitis: Recognition and Principles of Management. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2014; 22(9):586-594. [10] Senneville E, Nguyen S.Current pharmacotherapy options for osteomyelitis: convergences, divergences and lessons to be drawn.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2013;14(6):723-734. [11] Inanmaz ME, Uslu M, Isik C, et al.Extracorporeal shockwave increases the effectiveness of systemic antibiotic treatment in implant-related chronic osteomyelitis: experimental study in a rat model.J Orthop Res. 2014;32(6):752-756. [12] Vergidis P, Schmidt-Malan SM, Mandrekar JN, et al. Comparative activities of vancomycin, tigecycline and rifampin in a rat model of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus osteomyelitis.J Infect. 2015;70(6):609-615. [13] Gahukamble AD, McDowell A, Post V, et al.Propionibacterium acnes and Staphylococcus lugdunensis cause pyogenic osteomyelitis in an intramedullary nail model in rabbits.J Clin Microbiol. 2014;52(5):1595-1606. [14] 闻一新,周田华,徐永清,等.兔胫骨金黄色葡萄球菌慢性骨髓炎模型的制备[J].实用骨科杂志,2013,19(11):1001-1003.[15] Ozturan KE, Yucel I, Kocoglu E, et al.Efficacy of moxifloxacin compared to teicoplanin in the treatment of implant-related chronic osteomyelitis in rats.J Orthop Res. 2010;28(10): 1368-1372.[16] Norden CW, Shinners E, Niederriter K.Clindamycin treatment of experimental chronic osteomyelitis due to Staphylococcus aureus.J Infect Dis. 1986;153(5):956-959. [17] 黄金亮,唐辉,范新宇.等.慢性难治性骨髓炎动物模型制备与鉴定[J]. 西南国防医药,2012,22(3):236-239. [18] Odekerken JC,Arts JJ,Surtel DA,et al. A rabbit osteomyelitis model for the longitudinal assessment of early post -operative implant infections. J Orthop Surg Res.2013;4(8):38.[19] 陈孝平.外科常用实验方法及动物模型的建立[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2003:380.[20] 杜颖,徐文瑜,任珺,等.热原检查用家兔正常体温的统计分析[J]. 实验动物科学与管理,2003,20(1):17-19.[21] Kaarsemaker S,Walenkamp GH,vd Bogaard AE.New model for chronic osteomyelitis with staphylococcus aureus in sheep. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1997;339:246 -252.[22] Petty W,Spanier S,Shuster JJ,et al.The influence of skeletal implants on incidence of infection. Experiments in a canine model.J Bone Joint Surg Am.1985;67(8):1236-1244.[23] 刘立峰,邹林,蔡锦方.创伤性骨髓炎[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009, 17(10):766-768.[24] Horn J, Schlegel U, Krettek C,et al.Infection resistance of unreamed solid, hollow slotted and cannulated intramedullary nails: An in-vivo experimental comparison.J Orthop Res.2005; 23(4):810-815.[25] 高翠芳,李晓泉. 5%鱼肝油酸钠对慢性骨髓炎造模的影响[J].中医正骨,2002,14(9):12-13.[26] Helbig L,Simank HG,Lorenz H,et al,Establishment of a new methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus animal model of osteomyelitis. Int Orthop.2014;38(4):891-897. |
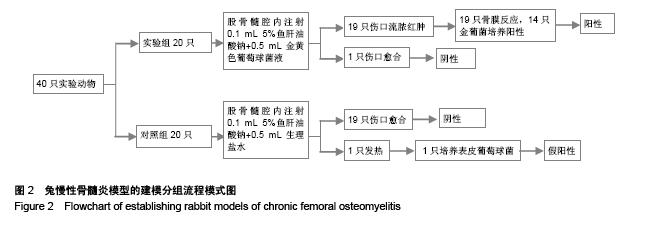
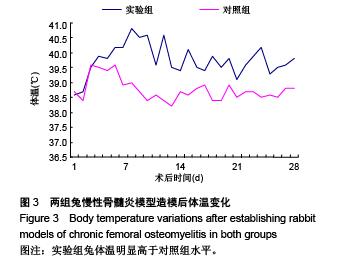
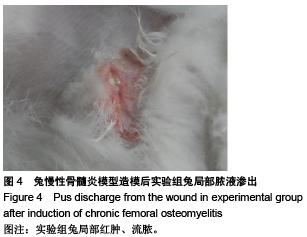
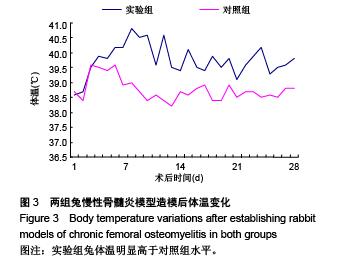
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)