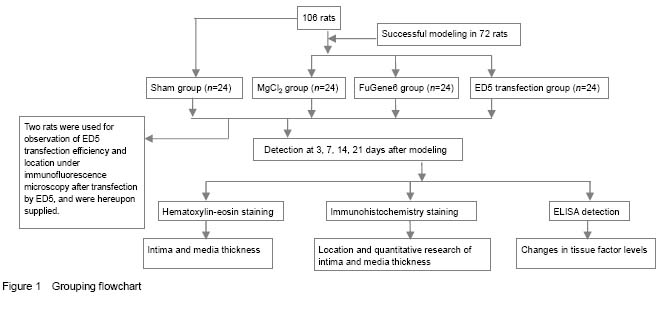
Quantitative analysis of experimental animals
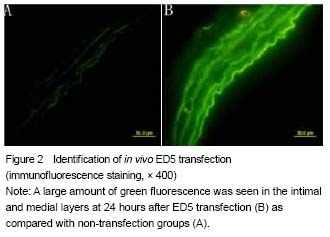
Totally 106 rats were selected, two of which were identified under immunofluorescence microscopy after transfection by ED5, and hereupon supplied. Twenty-four rats in the sham group had no loss, and another 72 rats were modeled successfully and included in result analysis, with 24 rats in each group (
Figure 1).
Quantitative analysis of experimental animals
Totally 106 rats were selected, two of which were identified under immunofluorescence microscopy after transfection by ED5, and hereupon supplied. Twenty-four rats in the sham group had no loss, and another 72 rats were modeled successfully and included in result analysis, with 24 rats in each group (
Figure 1).
Pathological and morphological changes in rats with carotid artery injury after ED5 transfection
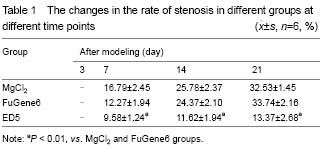
In the sham group, the intima of the carotid artery was complete; at 3 days after modeling, endothelial denudation was found in the MgCl2 group and FuGene6 group, and visible thrombus formed, and moreover, there were a lot of infiltrated inflammatory cells; mild intimal hyperplasia occurred at 7 days after modeling and endometrial hyperplasia became remarkable at 21 days after modeling, and there were more vascular smooth muscle cells and collagen fibers which were disorganized and showed different forms. Compared with MgCl2 and FuGene6 groups, intimal hyperplasia group in the ED5 transfection group was significantly reduced at all time points (
P < 0.01), and moreover, the number of intimal vascular smooth muscle cells and inflammatory cells was also significantly reduced and no thrombosis formed (
Figure 3, Table 1).
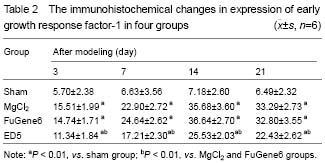
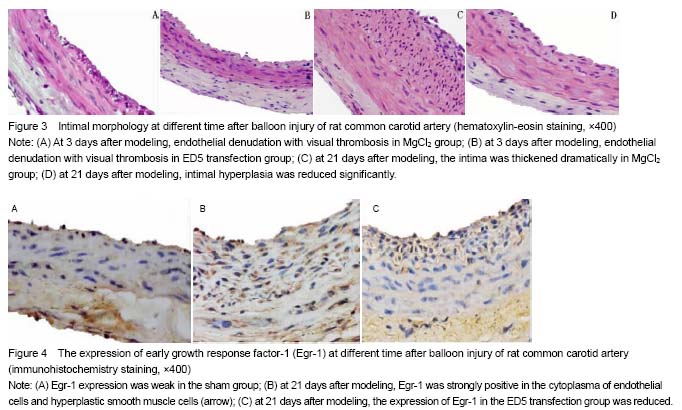
Expression of Egr-1 in rats with carotid artery injury after ED5 transfection
Immunohistochemical staining results showed the Egr-1 expressed weakly in the sham group, but exhibited a high expression at 3, 7, 14, 21 days after modeling. ED5 could significantly reduce the expression of Egr-1, which was significantly different from that in the MgCl2 and FuGene6 groups at the same time (
P < 0.01;
Figure 4 and Table 2).
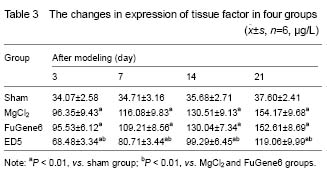
Changes in plasma tissue factor levels in rats with carotid artery injury at different time after ED5 transfection
ELISA results showed that only a small amount of vascular tissue factors expressed in the sham group, and the expression of tissue factor was gradually increased in the MgCl2 and FuGene6 groups after balloon dilation, which was significantly higher than that in the sham group (
P < 0.01). However, ED5 could significantly reduce the expression of tissue factor compared with the MgCl2 and FuGene6 (
P < 0.01;
Table 3). It indicated that ED5 can certainly inhibit expression of tissue factor induced by endothelial injury.