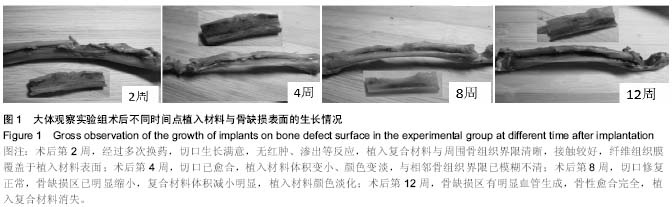
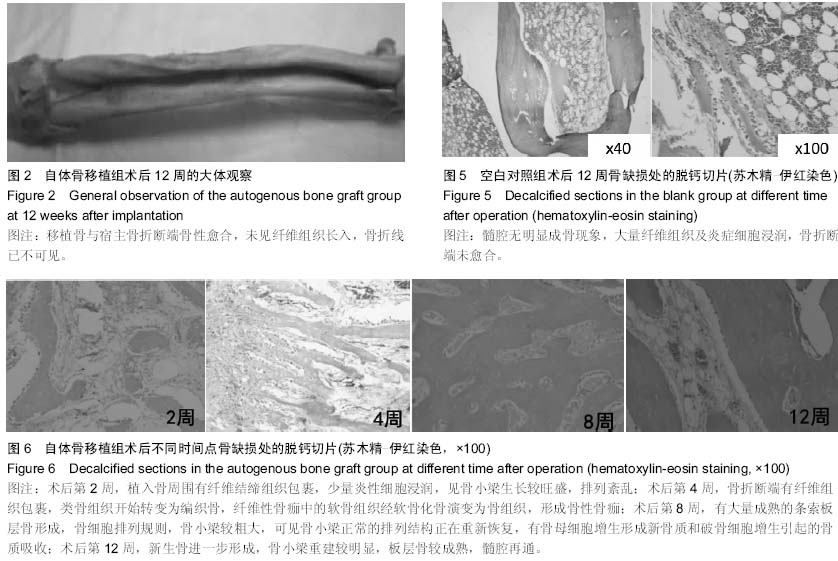
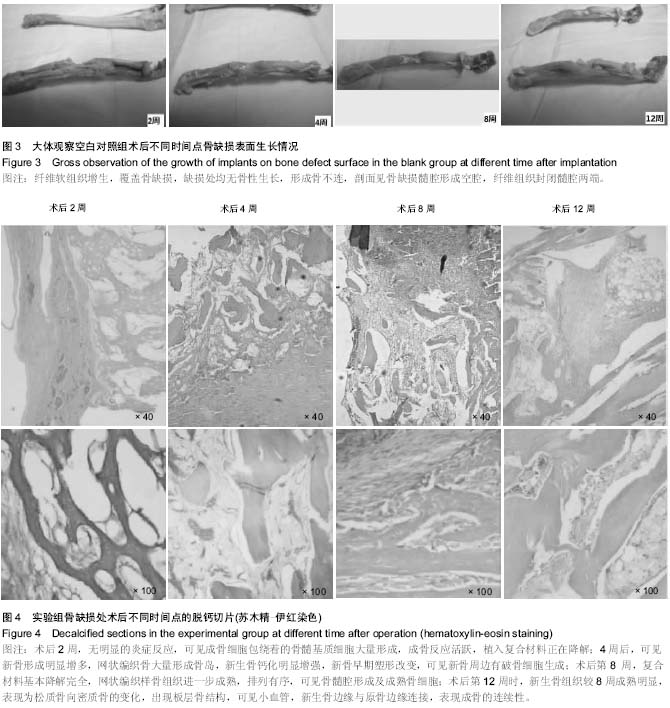
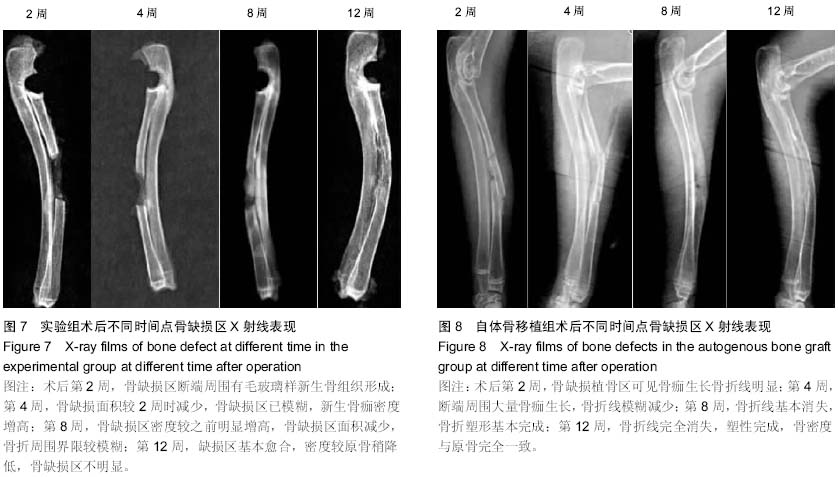
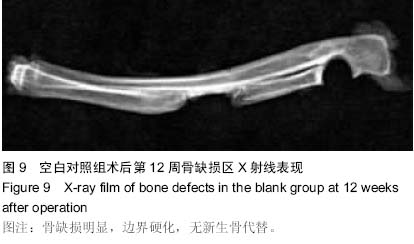
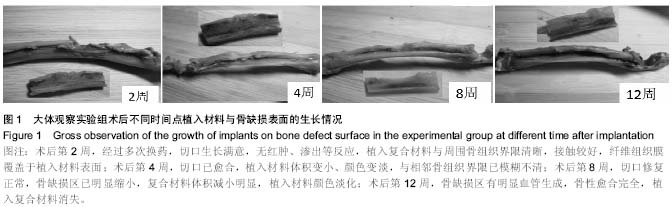
| [1] 谢建雅,周磊,郭毅.利用兔胫骨干骺端骨缺损模型对骨代用品研究的实验方法探讨[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2009,25(6):329-331.
[2] 秦辉,许建中,王序全,等.组织工程用大段负重骨缺损动物模型的建立[J].中国临床康复,2004,8(20):3974-3975.
[3] Schmitz JP,Hollinger JO.The critical size defect as an experimental model forcraniomandibulofacial nonunions.Clin Orthop Relat Res.1986;(205):299-308.
[4] 赵峰,尹玉姬,宋雪峰.壳聚糖-明胶网络/羟基磷灰石复合材料支架的研究-制备及形貌[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2001,15(5): 276-279.
[5] Richter F,Schnorr D,Deger S,et al.Improvement of hemostasis in open and laparoscopically performedpartial nephrectomy using a gelatin matrix-thrombin tissue sealant (FloSeal). Urology.2003;61(1):73-77.
[6] Grevstad HJ,Bone OE.Effects of doxycycline on surgically induced osteoclast recruitment in therat.Eur J Oral Sci. 1995; 103(3):156-159.
[7] 陈玉清,吴皆正,王连星.堇青石的合成及应用[J].中国陶瓷,1992, 5(3):38-43.
[8] Isik AG,Tarim B,Hafez AA,et al.A comparative scanning electron microscopic study on the characteristicsof demineralized dentin root surface using different tetracycline HCl concentrations and applicationtimes.J Periodontol. 2000; 71(2):219-225.
[9] Weiner S,Addadi L,Wagner HD. Materials design in biology. Mat Sci Eng C.2000;11:1-8.
[10] Green D,Walsh D,Mann S,et al.The potential of biomimesis in bone tissue engineering: lessons from the design and synthesis of invertebrate skeletons.Bone. 2002;30(6): 810-815.
[11] Douglas T,Hempel U,Mietrach C,et al.Fibrils of different collagen types containing immobilizedproteoglycans (PGs) as coatings:characterization and influence on osteoblast behaviour.Biomol Eng.2007;24(5):455-458.
[12] Brodie JC,Merry J,Grant MH.The mechanical properties of calcium phosphate ceramics modified bycollagen coating and populated by osteoblasts.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2006;17(1): 43-48.
[13] 胡庆柳.仿松质骨的胶原/纳米羟基磷灰石人工骨修复兔大段骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(45):8935.
[14] Kong L,Ao Q,Wang A,et al.Preparation and characterization of a multilayer biomimetic scaffold for bonetissue engineering. J Biomater Appl.2007;22(3):223-239.
[15] Waked W,Grauer J.Silicates and bone fusion.Orthopedics. 2008;31(6):591-597.
[16] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006.
[17] Lill CA,Hesseln J,Schlegel U,et al.Biomechanical evaluation of healing in a non-critical defect in alarge animal model of osteoporosis.J Orthop Res. 2003;21(5):836-842.
[18] Bosch C,Melsen B,Vargervik K.Importance of the critical-size bone defect in testing boneregenerating materials.J Craniofac Surg.1998;9(4):310-316.
[19] 李冀,王志强,原林.腔隙性骨缺损实验动物模型的建立[J].中国临床康复,2005,9(10):80-82.
[20] Li J,Jin L,Wang M,et al.Repair of rat cranial bone defect by using bone morphogenetic protein-2-related peptide combined with microspheres composed of polylactic acid/polyglycolic acid copolymer and chitosan.Biomed Mater. 2015;10(4):045004.
[21] Dhivya S,Saravanan S,Sastry TP,et al. Nanohydroxyapatite-reinforced chitosan composite hydrogel for bone tissue repair in vitro and in vivo.J Nanobiotechnology. 2015;13:40. doi:10.1186/s12951-015-0099-z.
[22] Han F,Yang X,Zhao J,et al.Photocrosslinked layered gelatin-chitosan hydrogel with graded compositions for osteochondral defect repair.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2015; 26(4):160.
[23] Mohammadi R, Amini K.Guided bone regeneration of mandibles using chitosan scaffold seeded with characterized uncultured omental adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction: an animal study.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2015;30(1): 216-222.
[24] Yao AH,Li XD,Xiong L,et al.Hollow hydroxyapatite microspheres/chitosan composite as a sustained delivery vehicle for rhBMP-2 in the treatment of bone defects.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2015;26(1):5336.
[25] Jia S,Yang X,Song W,et al.Incorporation of osteogenic and angiogenic small interfering RNAs into chitosan sponge for bone tissue engineering.Int J Nanomedicine. 2014;9:5307- 5316.
[26] Han F,Zhou F,Yang X,et al.A pilot study of conically graded chitosan-gelatin hydrogel/PLGA scaffold with dual-delivery of TGF-β1 and BMP-2 for regeneration of cartilage-bone interface.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2014.doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33314. [Epub ahead of print]
[27] 彭湘红,万昆.壳聚糖/纳米多层结构羟基磷灰石/明胶复合膜的性能[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(14):2777-2779.
[28] 李瑞琦,张国平,任立中,等.纳米羟基磷灰石及其复合生物材料的特征及应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(19): 3748-3749.
[29] 叶成红,奚廷斐.纳米技术在医用材料领域中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(45):8897-8900.
[30] 李志宏,武继民,李瑞欣.纳米羟基磷灰石及其复合材料的研究进展[J].医疗卫生装备, 2007,28(4):30-31. |