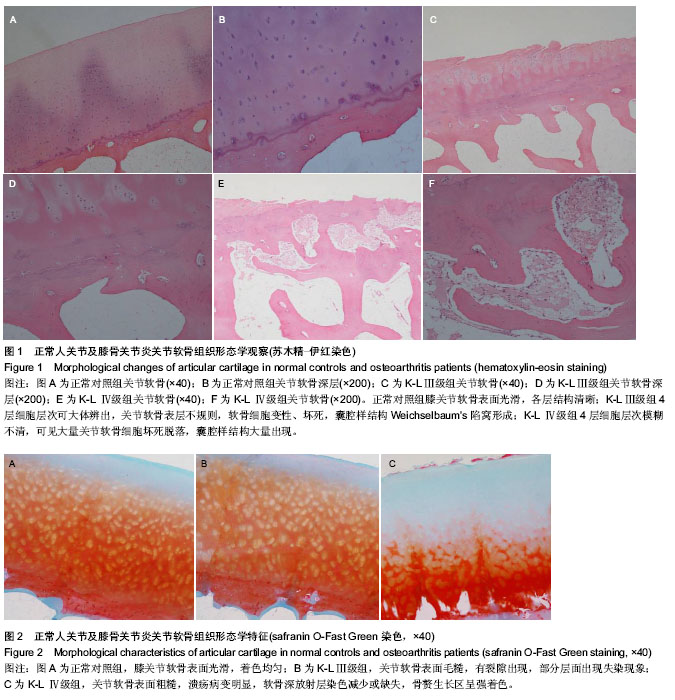
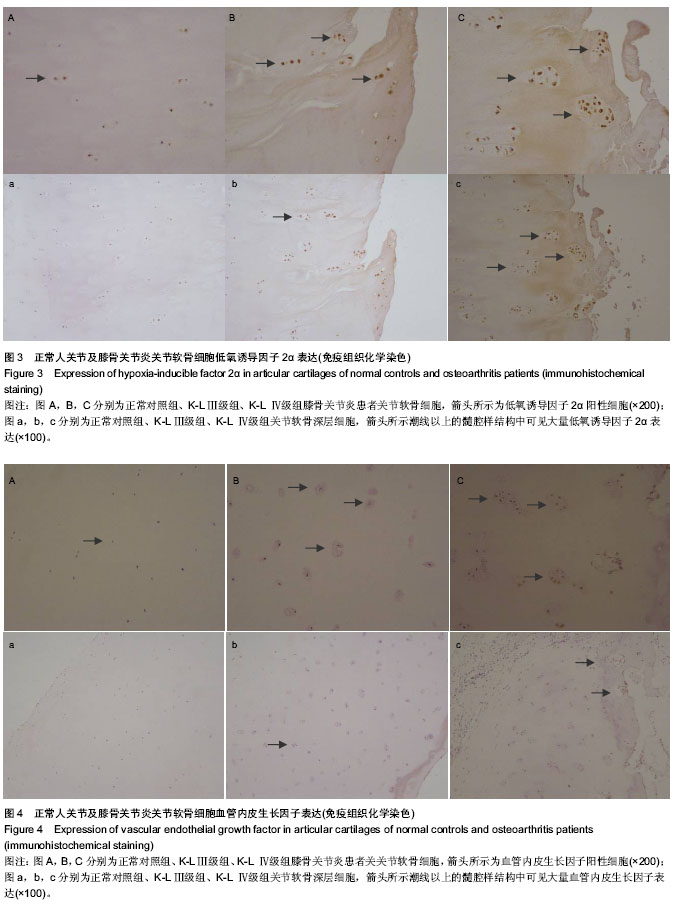
| [1] Schipani E, Ryan HE, Didrickson S, et al. Hypoxia in cartilage: HIF-1α is essential for chondrocyte growth arrest and survival. Genes Dev.2001;15(21):2865-2876.
[2] Stewar AJ,Houston B,Farquharson C. Elevated expression of hypoxia inducible factor-2alpha in terminally differentiating growth plate chondrocytes.Cell Physiol. 2006;206(2): 435-440.
[3] Saito T, Fukai A, Mabuchi A, et al. Transcriptional regulation of endochondral ossification by HIF-2 [alpha] during skeletal growth and osteoarthritis development. Nature medicine. 2010;16(6):678-686.
[4] Yang S, Kim J, Ryu JH, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2 [alpha] is a catabolic regulator of osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Nature medicine.2010;16(6):687-693.
[5] Nakajima M, Shi D, Dai J, et al. A large‐scale replication study for the association of rs17039192 in HIF-2α with knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(8):1244-1248.
[6] Goldring MB, Otero M.Inflammation in osteoarthritis. Current opinion in rheumatology. 2011;23(5):471.
[7] Walsh DA, McWilliams DF, Turley MJ, et al. Angiogenesis and nerve growth factor at the osteochondral junction in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Rheumatology.2010; 49(10):1852-1861.
[8] Yamairi F, Utsumi H, Ono Y, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) associated with histopathological changes in rodent models of osteoarthritis. J toxicol pathol.2011;24(2):137.
[9] Ludin A, Sela JJ, Samuni Y,et al.Injection of vascular endothelial growth factor into knee induces osteoarthritis in mice.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(3):491-497.
[10] Kellgren JH, Lawrence JS. Radiological assessment of osteo-arthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis.1957;16(4):494-502.
[11] Lequesne MG, Mery C, Samson M, et al. Indexes of severity for osteoarthritis of the hip and knee: validation-value in comparison with other assessment tests. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology.1987;16(S65):85-89.
[12] Mankin HJ,Dorfman H,Lippiello L,et al.Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips II.Correlation of morphology with biochemical and metabolic data. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery. 1971;53(3):523-537.
[13] Pelletier JP,Jovanovic D,Fernandes JC,et al.Reduced progression of experimental osteoarthritis in vivo by selective inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Arthritis & Rheumatism.1998;41(7):1275-1286.
[14] Bonde HV, Talman ML, Kofoed H. The area of the tidemark in osteoarthritis–a three‐dimensional stereological study in 21 patients. Apmis.2005;113(5):349-352.
[15] Lyons T J, Stoddart R W, McClure S F, et al. The tidemark of the chondro-osseous junction of the normal human knee joint. Journal of molecular histology.2005; 36(3):207-215.
[16] Goldring S, Goldring M. Bone and cartilage in osteoarthritis: is what's best for one good or bad for the other?. Arthritis Res Therapy.2010;12(5):143.
[17] Suri S, Walsh D A. Osteochondral alterations in osteoarthritis. Bone.2012;51(2):204-211.
[18] Zhou J L, Liu S Q, Qiu B, et al. Effects of hyaluronan on vascular endothelial growth factor and receptor-2 expression in a rabbit osteoarthritis model. J Orthopaedic Sci. 2009; 14(3): 313-319.
[19] Jansen H, Meffert R H, Birkenfeld F, et al. Detection of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in moderate osteoarthritis in a rabbit model. Annals of Anatomy- Anatomischer Anzeiger.2012;194(5):452-456.
[20] Pufe T, Harde V, Petersen W, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces matrix metalloproteinase expression in immortalized chondrocytes. The Journal of pathology.2004;202(3):367-374.
[21] Chen XY, Hao YR, Wang Z,et al. The effect of vascular endothelial growth factor on aggrecan and type II collagen expression in rat articular chondrocytes. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(11):3359-3364.
[22] Ryu JH,Shin Y,Huh YH,et al.Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α regulates Fas-mediated chondrocyte apoptosis during osteoarthritic cartilage destruction. Cell Death & Differentiation.2012;19(3):440-450.
[23] Jansen H, Meffert RH, Birkenfeld F, et al. Detection of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in moderate osteoarthritis in a rabbit model. Annals of Anatomy-Anatomischer Anzeiger.2012;194(5):452-456.
[24] Takeda N, Maemura K, Imai Y, et al. Endothelial PAS domain protein 1 gene promotes angiogenesis through the transactivation of both vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor, Flt-1. Circulation research.2004;95(2):146-153.
[25] Saito T,Kawaguchi H.HIF-2α as a possible therapeutic target of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage.2010;18(12): 1552-1556.
[26] Wu L, Huang X, Li L, et al. Insights on Biology and Pathology of HIF-1α/-2α, TGF/β, Wnt/β-Catenin, and NF-κB Pathways in Osteoarthritis.Current pharmaceutical design.2012;18(22): 3293-3312. |