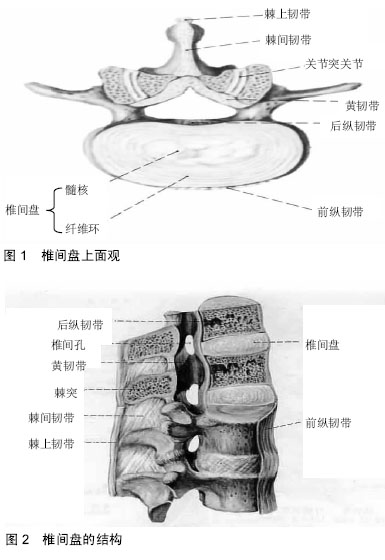
| [1] Joud A,Petersson IF,Englund M. Low back pain: epidemiology of consultations.Arthritis Care Res(Hoboken). 2012;64(7):1084-1088.
[2] Ogata K, Whiteside LA.Nutritional pathways of the itnervertebral disc:An experimental study using hydrogen washout technique.Spine.1981;6(3):211-216.
[3] Howard BV, Rodriguez BL,Bennett PH,et al.Prevention Conference VI:Diabetes and CardioVaScular disease: Writing Group I:epidemiology.Circulation. 2002;105:e132-137.
[4] Freedman MK,Hilibrand AS,Blood EA,et al.The impact of diabetes on the outcomes of surgical and nonsurgical treatment of patients in the spine patient outcomes research trial.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2011;36:290-307.
[5] Anekstein Y,Smorgick Y,Lotan R,et al.Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for the development of lumbar spinal stenosis. Isr Med Assoc J.2010;12(1):16-20.
[6] Illien-Junger S, Grosjean F, Laudier DM, et al.Combined Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-AGE Drug Treatments Have a Protective Effect on Intervertebral Discs in Mice with Diabetes. PLOS One.2013;8(5):e64302.
[7] Chen S,Liao M,Li J,Peng H,et al.The correlation between microvessel pathological changes of the endplate and degeneration of the intervertebral disc in diabetic rats.Exp There Med.2013;5(3):711-717.
[8] 顾韬,阮狄克.生物力学因素对椎间盘退变的影响及机理[J]. 中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2011, 21(6):523-526.
[9] Kepler CK, Ponnappan RK, Tannoury CA, et al. The molecular basis of intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J.2013;13(3):318-330.
[10] Kalichman L,Hunter DJ. The genetics of intervertebral disc degeneration. Associated genes. Joint Bone Spine.2008; 75(4):388-396.
[11] Yang SH,Wu CC,Shih TT,et al. Invitro study on interaction between human nucleus pulposus cells and mesen- chymal stem cells through paracrine stimulation. Spine.2008; 33(18): 1951-1957.
[12] Zhao CQ, Wang LM, Jiang LS, et al. The cell biology of intervertebral disc aging and degeneration. Ageing Res Rev. 2007;6(3): 247-261.
[13] Haefeli M,Kalberer F,Saegesser D,et al. The course of macroscopic degeneration in the human lumbar in-terver- tebraldisc. Spine.2006;31(14):1522-1531.
[14] Jones P,Gardner L,Menage J,et al. Intervertebral disc cells as competent phagocytes in vitro: implications for cell death in disc degeneration. Arthritis Res Ther.2008;10(4): R86.
[15] Wang HQ,Yu XD,Liu ZH,et al. Human nucleus pulposus cell cultures and disc degeneration grading systems: comment on the article by Le Maitre et al. Arthritis Rheum.2010;62(1): 301-302 .
[16] Stephan S,Johnson WE,Roberts S. The influence of nutrient supply and cell density on the growth and survival of interverte- bral disc cells in 3D culture. Eur Cell Mater. 2011;22: 97-108 .
[17] Won HY,Park JB,Park EY,et al. Effect of hyper-glyce- mia on apoptosis of notochordal cells and intervertebral discdegeneration indiabet icrats. JN eurosurg Spine. 2009; 11(6):741-748.
[18] Jiang L,Zhang X,Zheng X,et al.Apoptosis,Senescence,and Autophagy in Rat Nucleus Pulposus Cells:Implications for Diabetic Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2013 ;31(5):692-702.
[19] 杜伟,申勇,李宝俊,等.细胞因子IL-1α、IL-6、TNF-α、MMP3 与颈椎间盘退变机制的相关性研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2012, 20(3):259-262.
[20] Cui LY,Liu SL,Ding Y,et al. IL-1beta sensitizes rat in- terverte-bral disc cells to Fas ligand mediated apoptosis in vitro. ActaPharmacol Sin.2007;28(10):1671-1676.
[21] Wang J,Tang T,Yang H,et al. The expression of fas lig- and on normal and stabbed-disc cells in a rabbit model of intervertebral disc degeneration: a possible pathogenesis. JN eurosurg Spine.2007;6(5):425-430.
[22] Tsuru M, Nagata K, Jimi A,et al.,Effect ofAGEs on human disc herniation:intervertebral disc hernia is also effected by AGEs. Kurume Med J. 2002;49(1-2):7-13.
[23] 鲍恒,侯莜魁.糖尿病大鼠椎间盘细胞凋亡的观察[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(7):434-437.
[24] Obrosova IG, Chung SS, Kador PF. Diabetic cataracts: mechanisms and management.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2010;26(3):172-180.
[25] Jackson AR, Huang CY, Gu WY. Effect of endplate calcification and mechanical deformation on the distribution of glucose in inter-vertebral disc: a 3D finite element study. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin.2011;14(2):195.
[26] 陈森,徐振华,贾吉光,等.糖尿病大鼠终板微血管改变与髓核细胞凋亡的关系[J].武汉大学学报:医学版, 2008. 29(5):584- 586.
[27] Mousa SA, Shaqura M, Brendl U, et al. Involvement of the periph-eral sensory and sympathetic nervous system in the vascular en-dothelial expression of ICAM-1 and the recruitment of opioid-con-taining immune cells to inhibit inflammatory pain. Brain Behav Immun.2010;24(8):1310.
[28] 王凯,张亮.腰椎软骨终板细胞凋亡与椎间盘退变的关系[J].天津医科大学学报,2012,18(1),97-99.
[29] Liu YJ,Huang GS,Juan CJ,et al.Intervertebral disk degenerationrelated to reduced vertebral marrow perfusion at dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI.Am J Roentqenol.2009; 192(4):974-979.
[30] Yurube T, Takada T, Suzuki T, et al.Rat tail static compression mode,mimics extracellular matrix metabolic imbalances of matrix metalloproteinases,aggrecanase,and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in intervertebraldisc degeneratwn. Arthritis Res Ther. 2012;14(2):R51.
[31] Lee SW, Song KE, Shin DS, et al.Alterations in peripheral blood levels of TIMP-J,MMP-Z and MMP-9 in patients with type-2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2005;69(2):175- 179.
[32] Nakashima S, Matsuyama Y, Takahashi K, et al. Regeneration of intervertebral disc by the intradiscal application of cross-linked hyaluronate hydrogel and cross-linked chondroitin sulfate hydrogel in a rabbit model of intervertebral disc injury. Biomed Mater Eng. 2009;19(6): 421-429.
[33] Henriksson HB, Svanvik T, Jonsson M, et al. Transplantation of human mesenchymal stems cells into intervertebral discs in a xenogeneic porcine model. Spine. 2009;34(2):141-148.
[34] Hee HT, Ismail HD, Lim CT, et al. Effects of implantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells, disc distraction and combined therapy on reversing degeneration of the intervertebral disc.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010;92(5):726- 736. |