中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (20): 3173-3177.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.20.011
• 口腔组织构建 oral tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
成人AngleII类错牙合软硬组织颅面结构特征:计算机X射线头影测量
李晓光1,满大鹏1,齐炜峰2,孔 宇1
- 1佳木斯大学附属第二医院(口腔医院)正畸科,黑龙江省佳木斯市 154002;2杭州口腔医院有限公司正畸科,浙江省杭州市 310000
Craniofacial tissue characteristics in adult Angle class II malocclusions: cephalometric X-ray measurement
Li Xiao-guang1, Man Da-peng1, Qi Wei-feng2, Kong Yu1
- 1Department of Orthodontics, Second Affiliated Hospital of Jiamusi University, Jiamusi 154002, Heilongjiang Province, China; 2Department of Orthodontics, Stomatological Hospital of Hangzhou, Hangzhou 310000, Zhejiang Province, China
摘要:
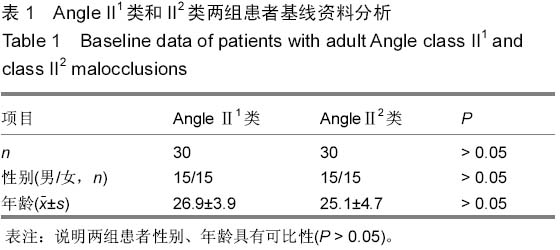
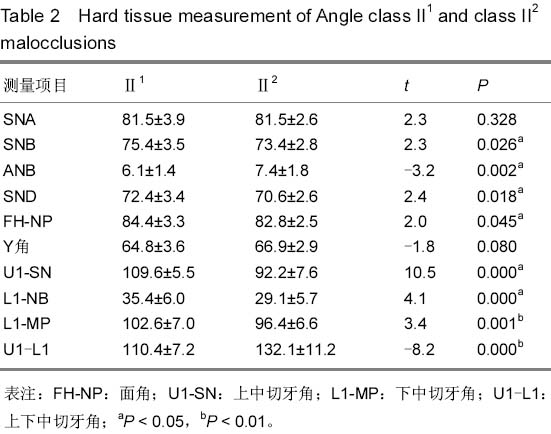
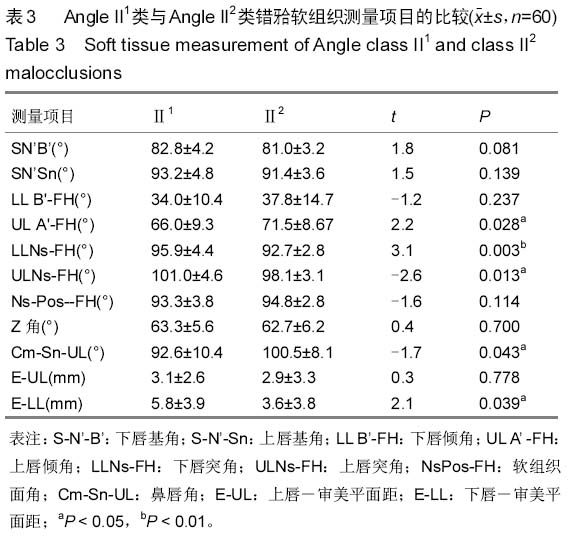
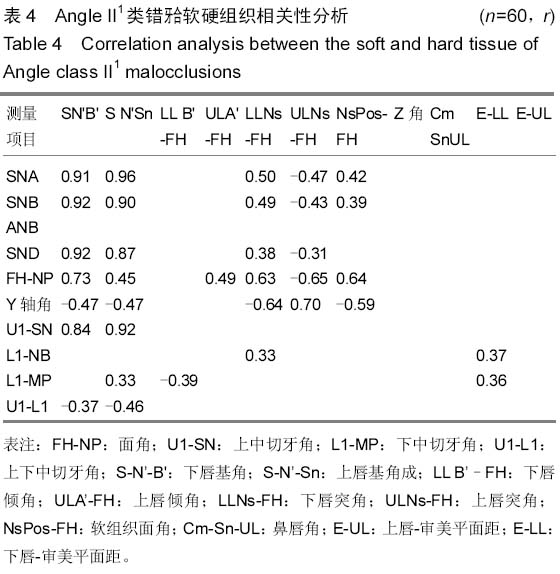
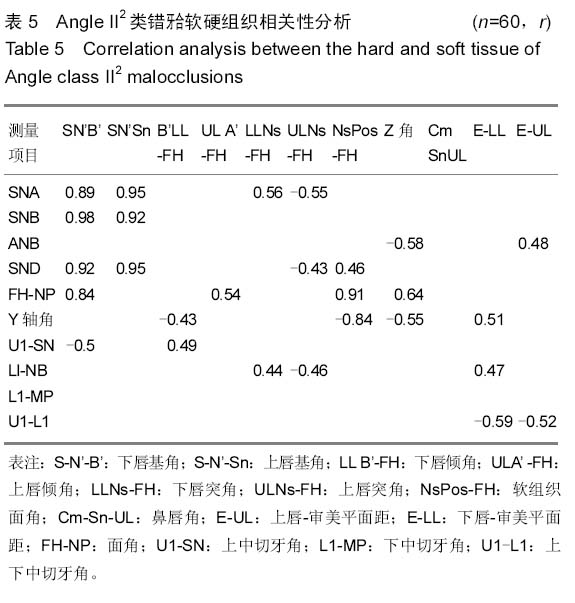
背景:研究表明,覆盖在硬组织之上的软组织的厚度存在有较大的差异,不是均匀地覆盖在硬组织之上,即临床治疗错牙合畸形时,仅仅单纯进行硬组织测量将不能获得理想的侧貌外形。 目的:分析成人Angle II类错牙合软硬组织颅面结构特征,并分析Angle II1类与II2类软硬组织相关性。 方法:从2011至2014年佳木斯大学附属口腔医院正畸科门诊病例中选取成人Angle II类错牙合畸形患者60例,年龄在18-38岁之间,平均26.3岁,男女各半,其中Angle II1类和II2类各30例,采用计算机X射线头影测量技术对比分析Angle II1类和II2类错牙合畸形软硬组织测量项目的差异以及其软硬组织相关性。 结果与结论:①硬组织测量结果:两组患者SNB角(蝶鞍中心点、鼻根点及下齿槽座点所构成的角)、SND角(蝶鞍中心点、鼻根点及下颌联合部中心点所构成的角)、ANB角(上齿槽座点、鼻根点与下齿槽座点构成的角)、面角(FH-NP)、上中切牙角(U1-SN,P < 0.001)、LI-NB角(P < 0.01)、下中切牙角(L1-MP,P < 0.01)、上下中切牙角(U1-L1,P < 0.001)的差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。②软组织测量结果:两组患者上唇倾角(ULA’ -FH)、下唇突角(LLNs-FH)、上唇突角(ULNs-FH)、鼻唇角(CmSnUL)、下唇-审美平面距(E-LL)的差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。③两组患者软硬组织各测量项目间有相关,相关性高低存在差别。结果表明AngleII1类错牙合的上颌骨及上前牙的突度对下唇部的位置有一定的影响。而Angle II2类只有上颌突度对下唇部软组织的位置的影响。Angle II2类错牙合颏部软组织变异较小,而Angle II1类错牙合的颏部软组织变异较大。临床治疗成人Angle II类错牙合畸形患者制定方案时,需结合其各自的软硬组织结构特点进行正畸、正颌外科治疗以及方案的制定。
中图分类号: