|
[1] 邓洁.对人工肝安全有效性研究相关问题探讨[J].中国血液净化, 2011,10(8):458-460.
[2] Rafael B,Maria C,Javier V.Liver support systems:will theyever reach primetime. Curr Gastroenterol Rep.2013;15(3):1-7.
[3] 王英杰.人工肝在肝衰竭中的应用与评价[J].实用肝脏病杂志, 2013,16(1):20-21.
[4] Ryska O,Pantoflicek T,Laszikova E,et al.Artificial liver supportsystem reduces intracranial pressure more sffectively than bioartificial system:an experimental study.Int J Artif Organs. 2012;35(7):503-510.
[5] Rademacher S,Oppert M,Jörres A.Artificial extracorporeal liber support therapy inpatients with severe liver failure.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.2011;5(5):591-599.
[6] 郭予斌,李爱民,刘思德.生物人工肝细胞材料的研究进展[J].现代消化及介入诊疗,2013,18(1):53-55.
[7] 刘赛兰,章瀚文,潘天慧,等.猪内源性逆转录病毒与异种移植及生物人工肝安全性问题[J].肝脏,2013,18(2):125-129.
[8] Yamanakas T.Induction of pluripotent stem cell from mouse embiyonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell.2006;126(4):663-676.
[9] Lu LL,Liu YJ,Yang SG,et al.Isolation and characterization of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells with hematopoiesis-supportive function and other potentials. Haematologica.2006;91:1017-1026.
[10] Karahuseyinoglu S,Cinar O,Kilic E,et al. Biology of stem cells in human umbilical cord stroma: in situ and in vitro surveys. Stem Cells.2007;25(2):319-331.
[11] Weiss ML,Medicetty S,Bledsoe AR,et al.Human umbilical cord matrix stem cells: p reliminary characterization and effect oftransp lantation in a rodent model of Parkinsonps disease. Stem Cells.2006;24:781-792.
[12] Sudo K,Kanno M,Miharada K,et al.Mesenchymal progenitors able to differentiate into osteogenic, chondrogenic, and/or adipogenic cells in vitro are present in most primary fibroblast-like cell populations.Stem Cells.2007;25:1610-1617.
[13] Hardy SA,Maltman DJ,Przyborski SA.Mesenchymal stem cells as mediators of neural differentiation.Curr Stem Cell Res Ther.2008;3:43-52.
[14] Titorencu I,Jinga VV,Constantinescu E,et al.Proliferation, differentiation and characterization of osteoblasts from human BM mesenchymal cells. Cytotherapy.2007;9:682-696.
[15] Troyer DL,Weiss ML.Wharton's jelly-derived cells are a primitive stromal cell population.Stem Cells.2008;26(3): 591-599.
[16] Kasuya J,Sudo R,Tamogami R,et al.Reconstruction of 3D stacked hepatocyte tissues use degradable, microporouspoly (d,l-lactide-co-glycolide)membranes.Biomaterials. 2012;33(9): 2693-2700.
[17] Moran EC,Baptista PM,Evans DW,et al.Evaluation of parenchymal fluid pressure in native and decellularized liver tissue.Biomed Sci Instrum.2012;4(8):303-309.
[18] Kasoju N,Bora U.Silk fibroin based biomimetic artificial extracellular matrix for hepatic tissue engineering applications. Biomed Mater.2012;7(4):1045-1055.
[19] Ducatti DR,Massi A,Noseda MD,et al.Production of carbohydrate building blocks from red seaweed polysaccharides. Efficient conversion of galactans into C-glycosyl aldehydes.Org Biomol Chem.2009;7(3):576-588.
[20] Gao C,Liu M,Chen J,et al.Interactions between bovine serum albumin and oxidized sodium alginate in solution.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.2011;22(12):1639-1650.
[21] Okano T,Yamada N,Sakai H,et al.A novel recovery system for cultured cells using plasma-treated polystyrene dishes grafted with poly(N-isopropylacrylamide).J Biomed Mater Res.1993; 27(10):1243-1251.
[22] Miyoshi H,Ehashi T,Kawai H,et al.Three-dimensional perfusion cultures of mouse and pig fetal liver cells in a packed-bed reactor:effect of medium flow rate on cell numbers and hepatic functions.J Biotechnol. 2010;148(4): 226-322.
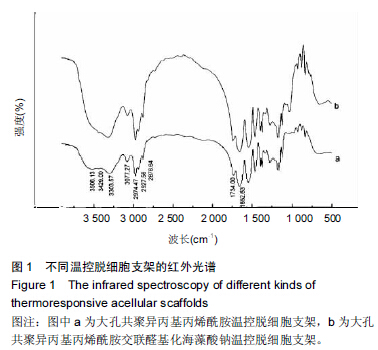
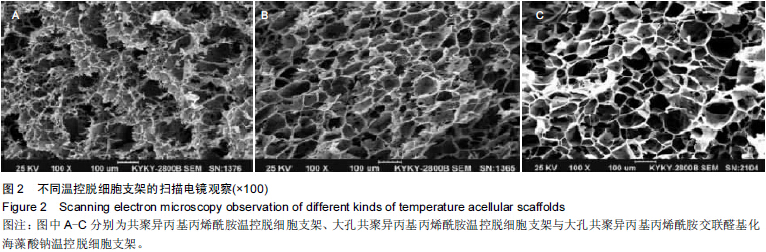
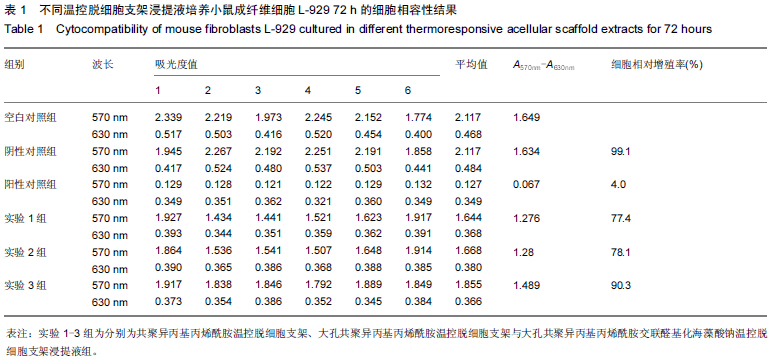
[23] 于美丽,杜智,韩涛,等.醛基化海藻多糖复合材料作为人工肝载体的可行性[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(25):4660-4667
[24] Behbahan IS,Duan Y,Lam A,et al.New approaches in the differentiation of human embryonic stem cells and induced pluripotent stem cells toward hepatocytes.Stem Cell Rev.2011; 7(3):748-759.
[25] Yi F,Liu GH,Izpisua Belmonte JC.Human induced pluripotent stem cells derived hepatocytes: rising promise for disease modeling, drug development and cell therapy. Protein Cell. 2012;3(4):246-250.
[26] Mohsin S,Shams S,Ali Nasir G,et al.Enhanced hepatic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells after pretreatment with injured liver tissue.Differentiation.2011;81(1):42-48.
[27] Takahashi K,Yamanaka S.Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures bydefined factors.Cel1.2006;126(4):663-676.
[28] Moeller HC,Mian MK,Shrivastava S,et al.A microwell array system for stem cell culture. Biomaterials.2008;29(6): 752-763.
[29] Vierbuchen T,Ostermeier A,Pang ZP,et al.Direct conversion of fibroblasts to functional neurons by defined factors.Nature. 2010;463(7284):1035-1041.
[30] Ieda M,Fu JD,Delgado-Olguin P,et al.Direct Reprogramming of Fibroblasts into Functional Cardiomyocytes by Defined Factors.Cell.2010;142(3):375-386.
|