中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (47): 7589-7596.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.47.008
• 组织工程骨及软骨材料 tissue-engineered bone and cartilage materials • 上一篇 下一篇
以羟基丁酸酯与羟基已酸酯共聚物为支架材料构建组织工程喉形态软骨
孙安科1,孟庆延2,李万同2,刘松波3,陈 伟4
- 解放军沈阳军区总医院,1耳鼻咽喉科,2烧伤与整形美容科,3显微外科,4医学实验科,辽宁省沈阳市 110016
-
收稿日期:2015-09-12出版日期:2015-11-19发布日期:2015-11-19 -
通讯作者:孙安科,解放军沈阳军区总医院耳鼻咽喉科,辽宁省沈阳市 110016 -
作者简介:孙安科,男,1962年生,河南省南阳市人,汉族,1985年解放军第二军医大学毕业,博士,主任医师,主要从事软骨组织工程与喉软骨功能重建研究。 -
基金资助:沈阳军区总医院院级重点基金课题(zy2009z0019)
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) as a scaffold to construct tissue-engineered larynx-shaped cartilage
Sun An-ke1, Meng Qing-yan2, Li Wan-tong2, Liu Song-bo3 , Chen Wei4
- 1 Department of Otolaryngology, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Area Command, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China
2 Department of Burns and Aesthetic Medicine, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Area Command, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China3 Department of Microsurgery, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Area Command, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China4 Department of Experimental Medicine, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Area Command, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2015-09-12Online:2015-11-19Published:2015-11-19 -
Contact:Sun An-ke, Department of Otolaryngology, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Area Command, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Sun An-ke, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Otolaryngology, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Area Command, Shenyang 110016, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the Key Fund of General Hospital of Shenyang Military Area Command, No. zy2009z0019
摘要:
背景:再生预定形态组织工程软骨的研究为喉软骨病损的修复与重建提供了新思路与新方法。然而,由于喉软骨形态、部位与功能的特殊性,迄今在此领域软骨组织工程研究并未呈现出其应有的优势。
引用本文
孙安科,孟庆延,李万同,刘松波,陈 伟. 以羟基丁酸酯与羟基已酸酯共聚物为支架材料构建组织工程喉形态软骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(47): 7589-7596.
Sun An-ke, Meng Qing-yan, Li Wan-tong, Liu Song-bo,Chen Wei. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) as a scaffold to construct tissue-engineered larynx-shaped cartilage[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(47): 7589-7596.
Quantitative analysis of experimental animals
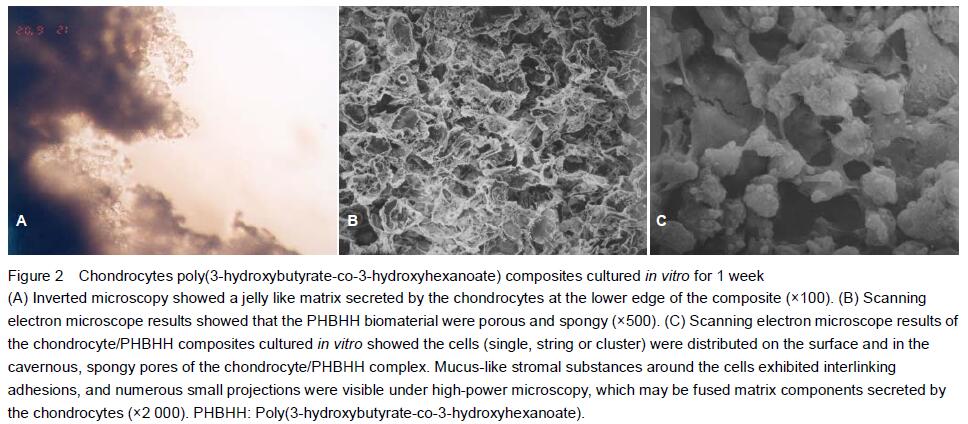
Experimental observation results in vitro

General morphology
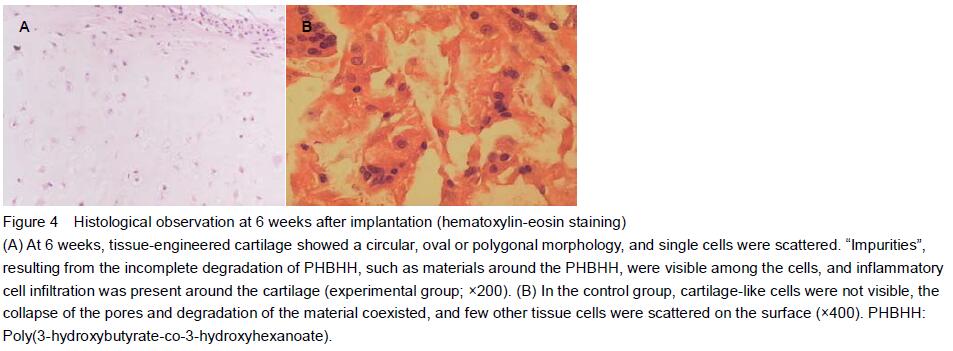
Hematoxylin-eosin staining results
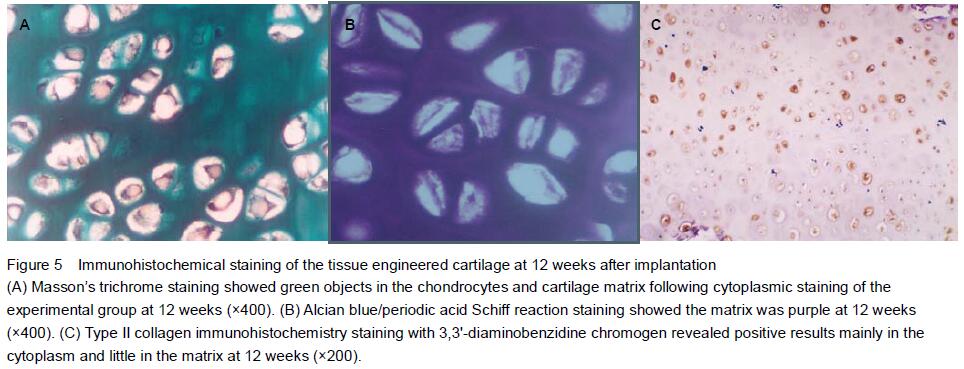
Masson’s trichrome staining results
| [1] Sterodimas A, de Faria J. Human auricular tissue engineering in an immunocompetent animal model. Aesthet Surg J. 2013;33(2):283-289. [2] Cheng NC, Estes BT, Young TH, et al. Engineered cartilage using primary chondrocytes cultured in a porous cartilage derived matrix. Regen Med. 2011;6(1):81-93.
[3] Fishman JM, De Coppi P, Elliott MJ, et al. Airway tissue engineering. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2011;11(12):1623 1635.
[4] Fisher MB, Mauck RL. Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: recent innovations and the transition to translation. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2013;19(1):1-13.
[5] Lu T, Li Y and Chen T. Techniques for fabrication and construction of three dimensional scaffolds for tissue engi¬neering. Int J Nanomedicine. 2013;8(3):337-350.
[6] Deng Y, Lin XS, Zheng Z, et al. Poly (hydroxybutyrate-co- hydroxyhexanoate) promoted production of extracellular matrix of articular cartilage chondrocytes in vitro. Biomaterials. 2003;24(23):4273-4281.
[7] Veleirinho B, Coelho DS, Dias PF, et al. Nanofibrous poly (3- hydroxybutyrate-co-3 hydroxyvalerate)/chitosan scaffolds for skin regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2012;51(4):343-350.
[8] Sun AK, Sun J, Sun W, et al. Applicability and biodegradability in vivo upon polyglycolic acid nonwoven mesh and poly (3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) porous sponge as scaffolds for tissue engineered cartilage. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2014;18(8):1172-1178.
[9] Zhang WJ, Cao YL. Progress and challenges in tissue engineering: the development of national tissue engineering center in China. Scientia Sinica (Vitae). 2014;44(2):132-138.
[10] Mikos AG, Sarakinos G, Leite SM, et al. Laminated three dimensional biodegradable foams for use in tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 1993;14(5):323-330.
[11] Zhang R, Ma PX. Poly (alpha-hydroxylacids)/hydroxyaptite porous composites for bone tissue engineering. I. Preparation and morphology. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;44(4):446-455.
[12] Sun AK, Hu P, Li WT, et al. Fabrication of larynx-shape porous PHBHH for cartilage tissue engineering and the cytocompatibility with chondrocytes. Tinglixue Ji Yanyujibing Zazhi. 2011;19(6):558-561.
[13] Gilpin DA, Weidenbecher MS, Dennis JE. Scaffold free tissue engineered cartilage implants for laryngotracheal reconstruction. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(3):612-617.
[14] Shahin K, Doran PM. Improved seeding of chondrocytes into polyglycolic acid scaffolds using semi static and alginate loading methods. Biotechnol Prog. 2011;27(1):191-200.
[15] El Sayed K, Marzahn U, John T, et al. PGA associated heterotopic chondrocyte cocultures: implications of nasoseptal and auricular chondrocytes in articular cartilage repair. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2013;7(1):61-72.
[16] Chaim IA, Sabino MA, Mendt M, et al. Evaluation of the potential of novel PCL-PPDX biodegradable scaffolds as support materials for cartilage tissue engineering. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012;6(4):272-279.
[17] Xue J, Feng B, Zheng R, et al. Engineering ear shaped cartilage using electrospun fibrous membranes of gelatin/ polycaprolactone. Biomaterials. 2013;34(11):2624- 2631.
[18] Liu SY, Chen JY, Chen QQ, et al. Construction of tissue-engineered cartilage with cross-linked sodium hyaluronate as scafold materials in vitro. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2014;18(8):1191-1197.
[19] Chen ZF, Wu YL, Ma RN, et al. The construction of tissue engineering cartilage with a new poly-β-hydroxybutyrate scaffold. Xiandai Shengwu Yixue Jinzhan. 2013;13(4): 627-630.
[20] Zhao K, Deng Y, Chun CJ, et al. Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) scaffolds with good mechanical properties and biocom patibility. Biomaterials. 2003;24(6):1041-1045. |
| [1] | 吴 训, 孟娟红, 张建运, 王 亮. 浓缩生长因子修复兔髁突全层软骨损伤[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1166-1171. |
| [2] | 李嘉程, 梁学振, 刘金豹, 许 波, 李 刚. 骨性关节炎mRNA差异表达谱及竞争性内源RNA调控的网络分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1212-1217. |
| [3] | 耿秋东, 葛海雅, 王和鸣, 李 楠. 基于网络药理学探讨龟鹿二仙胶治疗骨关节炎的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [4] | 刘翔翔, 黄云梅, 陈文列, 林如辉, 卢小冬, 李钻芳, 许亚晔, 黄美雅, 李西海. 早期骨关节炎模型大鼠半月板白区细胞的超微结构变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(8): 1237-1242. |
| [5] | 万 然, 史 旭, 刘京松, 王岩松. 间充质干细胞分泌组治疗脊髓损伤的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [6] | 曾燕华, 郝延磊. 许旺细胞体外培养及纯化的系统性综述[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [7] | 侯婧瑛, 于萌蕾, 郭天柱, 龙会宝, 吴 浩. 缺氧预处理激活HIF-1α/MALAT1/VEGFA通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞生存和血管再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 985-990. |
| [8] | 王 丰, 周立宇, 赛吉拉夫, 齐士斌, 马艳霞, 韦善文. CaMKⅡ-Smad1促进外周神经的轴突再生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(7): 1064-1068. |
| [9] | 何祥忠, 陈海云, 刘 军, 吕 阳, 潘建科, 杨文斌, 何静雯, 黄俊翰. 富血小板血浆联合微骨折对比微骨折治疗膝关节软骨病变的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [10] | 刘 欣, 颜飞华, 洪坤豪. 调控水通道蛋白表达延缓膝骨关节炎模型大鼠软骨退变[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [11] | 马泽涛, 曾 晖, 王德利, 翁 鉴, 冯 松. 微小RNA-138-5p与软骨细胞增殖和自噬的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(5): 674-678. |
| [12] | 谢崇新, 张 磊. 保留与不保留残端重建前交叉韧带术后膝关节退变的比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| [13] | 邓桢翰, 黄 勇, 肖璐璐, 陈昱霖, 朱伟民, 陆 伟, 王大平. 骨形态发生蛋白在关节软骨再生过程中的作用与应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(5): 798-806. |
| [14] | 王玉姣, 刘 丹, 孙 嵩, 孙 勇. 改良型富血小板纤维蛋白复合双相磷酸钙可促进兔骨髓间充质干细胞的活性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [15] | 刘江锋. 纳米羟基磷灰石/聚酰胺66复合材料联合锁定钢板治疗股骨骨纤维异常增殖症[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 542-547. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
MATERIALS AND METHODS
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
实验将新型生物材料聚羟基丁酸酯与聚羟基己酸酯共聚物塑形成中空半喇叭形态,并与软骨种子细胞相复合,采用筋膜衬里、肌筋膜瓣充填与包裹技术构建中空半喇叭形态组织工程喉软骨,为肌筋膜瓣复合组织工程化软骨修复重建喉软骨支架功能提供实验依据。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
聚羟基烷酸酯类材料的特点?是由微生物产生的聚酯类天然物质,具有生物相容性好、无致炎性、无排斥性和易降解等特点。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||