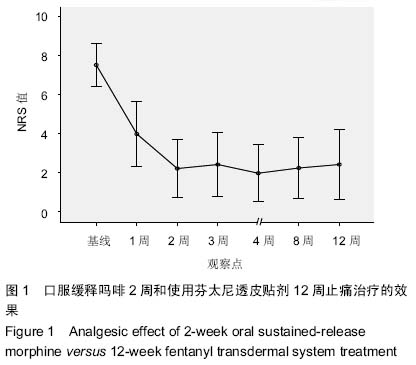
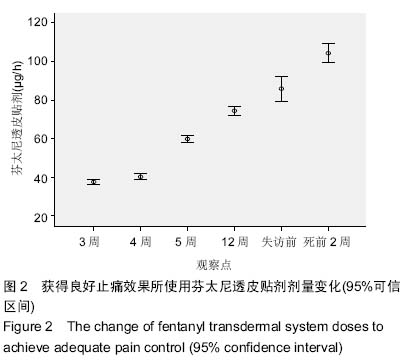
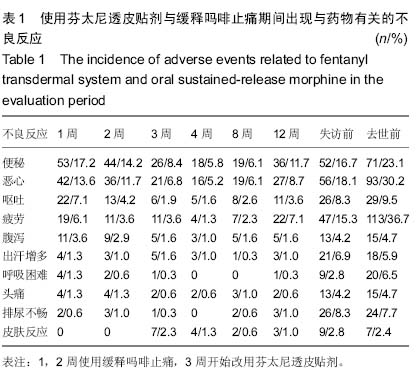
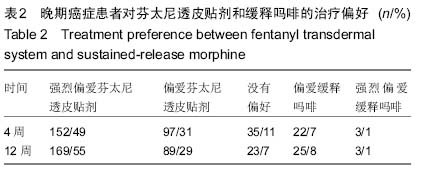
| [1] Cerezo L, Marin A, Zapatero A, et al. Prospective clinical evaluation of transdermal fentanyl for the treatment of cancer pain . Revista de Oncología.2000;2(3): 159-163.
[2] Hadley G, Derry S, Moore RA, et al. Transdermal fentanyl for cancer pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;10: CD010270.
[3] Caraceni A, Hanks G, Kaasa S, et al. Use of opioid analgesics in the treatment of cancer pain: evidence-based recommendations from the EAPC. Lancet Oncol.2012;13(2): e58-e68.
[4] Klepstad P, Kaasa S, Jystad Å, et al. Immediate-or sustained-release morphine for dose finding during start of morphine to cancer patients: a randomized, double-blind trial. Pain.2003;101(1):193-198.
[5] Broomhead A, Kerr R,Tester W, et al.Comparison of a once-a-day sustained-release morphine formulation with standard oral morphine treatment for cancer pain. J Pain Symptom Manage.1997;14(2):63-73.
[6] Korte W, Morant R. Transdermal fentanyl in uncontrolled cancer pain: titration on a day-to-day basis as a procedure for safe and effective dose finding-a pilot study in 20 patients.Support Care Cancer.1994;2(2):123-127.
[7] Milligan K,Lanteri-Minet M,Borchert K,et al.Evaluation of long-term efficacy and safety of transdermal fentanyl in the treatment of chronic noncancer pain. J Pain.2001;2(4): 197-204.
[8] Trescot AM,Helm S,Hansen H,et al.Opioids in the management of chronic non-cancer pain: an update of American Society of the Interventional Pain Physicians’(ASIPP) Guidelines.Pain Physician.2008;11(2 Suppl): S5-S62.
[9] Nugent M,Davis C,Brooks D,et al.Long-term observations of patients receiving transdermal fentanyl after a randomized trial.J Pain Symptom Manage.2001;21(5): 385-391.
[10] Schneir A ,Ly BT, Smollin C , et al. 2012 Annual Meeting of the North American Congress of Clinical Toxicology (NACCT) October 1–6, 2012 Las Vegas,NV, USA.J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 2012;50:574-720.
[11] Hawley P.Case report of severe bradycardia due to transdermal fentanyl. Palliat Med.2013;27(8):793-795.
[12] Colak S,Erdogan MO,Afacan MA,et al.Neuropsychiatric side effects due to a transdermal fentanyl patch: hallucinations.Am J Emerg Med.2015;33(3):477.e1-2.
[13] Sabatowski R, Schwalen S,Rettig K,et al. Driving Ability Under Long-Term Treatment with Transdermal Fentanyl.J Pain Symptom Manage.2003;25(1):38-47.
[14] Nelson L,Schwaner R.Transdermal fentanyl: pharmacology and toxicology.J Med Toxicol. 2009;5(4):230-241.
[15] Downie WW,Leatham PA,Rhind VM,et al.Studies with pain rating scales. Ann Rheum Dis. 1978;37(4):378-381.
[16] Swarm R,Abernethy AP,Anghelescu DL,et al. Adult cancer pain. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.2010;8(9):1046-1086.
[17] Samala RV, Bloise R, Davis M. Efficacy and Safety of a Six-Hour Continuous Overlap Method for Converting Intravenous to Transdermal Fentanyl in Cancer Pain. J Pain Symptom Manage.2014;48(1):132-136.
[18] Hanks GW,Conno F,Cherny N,et al.Morphine and alternative opioids in cancer pain: the EAPC recommendations.Br J Cancer.2001;84(5):587-593.
[19] Muijsers RB,Wagstaff AJ.Transdermal fentanyl: An updated review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in chronic cancer pain control. Drugs.2001;61: 2289-2307.
[20] Gourlay GK.Treatment of cancer pain with transdermal fentanyl.Lancet Oncol.2001; 2:165-172.
[21] Zech D,Grond S,Lynch J,et al.Transdermal fentanyl and initial dose-finding with patient-controlled analgesia in cancer pain. A pilot study with 20 terminally ill cancer patients. Pain.1992; 50:293-301.
[22] Hanks GW,Conno F,Ripamoti C,et al.Morphine in cancer pain: modes of administration. Expert Working Group of the European Association for Palliative Care. Br Med J.1996; 312:823-826.
[23] Samolsky Dekel BG,Tomasi M,Vasarri A,et al. Opioid titration with sustained-release oxycodone and immediate-release morphine for moderate/severe cancer pain: a pilot assessment of the CoDem protocol.J Opioid Manag.2014; 10(1):29-38.
[24] Pergolizzi J,Böger RH,Budd K,et al.Opioids and the Management of Chronic Severe Pain in the Elderly: Consensus Statement of an International Expert Panel with Focus on the Six Clinically Most Often Used World Health Organization step III Opioids (Buprenorphine, Fentanyl, Hydromorphone, Methadone, Morphine, Oxycodone).Pain Pract.2008;8(4):287-313.
[25] Zech D,Lehmann KA.Transdermal fentanyl in combination with initial intravenous dose titration by patient-controlled analgesia.Anticancer Drugs.1995;6 Suppl 3:44-49.
[26] Donner B, Zenz M,Strumpf M,et al. Long-term treatment of cancer pain with transdermal fentanyl.J Pain Symptom Manage.1998;15(3):168-175.
[27] Zhu Y,Song G,Liu D,et al.Multicenter clinical study for evaluation of efficacy and safety of transdermal fentanyl matrix patch in treatment of moderate to severe cancer pain in 474 Chinese cancer patients.Chin J Cancer Res.2011;23(4): 317-322.
[28] Lane ME. The transdermal delivery of fentanyl.Eur J Pharm Biopharm.2013;84(3): 449-455.
[29] Mystakidou K, Tsilika E, Parpa E, et al.Long-term cancer pain management in morphine pre-treated and opioid naive patients with transdermal fentanyl. Int J Cancer.2003; 107(3): 486-492. |