[2] 王焕彬,陈枝. 不同麻醉方法对老年患者全髋置换术后认知功能障碍发生率的比较[J]. 中国医学创新,2013,10(26):118-120.
[3] Harris WH.Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabularfractures:treatment by mold arthroplasty, an end-result study using a newmethod of result evaluation.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;51(4):737-755.
[4] 吴章飞雪,于燕燕,徐枝楼,等.品管圈活动在精神科老年病房基础护理质量管理中的作用[J].中华护理杂志,2013,48(2): 127-130.
[5] 陈凯敏,张伟明,于哲一,等.人工髋关节翻修术后早期程序化康复干预的效果评估[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(38):66-67.
[6] 汤宇,孙天胜.股骨偏心距与全髋关节置换术后假体功能及相关生物力学的变化[J].中国临床康复, 2006, 10(33): 133-135.
[7] 张海漳,唐梅.全髋关节置换术后早期随访对病人康复疗效的影响[J].中华医学护理杂志,2005,15(113):2281.
[8] 魏艳红,张晋,张菁. 关节镜下治疗16例股骨髋臼撞击症患者的康复护理[J].中华护理杂志,2009,44(12): 1073-1075.
[9] Rorabeck CH, Bourne BR. Soft tissue balancing of the hip: A con-ceptwhich has come of age. Presented at the 70th annualmee-ting of the American Academy ofOrthopaedic Surgeons. New Orleans, LA, 2003.
[10] Buvanendran A, Kroin JS,Tuman KJ,et al. Effects ofperioperative administration of a selective cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor on painmanagement and recovery of function after knee replacement: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2003; 290(18): 2411-2418.
[11] 于浩淼,白晓东,马立峰,等.环氧化酶2抑制剂帕瑞昔布、塞来昔布在 TKA 围手术期多模式镇痛中的效果研究[J].中华损伤与修复杂志:电子版,2014,9(6):634-639.
[12] 刘德明,王黎明,许春彦.中药熏蒸加手法治疗对全膝关节置换术围手术期的影响[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2012,20(2): 48-49.
[13] 张瑛,商月娥,杨新明.老年髋关节置换术后并发症的预防及预见性护理体会[J].中华损伤与修复杂志(电子版),2013,8(1): 80-83.
[14] Kiyama T,Naito M,Shinoda T,et al. Hip abductor strengths after total hip arthroplasty via the lateral and posterolateral approaches. J Arthtoplasty. 2010;25(1):76-80.
[15] Malviya A,Lingard EA,Malik A,et al.Hip flexion after Birmingham hip resurfacing:role of cup anterior femoeal head-neck offset,and head-neck ratio. J Arthtoplasty. 2010; 25(3):387-391.
[16] 武迪,段敏,王卫青.全膝关节置换术后膝关节肿胀、疼痛程度对膝关节功能的影响及护理[J].中国医药导报,2012,9(9): 128-134.
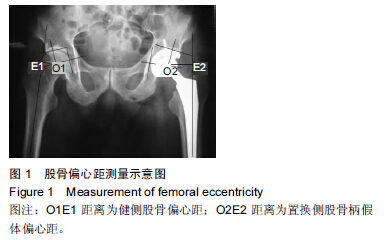
[17] 芦北极,孙俊英,施勤,等.全髋关节成形术后的偏心距测量对临床功能的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(14):1282-1286.
[18] 吕作刚,孔荣.股骨偏心距变化可影响髋关节置换后相关并发症的发生[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(13): 2309-2312.
[19] Wik TS,Enoksen C,Klaksvik J,et al. In vitro testing of the deformation pattern and initial stability of a cementless stem coupled to an experimental femoral head, with increased offset and altered femoral neck angles. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2011;225(8):797-808.
[20] Chamnongkich S,Asayama I, Kinsey TL, et al. Difference in hi p prosthesis femoral offset affects hi p abductor strength and gait characteristics during obstacle crossing. Orthop Clin North Am. 2012;43(5): e48-58.
[21] Brilhault JM,Ries MD. Posteriorly offset femoral component to restore anteroposterior position of the distal femur in revision total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2011;26(2): 214-217.
[22] Malviya A,Lingard EA,Malik A,et al. Hip flexion after Birmingham hi p resurfacing: role of cup anteversion, anterior femoral head-neck offset, and head-neck ratio. J Arthroplasty. 2010; 25(3): 387-391.
[23] 李永奖,蔡春元,杨国敬,等.后外侧微创小切口与传统全髓关节置换术的比较[J].临床骨科杂志,2010,13(2):153-157.
[24] 黄晓文,程力,何天达,等.前外侧小切口与常规后外侧切口全髓关节置换的疗效对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(9): 1538-1542.
[25] 余敏,王万春,李雨佳.前外侧与后外侧小切口人路行初次全髓置换手术效果比较[J].临床骨科杂志,2009,12(4):445-447.
[26] 崔巍,曲建波,杨方军,等.人工全髓关节置换术后关节脱位与手术人路的临床分析[J].黑龙江医学,2009,33(7):509-510.
[27] 陈立科,徐秋香,徐海涛,等.人工髋关节置换术后并发症分析及处理[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2011,22(8):663.
[28] 赵丽云,急赵诊手术中与麻醉师配合的护理体会[J].齐齐哈尔医学院学报,2010,31(8):1339-1341.
[29] 张海青,武文翠,李文炎.人工全髋关节置换术后护理[J].中国民族民间医药,2010,19(6):664-665.
[30] 刘贵芝,李萍.人工全髋关节置换术的康复训练指导及护理[J].护士进修杂志,2011,26(18):542-543.
[31] 申建兴.强直性脊柱炎全髋关节置换术临床治疗分析[J].中国社区医师,2011,13(26):70.
[32] 马若凡,陈铿,沈慧勇,等.强直性脊柱炎全髋关节置换术的疗效及并发症分析[J].实用医学杂志,2009,25(21):3636-3637.
[33] 陈余庆,季祝永,孙凤翔,等.全髋关节置换治疗强直性脊柱炎11例[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(48):9553-9554.
[34] 李其一,金今,翁习生,等.全髋关节置换治疗强直性脊柱炎24例[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(22):568-569.
[35] 郭林,陈昊,杨延伟,等.局部注射含氯诺昔康的镇痛药物抑制痛觉致敏作用对全膝关节置换手术后疼痛控制的影响研究[J].中华关节外科杂志:电子版,2011,5(6):693-697.
[36] Tezuka T, Inaba Y, Kobayashi N, et al. Effects of hip joint center location and femoral offset on abductor muscle strength after total hip arthroplasty. Mod Rheumatol. 2015; 25(4):630-636.
[37] von Roth P, Perka C, Mayr HO, et al. Reproducibility of femoral offset following short stem and straight stem total hip arthroplasty.Orthopedics. 2014;37(7):e678-684.
[38] Weber M, Woerner ML, Springorum HR, et al. Plain radiographs fail to reflect femoral offset in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(8):1661-1665.
[39] Liu YP, Hao YD.Restoration of femoral offset, rotation centers, limbs length equality of Chinese total hip arthroplasty patients. Pak J Med Sci. 2014;30(1):116-121.
[40] Shetty GM, Mullaji A, Bhayde S. Computer guided restoration of joint line and femoral offset in cruciate substituting total kneearthroplasty. Knee. 2012;19(5):611-616.