| [1]王端勋,闫小磊,朱光,等.101例胸腰段脊柱骨折合并脊髓损伤手术治疗[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2014,17(5):91-92.
[2]杨震,周焯家,简月奎,等.胸腰段脊椎脊髓损伤的临床治疗体会[J].医药前沿,2014,4(17): 211-213.
[3]程黎明,曾至立,杨志勇,等.脊柱脊髓损伤流行病学特点分析和手术疗效探讨[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2008,10(3):245-248.
[4]周建敏,双鸥,李健.不同入路内固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折合并脊髓损伤的临床观察[J].中国民族民间医药, 2013, 22(24): 30-30.
[5]管军辉,郑文标,肖柏松,等.单纯后路椎弓根螺钉固定、360度椎管减压并三柱植骨融合治疗胸腰椎脱位型骨折[J]. 浙江实用医学, 2014,19(3):192-194.
[6]王平,王彦平.胸腰段脊柱骨折合并脊髓损伤23例手术治疗体会[J].宁夏医学杂志,2013, 35(12):1208-1209.
[7]桂凯红.后路复位固定椎体间植骨融合治疗胸腰椎骨折脱位的临床疗效及对神经功能的影响[J].临床和实验医学杂志, 2014, 13(10):826-829.
[8]邱传军,张跃林.不同时间段手术治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折对患者神经损伤恢复的影响[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2014,17(18): 62-63.
[9]史玉林,王炳武,伦登兴,等.手术时机对胸腰椎骨折术后的影响[J]. 中国骨与关节外科,2013,6(4):345-348.
[10]曾忠友,吴鹏,唐宏超,等.椎弓根螺钉联合椎板关节突螺钉固定治疗腰椎骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2014,16(3):212-217.
[11]张相伟,孙建民,崔新刚,等.骨质疏松椎体压缩性骨折患者脊柱矢状面的失平衡[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(26):4224-4228.
[12]邓海涛,王清.椎弓根螺钉置入内固定治疗胸腰段骨折脱位后脊柱的生物力学变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(13): 2055-2058.
[13]吴卓,汪玉良.脊髓损伤动物模型的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,21(12):1086-1089.
[14]孔祥安,董力军,朱宏炎,等.不稳定胸腰椎骨折的后路内固定手术治疗[J].颈腰痛杂志,2013, 34(6):465-467.
[15]何福刚,黄崇新,张翅,等.后路内固定术治疗胸腰椎骨折手术方式的选择[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2013, 28(3):243-244.
[16]李程科,许明刚,王志光.保守治疗无神经损伤胸腰椎骨折的临床疗效[J]. 中国当代医药, 2013, 20(11):44-45.
[17]张绍文,李盛华,樊成虎.中西医结合保守治疗胸腰椎骨折470例临床疗效观察[J]. 西部中医药, 2013, 26(5):108-110.
[18]张云奇,杨成林.老年胸腰椎骨折的治疗现状[J].中国老年学杂志, 2013,33(12):3001-3002.
[19]郝定均.胸腰椎损伤程度评分系统在胸腰椎骨折治疗中的应用[J].美中国际创伤杂志,2013,12(2):22-24.
[20]吕游,张大明,李瑞,等.胸腰椎损伤分类及损伤程度评分在胸腰段骨折治疗中的临床意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2011, 18(8): 620-623.
[21]宋洪伟.脊柱骨折脱位合并脊髓损伤减压范围的探讨[J].中外健康文摘, 2009;6(2):53-54.
[22]吴锦春,何斌,鞠冀东.后路椎弓根钉治疗伴有脊髓损伤的多节段胸腰椎骨折[J].实用骨科杂志,2011,17(6):495-497.
[23]詹民.椎板开窗技术和椎板切开减压术治疗腰椎爆裂骨折的对照研究[J].现代医院,2014,14(5):37-39.
[24]陈太勇,龙凌丽,曹广如,等.经椎板间隙开窗伤椎椎体内植骨治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2014, 28(10): 1236-1240.
[25]孙智力.脊柱骨折的4种治疗方法探讨[J].中国医药科学,2012, 2(24):241-242.
[26]陶文明,彭昊,廉凯.胸腰椎椎弓根钉内固定术后螺钉断裂的原因分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(4): 397-399.
[27]麦伟,张维成,颜志坚.胸腰椎骨折合并脊髓损伤的手术时机探讨[J].中国医药, 2006, 1(1):44-45.
[28]温进杰,邢秉清,徐兆万.胸腰椎爆裂性骨折手术时间的选择[J]. 吉林医学,2007, 28(4):450-452.
[29]陈世忠.早期手术治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折的临床研究[J].中国医药导报, 2010,7(24):62-63.
[30]刘传安,程黎明.胸腰椎爆裂骨折的手术治疗进展[J].中华外科杂志, 2009;47(12)947-949.
[31]施鑫,赵建宁,王与荣,等.早期手术治疗胸腰椎爆裂性骨折[J]. 医学研究生学报, 2002, 15(3):238-240.
[32]姜晓幸,陈统一. 胸腰椎骨折手术方式及时间选择[J].中国临床医学, 2001, 8(1):46-48.
[33]杨俊,杨双石,刘竞龙,等.胸腰椎多节段骨折并四肢多发性骨折的外科治疗[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2007, 9(12):1196-1198.
[34]郝永宏, 董荣华, 赵合元,等. 胸腰椎爆裂骨折后路手术复位效果与手术时间的关系[J].天津医药, 2007, 35(3):195-196.
[35]苗巍. 胸腰椎爆裂性骨折手术及时间的选择对神经损伤恢复的影响探析[J].中国医药导刊, 2013, 5(7):1140-1142.
[36]罗永立,许汉权,庞祖才.胸腰椎骨折手术时机与隐性失血的相关性研究[J].吉林医学, 2011, 32(35):7448-7449.
[37]李绪华.脊柱骨折合并脊髓损伤手术治疗的效果以及重要性分析[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘(电子版),2013,13(11):203.
[38]赖欢乐,刘东光, 陈理端,等.胸腰椎爆裂性骨折患者手术前后的神经功能及椎体形态变化研究[J].海南医学院学报, 2013, 19(5): 661-663.
[39]付能高,陈小芬.经后路椎弓根螺钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的临床效果[J].现代医药卫生, 2013,29(2):207-208.
[40]付德生,林龙,王峰,等.后路钉棒系统治疗胸腰椎骨折并脊髓损伤[J]. 创伤外科杂志, 2013, 15(4):355-355. |
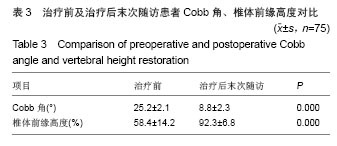
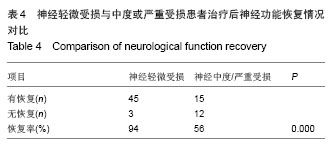
.jpg)
.jpg)