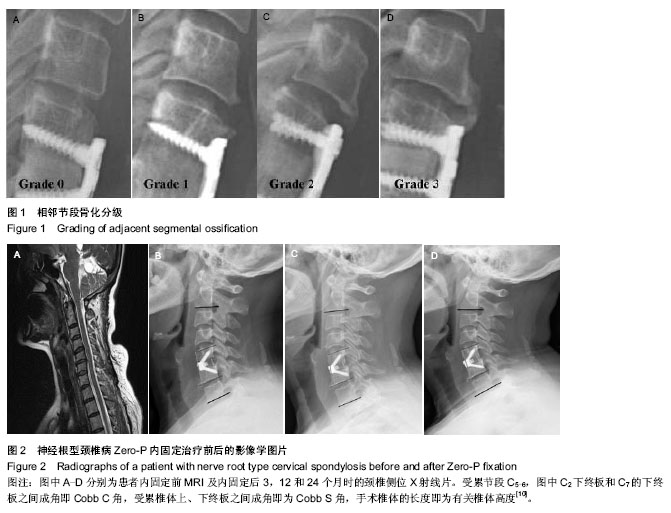
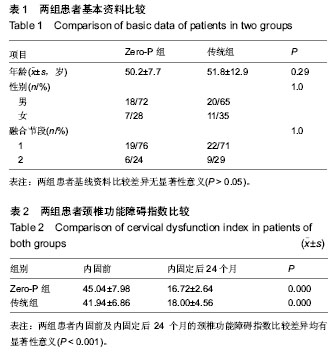
| [1] Smith GW, Robinson RA. The treatment of certain cervical spine disorders by anterior removal of the intervertebral disc and interbody fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am.1958; 40: 607- 624.
[2] Jacobs W, Willems PC, Kruyt M, et al. The Cochrane Collaboration: systematic review of anterior interbody fusion techniques for single and double level cervical degenerative disc disease. Spine. 2011;14:E950-960.
[3] Vanek P, Bradac O, DeLacy P, et al. Comparison of three fusiontechniques in the treatment of the degenerative cervical spine. Is autograft really “the golden standard”? Spine. 2012; 37:1645-1651.
[4] Kao FC,Niu CC, Chen LH.Maintenance of interbody space in one- and two-level anterior cervical interbody fusion: comparison of the effectiveness of autograft, allograft and cage. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; 430: 108-116.
[5] McAfee PC, Capuccino A, Cunningham BW, et al. Lower incidence of dysphagia with cervical arthroplasty compared with ACDF in a prospective randomized clinical trial. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2010; 23:1-7.
[6] Pitzen TR, Chrobok J, Stulik J, et al. Implant complications, Psion, loss of lordosis and outcome after anterior cervical plating with dynamic or rigid plates. Spine. 2009; 34: 641-646. [7] Shimamoto N, Cunningham BW, Dmitriev AE, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of stand-alone interbody fusion cage in the cervical spine. Spine. 2001;26: 432-436.
[8] Barbagallo GM, Romano D, Certo F,et al. Zero-P: a new zero-pro?le cage-plate device for single and multilevel ACDF. A single Institution series with four years maximum follow-up and review of the literature on zero-pro?le devices. J Eur Spine. 2013;22:868-878.
[9] 缪锦浩,匡勇,陈德玉,等.颈前路减压零切迹椎间植骨融合内固定系统治疗颈椎病的早期疗效分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012, 22(6):536-540.
[10] 王治栋,朱若夫,杨惠林,等. 路减压Zero-p椎间融合器与传统钛板联合cage融合内固定治疗脊髓型颈椎病的疗效比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2013,23(5):440-444.
[11] Vermon H, Mior S. The neck disability index: a study of reliability and validity. J Manip Physiol Ther. 1991; 14: 409-415.
[12] Odom GL,Finney W, Woodhall B. Cervical disc lesions. J Am Med Assoc.1958;166: 23-28.
[13] Vanek P, Bradac O, DeLacy P, et al. Anterior Interbody Fusion of the Cervical Spine With Zero-P Spacer. Spine. 2013;38: E792-797.
[14] Park JB, Cho YS, Riew KD. Development of adjacent-level ossi?cation in patients with an anterior cervical plate. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:558-563.
[15] Lee DH, Lee JS, Yi JS, et al. Anterior cervical plating technique to prevent adjacent-level ossi?cation development. Spine J. 2013;13: 823-829.
[16] Bohler J, Gaudernak T. Anterior plate stabilization for fracture dislocations of Loir cervical spine. J Trauma.1980; 20: 203-205.
[17] Lowery GI, McDonough RF. The signi?cance of hardware failure in anterior cervical plate ?xation. Patient with two to seven-year follow-up. Spine.1998; 23: 181-186.
[18] Gof?n J, van Loon J, Van Calenbergh F, et al. Long-term resultsafter anterior cervical fusion and osteosynthetic stabilization for fractures and/or dislocations of the cervical spine. J Spinal Disord. 1995;8:500-508; discussion 499.
[19] Park JB, Cho YS, Riew KD. Development of adjacent-level ossi?cation in patients with an anterior cervical plate. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005;87:558-563.
[20] Matge G. Cervical cage fusion with ?ve different implants: 250 cases. Acta Neurochirurg. 2002; 144: 539-549.
[21] Vavruch L, Hedlund R, Javid D, et al. A prospective randomized comparison between the Cloward procedure and a carbon ?brecage in the cervical spine: a clinical and radiologic study. Spine. 2002;27: 1694-1701.
[22] Fernández-Fairen M, Sala P, Dufoo M Jr, et al. Anterior cervical fusion with tantalum implant: a prospective randomized controlled study.Spine. 2008; 33: 465-472.
[23] Hacker RJ. A randomised prospective study of an anterior cervical fusion device with minimum two years follow-up results.J Neurosurg. 2000; 93: 222-226.
[24] Peolsson A, Vavruch L, Hedlund R. Long-term randomised comparison between a carbon ? bre cage and the Cloward procedure in the cervical spine. Eur Spine J. 2007;16: 173-178.
[25] Scholz M, Reyes PM, Schleicher P, et al. A new stand-alone cervical anterior interbody fusion. Biomechanical comparison with established anterior cervical ?xation device. Spine. 2009; 34: 156-160.
[26] Barsa P, Suchomel P. Factor affecting sagittal malalignment due to cage subsidence in stand-alone cage assisted anterior cervical fusion.Eur Spine J. 2007; 16: 1395-1400.
[27] Song KJ, Teghavi CE, Lee KB, et al. The ef?cacy of plate construct augmentative versus stand-alone in anterior cervical Psion. Spine. 2009;34: 2886-2892.
[28] Miao J, Shen Y, Kuang Y, et al. Early follow-up outcomes of new Zero-pro?le implant used in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(5):E193-197 |