中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (38): 6087-6091.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.38.004
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
两种不同处理方法对牙釉质结构及正畸托槽粘接强度的影响
高 杨1,张 明1,宫春梅2
- 1青岛市口腔医院,山东省青岛市 266001; 2潍坊医学院口腔医学院,山东省潍坊市 261053
-
出版日期:2015-09-17发布日期:2015-09-17 -
作者简介:高杨,男,1975年生,山东省潍坊市人,硕士,主治医师,主要从事口腔正畸学研究。
Effects of two different treatments on enamel structure and bond strength of orthodontic brackets
Gao Yang1, Zhang Ming1, Gong Chun-mei2
- 1Qingdao Stomatological Hospital, Qingdao 266001, Shandong Province, China; 2School of Stomatology, Weifang Medical University, Weifang 261053, Shandong Province, China
-
Online:2015-09-17Published:2015-09-17 -
About author:Gao Yang, Master, Attending physician, Qingdao Stomatological Hospital, Qingdao 266001, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
背景:当前临床托槽黏结前处理牙釉质的方法有酸蚀与喷砂两种,但将喷砂技术直接用于未处理牙釉质面的研究较少。
目的:观察酸蚀、喷砂处理方法对牙釉质表面的损伤程度,并比较两种不同牙釉质表面处理方法下金属托槽粘接强度的差异。
方法:将9颗人正畸拔除前磨牙随机均分为3组,分别进行喷砂、酸蚀与抛光清洁处理,扫描电镜下观察牙体表面粗化效果。将40颗人正畸拔除前磨牙随机均分为2组,分别进行喷砂、酸蚀处理,粘接托槽24 h后,利用材料力学实验机测定剪切强度,并统计粘接剂残留指数。
结果与结论:扫描电镜观察发现,抛光清洁处理组牙釉质表面光滑,无破坏;喷砂组与酸蚀组牙釉质遭到破坏,表面粗糙,并且喷砂组牙釉质的破坏程度更大。喷砂组粘接强度显著高于酸蚀组(P < 0.05),喷砂组与酸蚀组的粘接剂残留指数比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。表明相对于酸蚀处理,喷砂处理可提高牙釉质与托槽的粘接强度,但对牙釉质的破坏程度更大。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
高 杨,张 明,宫春梅. 两种不同处理方法对牙釉质结构及正畸托槽粘接强度的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(38): 6087-6091.
Gao Yang, Zhang Ming, Gong Chun-mei. Effects of two different treatments on enamel structure and bond strength of orthodontic brackets [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(38): 6087-6091.
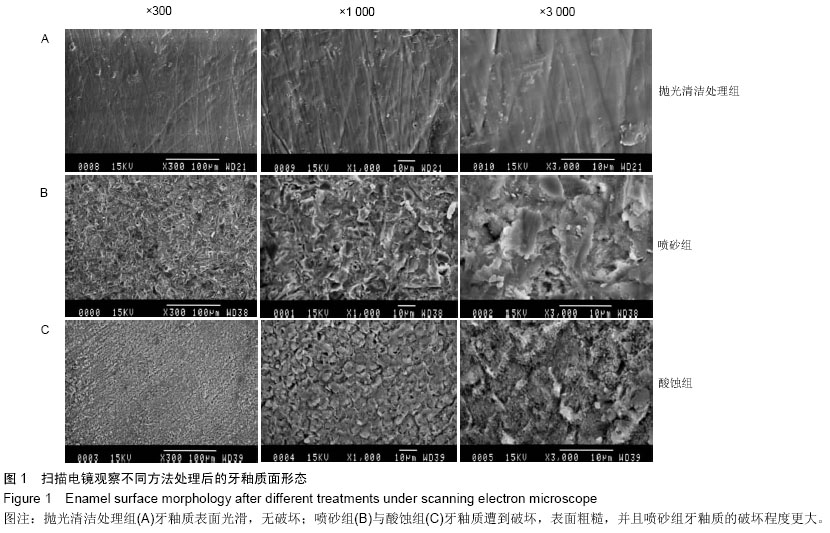
抛光清洁处理组:牙釉质面形态光滑,少量浅划痕,釉柱形态清晰可见,散布有规则的小圆形凸起,牙体组织几乎无损害,见图1A。
喷砂组:釉柱完整性遭到破坏,产生了大量孔隙,牙面呈高低不平的沟壑状,表面粗糙,3 000倍视野下发现孔隙直径较大,边缘锐利,牙釉质丧失量较大,形成的孔隙深度较深,见图1B。
酸蚀组:牙釉质大量丧失,产生大量孔隙,孔隙边缘平缓圆钝,3 000倍视野下可见牙釉质因脱矿而形成多孔的类似蜂窝样的结构,见图1C。由图1可以看出,与正常釉面相比,两种处理技术均能够破坏釉柱形态,增加牙面的摩擦系数,当树脂材料渗入孔隙能够形成机械嵌合,达到增加结合力的作用。与酸蚀组相比,喷砂组3 000倍视野下可见喷砂后牙釉质表面粗化效果更显著,可推断其形成的机械嵌合力更强。
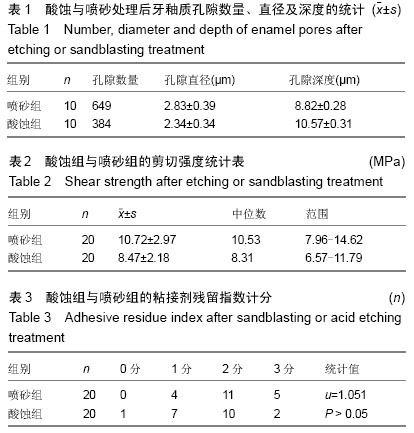
通过对喷砂、酸蚀处理后牙釉质孔隙直径、深度,单个视野下孔隙数量的结果进行分析,发现相同视野下喷砂组釉面上的孔隙数量为酸蚀组的1.7倍,两组孔隙直径、深度比较差异无显著性意义,经公式计算得出两组牙釉质丧失量差异显著,牙釉质经喷砂处理后的丧失程度比酸蚀处理的显著增强(12 080,5 815 µm3,P < 0.05),见表1。
2.2 托槽粘接强度测试及粘接剂残留指数统计 喷砂组的剪切强度显著高于酸蚀组(P < 0.05),结合电镜观察结果可说明牙釉质经喷砂处理后更为粗糙,机械嵌合力更强,托槽粘接强度比酸蚀处理更强(1.24,1.00 MPa/mm2),见表2。剪切检测完成后放大镜下观察可见,树脂粘接剂断裂处多位于粘接剂与托槽交界处及粘接剂内部,两组组间计分比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),见表3。表明在拆除托槽时对牙釉质损害方面两种处理方法无明显区别。
| [1] 谢晓华.环境湿度对正畸托槽粘接强度的影响的研究[D].福州:福建医科大学,2006. [2] 董敏.正畸固定矫治中影响牙面颜色因素的体外研究[D].福州:福建医科大学,2012. [3] Alawjali SS,Lui JL.Effect of one-step polishing system on the color stability of nanocomposites.J Dent.2013;41 Suppl 3: e53-61. [4] 焦海涛.不同底板脱落金属托槽经喷砂处理在粘接的体外实验研究[D].青岛:青岛大学, 2004. [5] 叶芳,廖小平,杨健,等.4种喷砂砂粒对牙釉质表面粗糙度影响的对比研究[J].口腔医学, 2009,29(7):340-341. [6] Gardner A,Hobson R.Variations in acid-etch patterns with different acids and etch times.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop, 2001,120(6):65-67. [7] 赵婧.牙面处理方法对托槽二次粘接强度的影响[D].山东:山东大学,2011. [8] Atsü S,Çatalba? B,Gelgör ?E.Effects of silica coating and silane surface conditioning on the bond strength of rebonded metal and ceramic brackets.J Appl Oral Sci. 2011;19(3): 233-239. [9] Ahrari F,Basafa M,Fekrazad R,et al.The efficacy of Er,Cr:YSGG laser in recond-itioning of metallic orthodontic bracket.Photomed Laser Surg.2012;30(1):41. [10] 石东晓,陈杰,刘珺.喷砂技术对牙釉质和正畸托槽间黏结强度的影响[J].广东牙病防止, 2007,15(4):155. [11] Canay S,Kocadereli I,Ak"ca E.The effect of enamel air abrasion on the retention of bonded metallic orthodontic brackets.Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2000;117(1):15-19. [12] Hesse M,Magin TM,Weber K.Genes for intermediate filament proteins and the draft sequence of the human genome:novel keratin genes and a surprising high number of pseudogenes related to keratin genes 8 and 18.J Cell Sci.2001;114(14): 2569-2575. [13] Espinar-Escalona E,Barrera-Mora JM,Llamas-Carreras JM,et al.Improvement in adhesion of the bracket to the tooth by sandblasting treatment.Mater sci Mater Med.2012;23: 605-611. [14] Al Jabbari YS,Zinelis S,Eliades G.Effect of sandblasting conditions on alumina retention in representative dental alloys.Dent Mater J.2012;31(2):249-255. [15] Robles-Ruíz JJ,Ciamponi AL,Medeiros IS,et al.Effect of lingual enamel sandblasting with aluminum oxide of different particle sizes in combination with phosphoric acid etching on indirect bonding of lingual brackets.Angle Orthod.2014;84(6): 1068-1073. [16] 张旭.正畸托槽脱落后两种底板处理方法对比分析[J].中国医药指南,2012,10(10):170. [17] Sen D,Poyrazoglu E,Tuncelli B,et al.Shear bond strength of resin luting cement to glass-infiltrated porous aluminum oxide cores.J Prosthet Dent. 2000;83(2):210-215. [18] Coulombe PA,Omary MB.Hard and soft principles defining the structure,function and regulation of keratin intemediate filaments.Curr Opin Cell Biol.2002;14(1):110-122. [19] Cal-Neto JP,Castro S,Moura PM,et al.Influence of enamel sandblasting prior to etching on shear bond strength of indirectly bonded lingual appliances.Angle Orthod.2011;81(1): 149. [20] 叶芳,廖小平,胡友德.喷砂洁治对牙釉质影响的实验研究[J].实用中西医结合临床,2011,11(3):52. [21] Türköz C,Ulusoy C.Evaluation of different enamel conditioning techniques for orthodontic bonding.Korean J Orthod.2012;42(1):32-38. |
| [1] | 陈子扬, 蒲 锐, 邓 爽, 袁凌燕. 外泌体对运动介导胰岛素抵抗类疾病的调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | 陈 扬, 黄邓高, 高元慧, 王顺兰, 曹 卉, 郑琳麟, 何浩伟, 罗思琴, 肖敬川, 张应爱, 张淑芳. 低强度脉冲场超声促进人脂肪间充质干细胞的增殖和黏附[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | 杨俊辉, 罗金莉, 袁小平. 人生长激素对人牙周膜干细胞增殖及成骨分化的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | 孙建威, 杨新明, 张 瑛. 孟鲁司特联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤模型大鼠[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | 高 珊, 黄东静, 洪海漫, 贾京桥, 孟 斐. 人胎盘间充质干细胞及诱导的胰岛样细胞移植治疗妊娠期糖尿病大鼠效果比较#br#[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | 郝晓娜, 张英杰, 李玉云, 许 涛. 过表达脯氨酰寡肽酶的骨髓间充质干细胞修复肝纤维化模型大鼠[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | 刘建友, 贾中伟, 牛佳伟, 曹鑫杰, 张 栋, 魏 杰. 构建股骨3D数字化模型提出一种新的股骨颈前倾角测量方法[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | 孟令杰, 钱 辉, 盛晓磊, 陆剑锋, 黄建平, 祁连港, 刘宗宝. 3D打印建模联合骨水泥成形微创治疗塌陷Sanders Ⅲ型跟骨骨折[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | 钱选昆, 黄合飞, 武成聪, 刘克廷, 欧 华, 张金鹏, 任 静, 万建杉. 计算机导航微创经椎间孔腰椎椎间融合治疗腰椎滑脱[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | 胡 靖, 向 阳, 叶 川, 韩子冀. 3D打印辅助与徒手置钉经皮椎弓根钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的1年随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | 舒启航, 廖亦佳, 薛静波, 晏怡果, 王 程. 新型颈椎3D打印多孔椎间融合器的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | 王一寒, 李 杨, 张 玲, 张 睿, 徐瑞达, 韩晓峰, 程光齐, 王伟力. 数字骨科三维可视化技术在股骨转子间骨折复位内固定中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | 孙玛骥, 王秋安, 张星晨, 郭 冲, 袁 峰, 郭开今. 新型颈椎前路经椎弓根固定钉板系统的研制及生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | 林 旺, 王盈盈, 郭卫中, 袁翠华, 许胜贵, 张申申, 林成寿. 胫骨平台后外侧柱骨折扩大外侧入路内固定增强力学稳定性及膝关节功能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | 朱 云, 陈 渝, 邱 皓, 刘 盾, 靳国荣, 陈诗谋, 翁 政. 对侧皮质锁定螺钉治疗骨质疏松股骨骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
1.1 设计 对比观察实验。
1.2 时间及地点 于2014年8月至2015年4月在青岛市口腔医院完成。
1.3 材料
实验用离体牙的收集和处理:纳入50颗实验用牙齿,均为2个月内因正畸需要在青岛市口腔医院正畸科拔除的人上颌前磨牙,牙齿在拔除后即刻洗净血渍,去除软组织,消毒后将实验用牙放入1%氯胺水中浸泡,并保存在4 ℃冰箱中。
实验牙的选择标准:拔牙患者年龄13-16周岁;牙齿完整且发育正常,无龋坏、缺损、裂纹、色素牙石沉积等;非氟斑牙、四环素牙、畸形牙。
|
正畸托槽粘接强度实验的材料和仪器:
|
|
|
材料和仪器
|
来源
|
|
GC粘接剂
|
日本而至公司
|
|
直丝弓托槽MBT
|
3M公司,美国
|
|
直径50 µm的氧化铝石英砂
|
RONDOflex,德国
|
|
气流喷砂机
|
MicroEtcher,美国Danville Materials公司
|
|
材料力学实验机
|
Autogragh,shimadzu,日本
|
|
扫描电镜(JsM-840)
|
日本
|
|
格鲁玛酸蚀剂
|
贺利式,德国
|
|
橡皮抛光杯、抛光膏
|
NUPRO,登士柏公司,美国
|
1.4.1 扫描电镜观察正常及喷砂、酸蚀处理后的牙面 随机选取备用的9颗离体牙,3颗经喷砂处理,3颗经酸蚀处理,3颗经抛光清洁处理作为空白对照。
抛光清洁处理:实验开始前,将橡皮抛光杯安装在慢速手机上,用不含氟的抛光膏抛光3组离体牙5 s,后用三用枪冲洗牙面10 s,吹干备用。
喷砂处理:将离体牙用体积分数为75%乙醇棉球清洁吹干后,以锡纸严密包裹,暴露出实验牙面。将气流喷砂机的砂盒装满直径50 µm的氧化铝石英砂砂粒,然后将气压调至490 kPa,水压调至350 kPa,调整喷嘴与牙面的喷射距离为3 mm,喷射角度为喷嘴与牙面呈90°。在密封箱中用50 µm直径的氧化铝石英砂砂粒处理牙面实验区,从合缘至牙釉质骨质界上下匀速移动,连续喷射15 s[10]。完成后清空砂盒里的砂粒,用喷砂机喷嘴以水、气冲洗牙面30 s,以去除牙面残留砂粒,吹干。
酸蚀处理:将备用的离体牙用体积分数75%乙醇棉球清洁牙面,吹干5 s,后用37%磷酸涂布在实验区酸蚀30 s,然后用三用气枪冲洗牙面5 s,吹干。
将所有牙齿标本送至青岛大学电镜实验室,在扫描电镜下对牙面形态进行观察、拍照,分别在300,1 000,3 000倍视野下分析比较两种表面处理方法对牙体表面的粗化效果。完成后将所有离体牙用锯式切片机以垂直于牙体长轴、平酸蚀区域中心的方向进行低速切片,将切好的牙体组织在室温下干燥处理24 h后,固定并进行喷金处理,以便进行电镜扫描。
1.4.2 托槽粘接强度测试及粘接剂残留指数统计 选取备用的40颗离体牙,依次在根尖部位标记1-40号,按照随机数字表法将离体牙均分为2组,分别进行相应的喷砂处理与酸蚀处理。
处理完成后的两组离体牙按粘接剂说明粘接托槽,托槽底板面积为11.80 mm2。粘接过程由同一个正畸专业医师完成(不知晓实验分组情况),托槽按临床冠中心的标准黏结,轻压托槽使之与牙面充分贴合,多余粘接剂用探针仔细清除。将粘接完成后的离体牙置于37 ℃恒温箱中水浴24 h。
托槽粘接强度测试:粘接完成24 h后,利用材料力学实验机分别对两组样本进行剪切力值测试。将两组样本依次放置在剪切刀孔上,托槽底板通过剪切刀孔,剪切方向与托槽槽沟垂直,刀具加载速度为1 mm/min,直至托槽脱落,实验机记录下最大剪切力值。
粘接剂残留指数统计:于10倍放大镜下观察两组样本托槽脱落后牙面上的粘接剂残留量,换算统计成粘接剂残留指数。
粘接剂残留指数分级:牙面无粘接剂残留,为0分;牙面粘接剂残留小于1/2,为1分;牙面粘接剂残留大于1/2,为2分;粘接剂全部残留于牙面,为3分。
1 当前临床托槽黏结前牙釉质的处理方法主要是酸蚀处理技术,但酸蚀技术可导致牙釉质脱矿,甚至继发龋的产生,造成牙釉质不可逆的损伤,并可影响牙釉质的颜色。 2 在临床正畸治疗中,喷砂技术被应用于托槽脱落后二次粘接前牙面及托槽的处理,研究表明喷砂处理后的托槽粘接强度可以达到8 MPa,能够满足临床需要,但将喷砂技术直接用于未处理牙釉质面的研究很少。 3 实验通过观察喷砂、酸蚀处理后离体牙牙釉质的结构,比较两种方法对牙釉质丧失量的影响,并检测两种技术处理牙面后托槽的粘接强度及粘接剂残留指数,发现相对于酸蚀处理,喷砂处理可提高牙釉质与托槽的粘接强度,但对牙釉质的破坏程度更大。
酸蚀技术通过酸蚀剂处理牙釉质表面:①清洁牙面,去除玷污层,暴露新鲜牙釉质。②极性化牙釉质表面,促进其与粘接材料的结合。③溶解牙釉质结构,增加釉面的摩擦系数,形成机械嵌合的作用。但酸蚀技术可导致牙釉质脱矿,甚至继发龋的产生,造成牙釉质不可逆的损伤,并可影响牙釉质的颜色,改变美学效果。人们在临床实践中发现酸蚀剂浓度、酸蚀时间、酸蚀后牙面清洁方法等都能可影响托槽粘接效果,Gardner等研究表明以37%磷酸酸蚀牙面30 s的粘接效果最好。但临床中酸蚀处理后粘接托槽的脱落率很高,因此寻找方便快捷,有足够粘接强度并能减少牙釉质脱矿丧失,预防继发龋发生的方法成为新的研究方向。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||