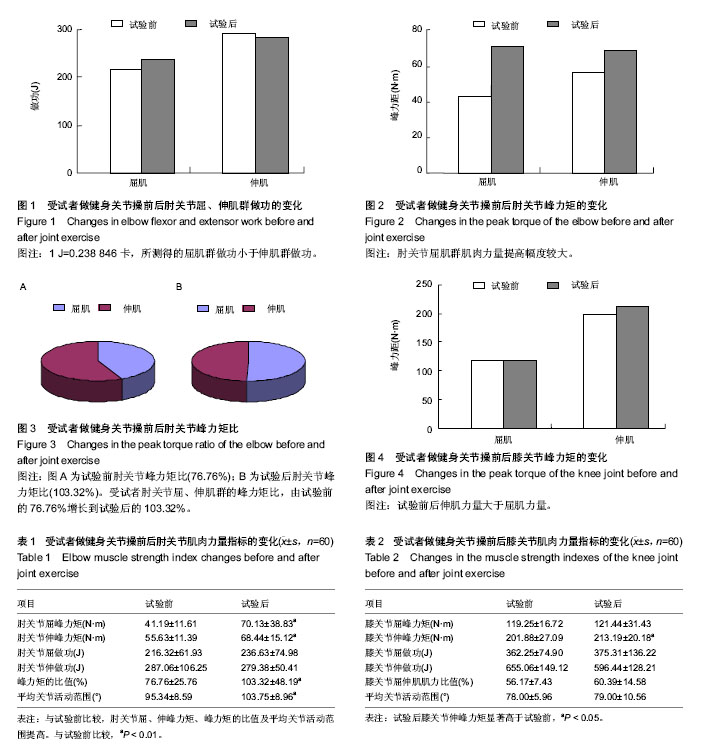
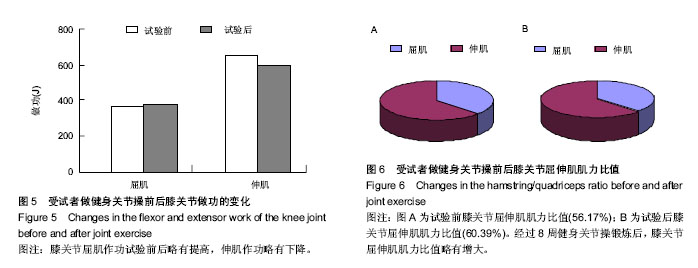
| [1] 许晓伟.柔韧素质考试办法之我见-以江苏省高考体育类专业统考中的柔韧素质考试为例[J].中国学校体育.2014(S1):19.
[2] 唐琳璇.武术专项大学生与普通大学生躯干屈伸肌群等速肌力测试的比较研究[D].首都体育学院,2008.
[3] 张葆欣,周道宏.健身关节操对中老年群体柔韧素质的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2007,11(52):10522-10542.
[4] 李晓兰.健身关节操对男生关节活动度影响的实验研究[J].价值工程,2011,(9):288-289.
[5] 张葆欣,周里,黄海,等.10周“健身关节操”运动方案对初中学生柔韧素质、平衡能力影响的研究[J],西安体育学院学报, 2012, (6):721-724.
[6] 张阳,张秋霞.单侧功能性踝关节不稳者踝内外翻等速肌力研究[J].体育研究与教育.2013,(5):118-122.
[7] 谷崎,王兵,文安,等.营养干预对女篮队员免疫机能影响的实验研究[J].西北大学学报:自然科学版,2009,39(6):998-1001.
[8] 荣湘江,尤桂杰,姚鸿恩.不同运动水平大学生躯干屈伸肌群等速肌力和耐力测定[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(2): 302-306.
[9] 徐秀林,蒋奇永,严荣国,等.基于蓝牙通信的等长肌力测试仪的设计[J].中国生物医学工程学报,2011,30(6):897-901.
[10] 张德辉,黄昌林,薛刚,等.陆军士兵躯干肌力参数常模的初步研究[J].中华劳动卫生职业病杂志,2005,23(3):215-216.
[11] 胡永善.等速技术在康复医学中应用介绍[C].中国康复医学会第三次康复治疗学术大会,2002.
[12] 汤文杰,王满宜,朱仕文.髋臼骨折Kocher-Langenbeck入路术后等速肌力测试:36例患肢髋关节周围力量分析[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(44):216-218.
[13] 李国平,陈晓鸣,张维娜.用等速测力法评定优秀运动员股四头肌和腘绳肌力量和耐力 [J].中国运动医学杂志, 1988,7(3): 143-190.
[14] 樊远志,龚利,严隽陶,等.推拿治疗对膝骨关节炎患者股四头肌功能的影响[J].上海中医药杂志,2010,44(10):57-60.
[15] 黄文宾,王家君,武常宏.对我国青少年足球运动员伸、屈膝等动力量及下肢爆发力特点研究[J].北京体育大学学报,2005,28(1): 68-70.
[16] 胡跃.小议女子“后腰”柔韧素质技能训练中应注意的问题[J].体育师友.2013(01):28-29.
[17] 侯立皓,许光旭,张桂林.等速肌力训练用于老年脑卒中后下肢功能恢复[J].实用老年医学,2009,23(4):299-300.
[18] Harter RA,Osternig LR,Standifer LW.Isokinetic evaluation of quadriceps and hamstrings symmetry following anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1990;71(7):465-468.
[19] 李翰君,刘卉,张新,于冰.关节肌力分布研究进展[J].北京体育大学学报.2013(07):83-87.
[20] Westing SH, Cresswell AG,Thorstensson .Muscle activation during maximal voluntary eccentric and concentric kneextension. EurJAppl A PhysiolOccupPhysiol. 1991;62(2): 104-108.
[21] 范建中.等速技术在临床康复中的应用[C].上海:中国康复医学会运动疗法分会第十一届全国康复学术大会.2011.
[22] Moolyk AN, Carey JP, Chiu LZ.Characteristics of Lower Extremity Work During the Impact Phase of Jumping and Weightlifting. J Strength Cond Res. 2013;27(12):3225-3232
[23] 李文川.积极、健康、幸福-《2008美国人身体活动指南》新启迪[J].中国体育科技,2012,(6):91-96.
[24] 梅汉超.竞技武术套路运动员竞技能力特征的演化及其相互关系[J].武汉体育学院学报, 2010,(11):58-61.
[25] 余竹生.攀爬运动中四肢双关节肌功能现象探讨[J].中国运动医学杂志,2013,(4):353-356 .
[26] 张德辉,黄昌林,刘鼎成.青年下背痛患者躯干肌力及腰椎曲度的临床研究[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2003,25(8):469-471. |