| [1]Jung HS, Kwon BS, Lee SW. Tumor-specific gene delivery using RNA-targeting Tetrahymena group I intron. Biotechnol Lett. 2005;27(8):567-574.
[2]He T, Wang Y, Xiang J, et al. In vivo tracking of novel SPIO-Molday ION rhodamine-B™-labeled human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells after lentivirus- mediated COX-2 silencing: a preliminary study. Curr Gene Ther. 2014;14(2):136-145.
[3]Sarzi-Puttini P, Cimmino MA, Scarpa R, et al. Osteoarthritis: an overview of the disease and its treatment strategies. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005;35(1 Suppl 1):1-10.
[4]Jain A, Stein BE, Skolasky RL, et al. Total joint arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a United States experience from 1992 through 2005. J Arthroplasty. 2012; 27(6):881-888.
[5]de Boer TN, Huisman AM, Polak AA, et al. The chondroprotective effect of selective COX-2 inhibition in osteoarthritis: ex vivo evaluation of human cartilage tissue after in vivo treatment. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2009;17(4): 482-488.
[6]Tseng SS, Lee MA, Reddi AH. Nonunions and the potential of stem cells in fracture-healing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90 Suppl 1:92-98.
[7]Thirunavukkarasu K, Pei Y, Wei T. Characterization of the human ADAMTS-5 (aggrecanase-2) gene promoter. Mol Biol Rep. 2007;34(4):225-231.
[8]Wang X, Grogan SP, Rieser F, et al. Tissue engineering of biphasic cartilage constructs using various biodegradable scaffolds: an in vitro study. Biomaterials. 2004;25(17): 3681-3678.
[9]Tortorella MD, Liu RQ, Burn T, et al. Characterization of human aggrecanase 2 (ADAM-TS5): substrate specificity studies and comparison with aggrecanase 1 (ADAM-TS4). Matrix Biol. 2002;21(6):499-511.
[10]Miller JA, Liu RQ, Davis GL, et al. A microplate assay specific for the enzyme aggrecanase. Anal Biochem. 2003; 314(2):260-265.
[11]Debnath T, Kim da H, Lim BO. Natural products as a source of anti-inflammatory agents associated with inflammatory bowel disease. Molecules. 2013;18(6):7253-7270.
[12]Depboylu C, Weihe E, Eiden LE. COX1 and COX2 expression in non-neuronal cellular compartments of the rhesus macaque brain during lentiviral infection. Neurobiol Dis. 2011;42(1):108-115.
[13]Attur M, Al-Mussawir HE, Patel J, et al. Prostaglandin E2 exerts catabolic effects in osteoarthritis cartilage: evidence for signaling via the EP4 receptor. J Immunol. 2008;181(7): 5082-5088.
[14]Hagmann S, Moradi B, Frank S, et al. Different culture media affect growth characteristics, surface marker distribution and chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2013;14:223.
[15]Ulivi V, Lenti M, Gentili C, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of monogalactosyldiacylglycerol in human articular cartilage in vitro: activation of an anti-inflammatory cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) pathway. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(3):R92.
[16]Wakefield AP, Ogborn MR, Ibrahim N, et al. A dietary conjugated linoleic acid treatment that slows renal disease progression alters renal cyclooxygenase-2-derived prostanoids in the Han: SPRD-cy rat. J Nutr Biochem. 2012; 23(8):908-914.
[17]Kurland ES, Rosen CJ, Cosman F, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-I in men with idiopathic osteoporosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82(9):2799-2805.
[18]Lazowski DA, Fraher LJ, Hodsman A, et al. Regional variation of insulin-like growth factor-I gene expression in mature rat bone and cartilage. Bone. 1994;15(5):563-576.
[19]Paveli? J, Matijevi? T, Knezevi? J. Biological & physiological aspects of action of insulin-like growth factor peptide family. Indian J Med Res. 2007;125(4):511-522.
[20]Xu ZY, Wang YZ, Zhang HN, et al. Construction and Detection of Bicistronic Eukaryotic Vector pIRSES2-EGFP- hIGF-1. Xiandai Shengwu Yixue Jinzhan. 2013;13(15): 2837-2840.
[21]He T, Zhang HN, Xiang JY, et al. Cyclooxygenase 2 silencing has no effects on oriented differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2014;18(14):2140-2146.
[22]Du QF, Zhang HN, Wang YZ, et al. Effects of aggrecanase-2 shRNA transfection on chondrocytes of rheumatoid arthritis patient leaded by lentivirus. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 2014;34(9):936-944.
[23]Wang DL, Xing DG, Wang L, et al. Effects of transplanting bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transfected by insulin- like growth factor-1 gene on fracture healing of rats with diabetes. Zhonghua Shiyan Waike Zazhi. 2012;29(3):518-520.
[24]Shao M, Hollar S, Chambliss D, et al. Targeting the insulin growth factor and the vascular endothelial growth factor pathways in ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(7): 1576-1586.
[25]Chen C, Xu Y, Song Y. IGF-1 gene-modified muscle-derived stem cells are resistant to oxidative stress via enhanced activation of IGF-1R/PI3K/AKT signaling and secretion of VEGF. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014;386(1-2):167-175.
[26]Olmos A, Díaz L, Avila E, et al. Associations between insulin-like growth factor I, vascular endothelial growth factor and its soluble receptor 1 in umbilical serum and endothelial cells obtained from normotensive and preeclamptic pregnancies. Growth Factors. 2013;31(4):123-129.
[27]Vane JR, Botting RM. Anti-inflammatory drugs and their mechanism of action. Inflamm Res. 1998;47 Suppl 2:S78-87.
[28]Vane J. Towards a better aspirin. Nature. 1994;367(6460): 215-216.
[29]Yan X, Yin L, Wang Y, et al. The low binding affinity of ADAMTS4 for citrullinated fibronectin may contribute to the destruction of joint cartilage in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013;31(2):201-206.
[30]Berenbaum F. Signaling transduction: target in osteoarthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2004;16(5):616-622.
[31]Shi S, Mercer S, Trippel SB. Effect of transfection strategy on growth factor overexpression by articular chondrocytes. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(1):103-109.
[32]Liu J, Jones KL, Sumer H, et al. Stable transgene expression in human embryonic stem cells after simple chemical transfection. Mol Reprod Dev. 2009;76(6): 580-586.
[33]Pfeifer A, Hofmann A. Lentiviral transgenesis. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;530:391-405.
[34]Sekiya I, Larson BL, Vuoristo JT, et al. Comparison of effect of BMP-2, -4, and -6 on in vitro cartilage formation of human adult stem cells from bone marrow stroma. Cell Tissue Res. 2005;320(2):269-276. |
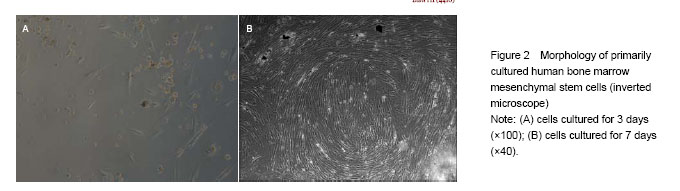
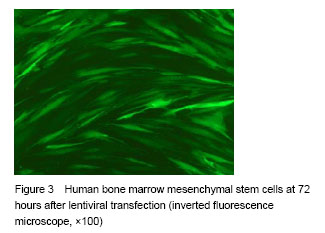
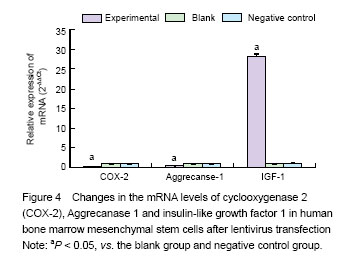
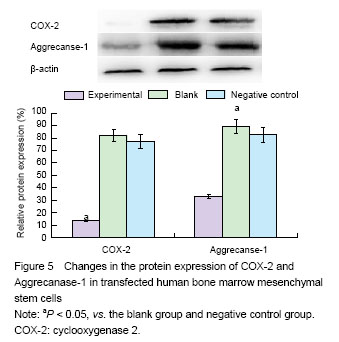
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)