| [1] Lugo L, Villalvilla A,Largo R.Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs): New alternatives for osteoarthritis? Maturitas.2014;77(4):380-384.
[2] Iagnocco A,Naredo E.Osteoarthritis: research update and clinical applications.Rheumatology.2012;51:vii2-5.
[3] 王健,陶海荣.雌激素及相关化合物干预骨关节炎作用机制:关节保护与骨软骨细胞的修复[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(33): 5372-5376.
[4] Little J, Higgins JP, Ioannidis JP,et.al.Strengthening the reporting of genetic association studies (STREGA): an extension of the STROBE statement. Eur J Epidemiol. 2009;24(1):37-55.
[5] Lau J,Ioannidis JP,Schmid CH.Quantitative Synthesis in Systematic Reviews[J]. Ann Intern Med.1997;127(9).820-826.
[6] Mantel N, Haenszel W.Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease.J Natl Cancer Inst.1959;22(4),719-748.
[7] DerSimonian R, Laird N. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials.1986;7(3):177-88.
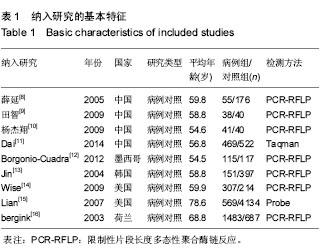
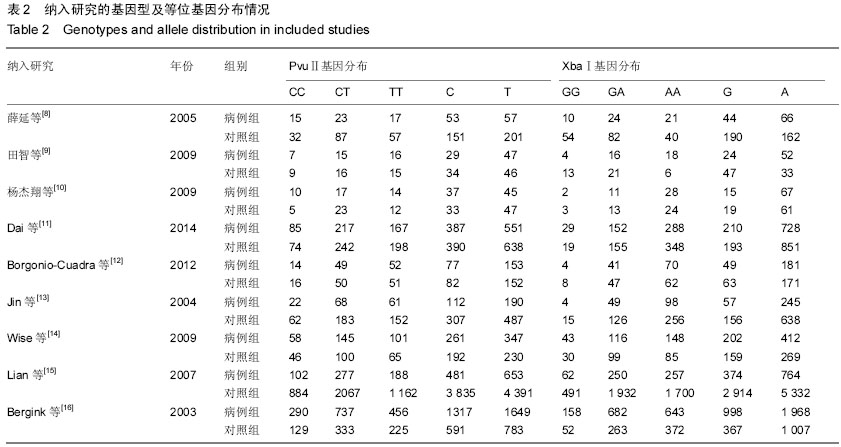
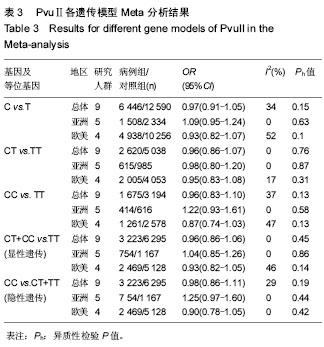
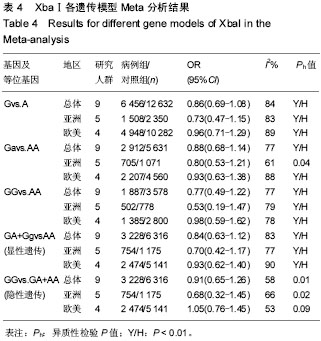
[8] 薛延,李东,姚力,等.北京地区女性骨关节炎患者雌激素受体等位基因多态性分析[J].中华外科杂志,2005,43(12):817-818.
[9] 田智,郭小芳,周锋,等.雌激素受体-α基因多态性与湖南女性原发性膝骨性关节炎的关系[J].实用预防医学,2009,16(6):1724- 1727.
[10] 杨杰翔,扶世杰,肖复燊,等.ER基因多态性与川南高氟地区人群膝骨性关节炎相关性的病例对照研究[J].华西医学, 2009,24(4): 826-829.
[11] Dai X, Wang C, Dai J,et al. Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms in estrogen receptor alpha gene with susceptibility to knee osteoarthritis: a case-control study in a chinese han population. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:151457
[12] Borgonio-Cuadra VM, González-Huerta C, Duarte-Salazár C, et al. Analysis of estrogen receptor alpha gene haplotype in Mexican mestizo patients with primary osteoarthritis of the knee. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(5):1425-1430.
[13] Jin SY, Hong SJ, Yang HI, et al. Estrogen receptor-α gene haplotype is associated with primary knee osteoarthritis in Korean population.Arthritis Res Ther. 2004;6(5):R415-421.
[14] Wise BL, Demissie S, Cupples LA,etal.The Relationship of Estrogen Receptor-α and -β Genes with Osteoarthritis of the Hand. J Rheumatol. 2009;36(12),2772-2779.
[15] Lian K, Lui L, Zmuda JM,et al. Estrogen receptor alpha genotype is associated with a reduced prevalence of radiographic hip osteoarthritis in elderly Caucasian women. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(8),972-978.
[16] Bergink AP, van Meurs JB, Loughlin J,et al. Estrogen receptor α gene haplotype is associated with radiographic osteoarthritis of the knee in elderly men and women. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48 (7):1913-1922.
[17] 刘昭国,廖永德,唐和孝,等.雌激素受体在乳腺癌中的研究进展[J].肿瘤防治研究,2012,39(7):869-871.
[18] Cheung E, Schwabish MA, Kraus WL.Chromatin exposes intrinsic differences in the transcriptional activities of estrogen receptors alpha and beta. EMBO J. 2003;22(3):600-611.
[19] Oshima Y, Matsuda K, Yoshida A,et al. Localization of estrogen receptors alpha and beta in the articular surface of the rat femur. Acta Histochem Cytochem. 2007;40(1):27-34.
[20] Ryder JJ, Garrison K, Song F,et al. Genetic associations in peripheral joint osteoarthritis and spinal degenerative disease: a systematic review.Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67(5):584-591.
[21] 卞子辰.雌激素及其受体与骨性关节炎相关性研究进展[J].医学综述,2014,20(7):1172-1174.
[22] Loughlin J, Sinsheimer JS. Association analysis of the vitamin D receptor gene, the type I collagen gene COL1A1, and the estrogen receptor gene in idiopathic osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2000;27(3):779-784.
[23] 刘源,李燕,孙月池,等.雌激素受体α基因 XbaⅠ位点多态性与骨关节炎易感性相关性的Meta分析[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版: 2013,(3):1161-1165.
[24] 王蕾,卢慧茹,王健,等.天津市老年人膝关节骨关节炎流行病学调查[J].中华老年医学杂志,2012,31(5):438-440.
[25] 张军锋,宋玲花,董海原,等.山西省农村地区症状性骨关节炎流行状况调查[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2014,18(7):444-448.
[26] Boccia S,De Feo E,Gallì P,et al.A systematic review evaluating the methodological aspects of meta-analyses of genetic association studies in cancer research. Eur J Epidemiol. 2010;25(11):765-775.
[27] 刘金涛,秦超英,党红,等.Meta分析中基于Q统计量服从卡方分布线性变换的异质性方差区间估计[J].中国循证医学杂志, 2012, 12(11):1404-1406.
[28] 仇瑶琴,贺佳.多水平统计模型在Meta分析异质性控制中的作用[J].中国循证医学杂志,2011,11(6):711-715. |