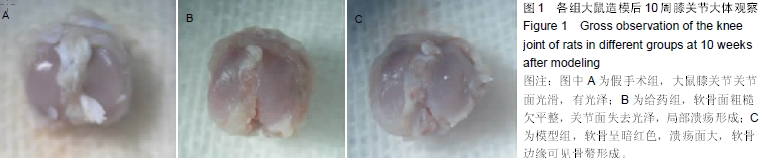
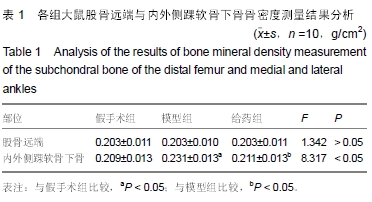
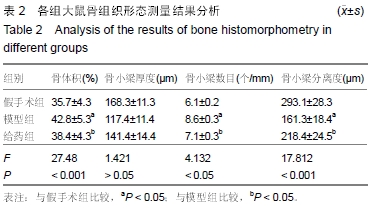
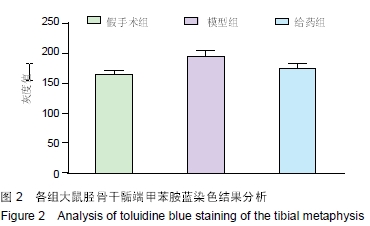
| [1] 谢功华,唐宇.骨关节炎发病相关因素与护理对策[J].内蒙古中医药, 2012,31(20):51.
[2] 王伟,王坤正,党小谦,等.中老年膝骨关节炎发病的相关因素[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(44):15-18.
[3] 孙书龙,孟祥奇,姜宏,等.四肢骨关节炎发病过程中软骨细胞死亡机制研究进展[J].内蒙古中医药,2012,31(17):136-138.
[4] 尤笑迎,杨红梅.兔膝骨性关节炎软骨损伤及降钙素的保护作用[J].天津医药,2012,40(7):688-691.
[5] 荊玉晓.老年性骨关节炎合并骨质疏松症性膝痛的临床治疗分析[J].中国保健营养(下旬刊),2014,24(6):3106-3107.
[6] 李永刚,唐海.鲑鱼降钙素在膝关节骨关节炎中的应用[J].国际外科学杂志,2012,39(7):457-461.
[7] 李涧,董启榕,谢宗刚,等.降钙素对骨关节炎大鼠关节软骨的影响[J].江苏医药,2014,40(1):4-6,封2-封3.
[8] 尤笑迎,杨红梅.降钙素对兔膝骨关节炎发病过程中细胞因子及关节软骨细胞凋亡的试验研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2012,18(3): 223-228.
[9] ManicourtDH,AzriaM,MindeholmL,et al.Oral salmon calcitonin reduces Lequesne's algofunctional index scores and decreases urinary and serum levels of biomarkers of joint metabolism in knee osteoarthritis.Arthritis Rheum.2006;54(10):3205-3211.
[10] 陈喜德,宋丽君,魏波,等.骨关节炎SD大鼠关节软骨中蛋白多糖与YKL-40的相关性[J].重庆医学,2014,43(10):1214-1217.
[11] Ito H,Hamerman JA.TREM-2, triggering receptor expressedon myeloid cell-2, negatively regulates TLR responses indendritic cells.Eur J Immunol. 2012;42(1):176-185.
[12] Gao X,Dong Y,Liu Z,et al. Silencing of triggering receptorexpressed on myeloid cells-2 enhances the inflammatoryresponses of alveolar macrophages to lipopolysaccharide.Mol Med Rep.2013;7(3):921-926.
[13] Chen Q,Zhang K,Jin Y,et al.Triggering receptor expressedon myeloid cells-2 protects against polymicrobial sepsis byenhancing bacterial clearance. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.2013;188(2):201-212.
[14] Crotti TN,Dharmapatni AA,Alias E,et al.Theimmunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif (ITAM)related factors are increased in synovial tissue andvasculature of rheumatoid arthritic joints. Arthritis Res Ther.2012;14(6):R245.
[15] 陈欢雪,王晓非.间充质干细胞移植治疗4种风湿性疾病:10年资料分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(14):2263-2268.
[16] Kaur K,Kalra S,Kaushal S.Systematic review of tofacitinib: anew drug for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Ther. 2014;36(7):1074-1086.
[17] Rajagopalan P,Hibar DP,Thompson PM.TREM2 andneurodegenerative disease.N Engl J Med.2013;369(16): 1565-1567.
[18] Sun M,Zhu M,Chen K,et al.TREM-2 promotes hostresistance against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection bysuppressing corneal inflammation via a PI3K/Akt signalingpathway.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2013;54(5):3451-3462.
[19] Suchankova M,Bucova M,Tibenska E,et al.Triggeringreceptor expressed on myeloid cells-1 and 2 inbronchoalveolar lavage fluid in pulmonary sarcoidosis.Respirology. 2013;18(3):455-462.
[20] Oh JH,Yang MJ,Heo JD,et al.Inflammatory response in ratlungs with recurrent exposure to welding fumes: atranscriptomic approach.Toxicol Ind Health. 2012;28(3):203-215.
[21] Paradowska-Gorycka A,Jurkowska M.Structure, expressionpattern and biological activity of molecular complexTREM-2/DAP12.Hum Immunol.2013;74(6):730-737.
[22] Zheng Y,Hou J,Peng L,et al.The pro-apoptotic andpro-inflammatory effects of calprotectin on human periodontalligament cells.PLoS One.2014;9(10):e110421.
[23] Zanin-Zhorov A,Weiss JM,Nyuydzefe MS,et al.Selectiveoral ROCK2 inhibitor down-regulates IL-21 and IL-17secretion in human T cells via STAT3-dependent mechanism.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2014;111(47):16814-16819.
[24] 侯春凤,孙闵,李树杰,等.小干扰RNA对人类风湿关节炎患者滑膜细胞基因表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(46):8062-8068.
[25] Sun M,Zhu M,Chen K,et al.TREM-2 promotes hostresistance against Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection bysuppressing corneal inflammation via a PI3K/Akt signalingpathway.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.2013;54(5):3451-3462.
[26] Liu Q,Zhao J,Tan R,et al.Parthenolide inhibitspro-inflammatory cytokine production and exhibits protectiveeffects on progression of collagen-induced arthritis in a ratmodel.Scand J Rheumatol. 2015;44(3):182-191.
[27] Damento G,Kavoussi SC,Materin MA,et al.Clinical andhistologic findings in patients with uveal melanomas aftertaking tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014;89(11): 1481-1486.
[28] Meier FM,McInnes IB.Small-molecule therapeutics inrheumatoid arthritis: scientific rationale, efficacy and safety.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2014;28(4):605-624.
[29] Goedken ER,Argiriadi MA,Banach DL,et al.TricyclicCovalent Inhibitors Selectively Target Jak3 through an ActiveSite Thiol. J Biol Chem.2015;290(8):4573-4589.
[30] Lis K,Kuzawińska O,Ba?kowiec-Iskra E.Tumor necrosisfactor inhibitors - state of knowledge.Arch Med Sci.2014;10(6): 1175-1185. |