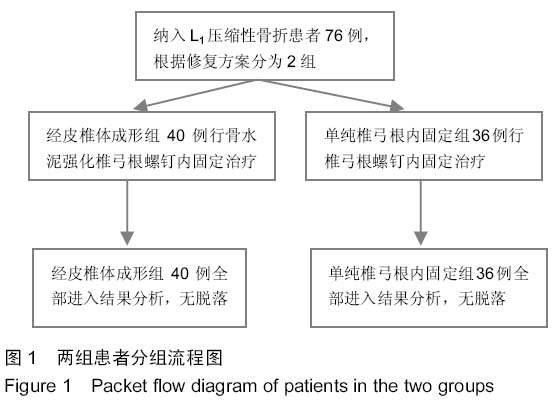
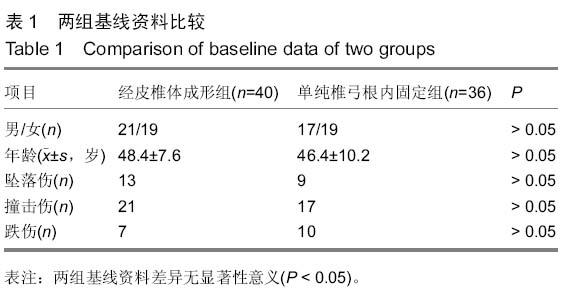
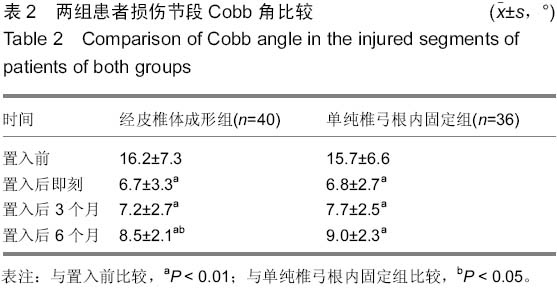
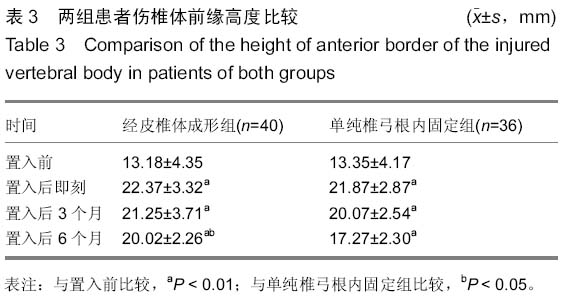
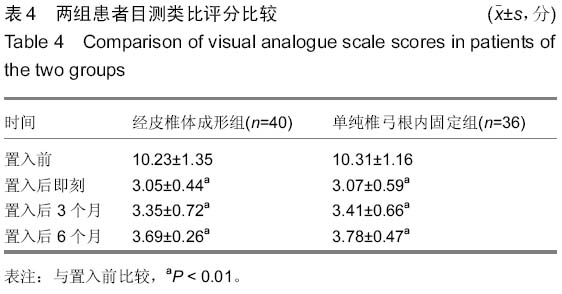
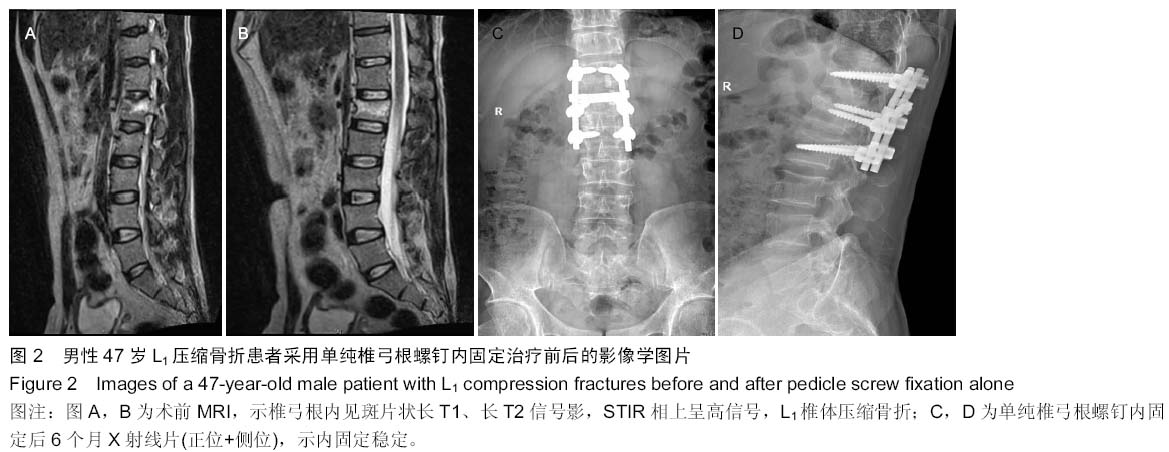
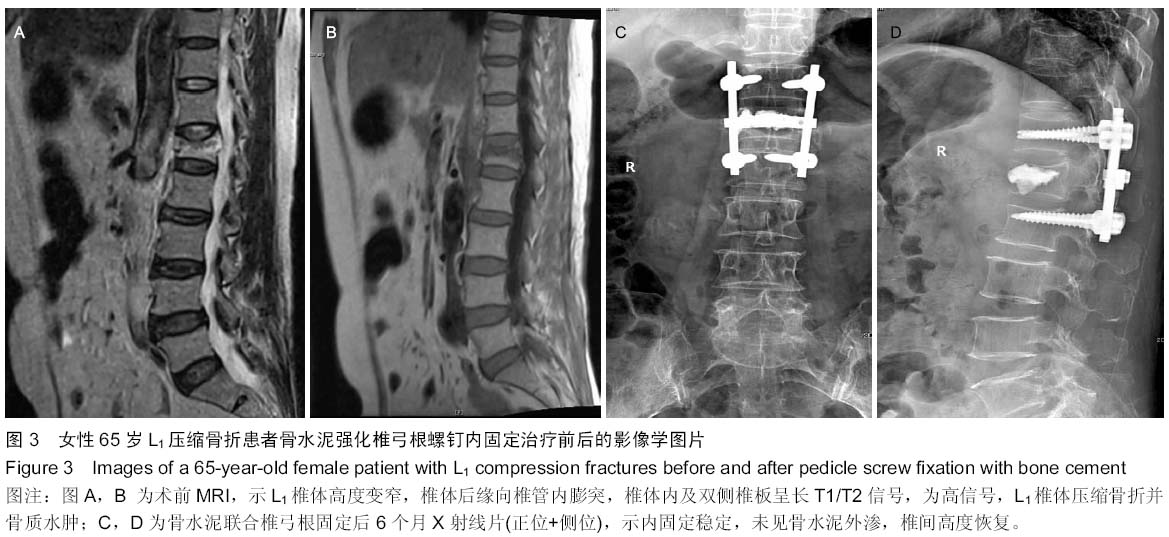
| [1] 胡家美,徐新华,乐敏莉,等.内固定联合椎体成形术对脊柱骨折患者Frankel分级、Cobb角及椎管侵占情况的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,8(33):134-136.
[2] 沈晓龙,张海龙,顾昕,等.微创经椎间孔椎间融合术联合单、双侧内固定治疗单间隙腰椎退变性疾病[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2014, 34(7):749-755.
[3] Rodríguez-Vela J,Lobo-Escolar A,Joven E,et al.Clinical outcomes of minimally invasive versus open approach for one-level transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion at the 3-to 4-year followup.Eur Spine J. 2013;22(12):2857-2863.
[4] Uchida K,Nakajima H,Yayama T,et al. Vertebroplasty- augmented short-segment posterior fixation of osteoporotic vertebral collapse with neurological deficit in the thoracolumbar spine:comparisons with posterior surgery without vertebroplasty and anterior surgery.J Neurosurg Spine.2010;13(5):612-621.
[5] Reinhold M, Knop C, Beisse R, et al. Operative treatment of traumatic fractures of the thorax and lumbar spine. Part II: surgical treatment and radiological findings. Unfallchirurg. 2009;112(2):149-167.
[6] 王生介,谭红略,赵金坤,等. 椎弓根螺钉固定结合硫酸钙椎体成形术治疗胸腰椎压缩性骨折的生物力学研究[J].临床骨科杂志,2010,13(1):80-83.
[7] 吴云刚,石志才,张晔,等. 骨水泥强化椎体提高椎弓根螺钉置入后的稳定性[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(42): 7951-7954.
[8] 岳文峰,夏虹,王建华.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定对骨质疏松患者有利无弊?[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(17):3081-3088.
[9] 凌钦杰,何二兴. 椎体成形术防治渗漏的研究进展[J]. 广东医学,2014,35(9):1450-1454.
[10] Rodrigues CP, Ribeiro SM, Neves N, et al. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy in the treatment of post traumatic kyphosis following an osteoporotic fracture of the thoracolumbar spine. Acta Reumatol Port. 2011;36(2):184-186.
[11] Josten C, Schmidt C, Spiegl U. Osteoporotic vertebral body fractures of the thoracolumbar spine: diagnostics and thera peutic strategies. Chirurg. 2012;83(10):866-874.
[12] Tian JW, Wang L, Xia T, et al. Posterior short segmental fixation combined with intermediate screws vs conventional intersegmental fixation for monosegmental thoracolumbar fractures. Orthopedics. 2011;34(8):e389-e396.
[13] 王智方,胡侦明,郝杰,等. 经椎弓根内固定治疗退行性腰椎侧凸并椎管狭窄症:半年随访矫正角度无丢失[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2014,18(17):2728-2733.
[14] Guan HG, Wang G, Huo ZM,et al.Minimally invasive surgical treatment for lumbar degenerative disease with IsoC-3D navigation under Mast Quadrant system. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2012;25(6):451-454.
[15] 祝孟坤,刘宏建,皮国富,等. 后路内固定术结合经皮椎体成形术治疗多节段胸腰椎骨质疏松性压缩骨折合并椎管狭窄[J]. 医药论坛杂志,2010,24(30):12-14.
[16] 马进峰,陈伯华,李娟,等. 经椎弓根植骨椎体成形联合椎弓根螺钉固定治疗胸腰椎骨折[J]. 中华创伤杂志,2013,29(6):513-515.
[17] 方永超,冯新民,陶玉平,等. 骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉内固定伤椎椎体成形术治疗伴神经症状的骨质疏松性椎体骨折[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(4):376-378.
[18] 李家谋,张昆亚,韩伟峰,等. 短节段椎弓根螺钉置入内固定椎体成形治疗胸腰椎骨折的生物力学检测[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(39):7284-7287.
[19] 杨岱青. 骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉内固定伤椎椎体成形术治疗骨质疏松性椎体骨折效果观察[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志,2013, 22(4):393-394.
[20] Marco RA,Meyer BC,Kushwaha VP. Thoracolumbar burst fractures trea-ted with posterior decompression and pedicle screw instrumentation sup-plemented with balloon-assisted vertebroplasty and calcium phosphate re-construction surgical/technigue. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2010;92(1):67-76.
[21] Jansson K, Blomqvist P, Svedmark P, et al. Thoracolumbar vertebral fractures in Sweden: an analysis of 13,496 patients admitted to hospital. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(6):431-437.
[22] 林欣,李家谋,张昆亚,等. 经皮椎体成形术与椎弓根螺钉固定治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折的生物力学研究[J]. 中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(9):861-863.
[23] 宓士军,周广军,孙敬宇,等. 膨胀式椎弓根螺钉固定联合椎体成形治疗严重骨质疏松椎体爆裂骨折[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2010, 6(16):519-521.
[24] Liao JC, Fan KF, Keorochana G, et al. Grafting after short-seg-columbar burst fracture: calcium sulfate cement versus autogenous iliac bone graft. Spine. 2010;35(15): 1482-1488.
[25] 于亮,蒋伟宇,赵刘军,等.骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定结合椎体后凸成形术治疗骨质疏松性胸腰段爆裂骨折[J].浙江中医药大学学报,2014,14(8):984-987.
[26] 刘达,康夏,郑伟,等.骨质疏松绵羊腰椎膨胀式椎弓根螺钉与骨水泥强化椎弓根螺钉固定稳定性的动态比较研究[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2014,24(8):747-751.
[27] 荆丹峰,许艺荠,孙太存,等.骨水泥注入中空侧孔椎弓根螺钉内固定骨质疏松性腰椎退变:强化技术要点[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(47):7556-7560.
[28] Knavel EM,Rad AE,Thielen KR,et al.Clinical outcomeswith hemivertebral filling during percutaneous vertebroplasty. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30(3):496-499.
[29] Anderson PA, Froyshteter AB, Tontz WL Jr, et al. Meta-analysis of vertebral augmentation compared with conservative treatment for osteoporetic spinal fractures. J Bone Miner Res.2013;28(2):372-382.
[30] Foumey DR,Dettori JR,Norvell DC,et al. Does minimal access tubularassisted spine surgery increase or decrease complications in spinal de-compression or fusion. Spine. 2010; 35(9):57-65.
[31] 柳超,刘建,王雷,等. 椎弓根螺钉短节段固定联合椎体成形术治疗单节段胸腰段骨质疏松性椎体爆裂骨折[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(4):347-351.
[32] Tomita S, Molloy S, Jasper LE, et al. Biomechanical comparison of kyphoplasty with different bone cements. Spine. 2004;29(11):1203-1207. |