| [1] Chung KF, J Thorac Dis. Approach to chronic cough: the neuropathic basis for cough hypersensitivity syndrome. 2014;6(Suppl 7):S699-S707.
[2] Sumalatha S, D Souza AS, Yadav JS, et al. An unorthodox innervation of the gluteus maximus muscle and other associated variations: a case report. Australas Med J. 2014; 7(10):419-422.
[3] Piao C, Li P, Liu G, et al. Viscoelasticity of repaired sciatic nerve by poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) tubes. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(33):3131-3138.
[4] Zhu S, Li J, Zhu Q, et al.Differentiation of human amniotic epithelial cells into Schwann like cells via indirect co culture withSchwann cells in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2014 [Epub ahead of print].
[5] Gordon A, Adamsky K, Vainshtein A, et al. Caspr and caspr2 are required for both radial and longitudinal organization of myelinated axons. J Neurosci. 2014;34(45): 14820-14826.
[6] Thoma EC, Merkl C, Heckel T, et al. Chemical conversion of human fibroblasts into functional schwann cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2014;3(4):539-547.
[7] Gao R, Wang L, Sun J, et al. MiR-204 promotes apoptosis in oxidative stress-induced rat Schwann cells by suppressing neuritin expression. FEBS Lett. 2014;588(17):3225-3232.
[8] Sulaiman W, Dreesen TD. Effect of local application of transforming growth factor-β at the nerve repair site following chronic axotomy and denervation on the expression of regeneration-associated genes.J Neurosurg. 2014;121(4): 859-874.
[9] Zong HB, Zhao HX, Zhao YL, et al. Nanoparticles carrying neurotrophin-3-modified Schwann cells promote repair of sciatic nerve defects.Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(14): 1262-1268.
[10] Ye FG, Li HY, Qiao GG,et al. Platelet-rich plasma gel in combination with Schwann cells for repair of sciatic nerve injury. Neural Regen Res.2012;7(29): 2286-2292.
[11] He B, Tao HY, Liu SQ. Neuroprotective effects of carboxymethylated chitosan on hydrogen peroxide induced apoptosis inSchwann cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;740: 127-134.
[12] Painter MW, Brosius Lutz A, Cheng YC, et al. Diminished Schwann cell repair responses underlie age-associated impaired axonal regeneration. Neuron. 2014;83(2): 331-343.
[13] Chen C, Tang P, Zhang X. Reconstruction of proper digital nerve defects in the thumb using a pedicle nerve graft. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;130(5):1089-1097.
[14] Yoon WY, Lee BI. Fingertip reconstruction using free toe tissue transfer without venous anastomosis. Arch Plast Surg. 2012;39(5):546-550.
[15] Park SY, Ki CS, Park YH, et al. Functional recovery guided by an electrospun silk fibroin conduit after sciatic nerve injury in rats. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2012 [Epub ahead of print].
[16] Mohammadi R, Amini K, Eskafian H. Betamethasone- enhanced vein graft conduit accelerates functional recovery in the rat sciatic nervegap. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;71(4): 786-792.
[17] Paun CC, Pijl BJ, Siemiatkowska AM, et al. A novel crumbs homolog 1 mutation in a family with retinitis pigmentosa, nanophthalmos, and optic disc drusen. Mol Vis. 2012;18: 2447-2453.
[18] Carr AL, Sun L, Lee E, et al. The human oncogene SCL/TAL1 interrupting locus is required for mammalian dopaminergic cell proliferation through the Sonic hedgehog pathway. Cell Signal. 2014;26(2):306-312.
[19] Mohammadi R, Sanaei N, Ahsan S, et al. Repair of nerve defect with chitosan graft supplemented by uncultured characterized stromal vascular fraction in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Int J Surg. 2014;12(1):33-40.
[20] Mohammadi R, Masoumi-Verki M, Ahsan S, et al. Improvement of peripheral nerve defects using a silicone conduit filled with hepatocyte growth factor. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2013;116(6):673-679.
[21] Marlin S, Chantot-Bastaraud S, David A, et al.Discovery of a large deletion of KAL1 in 2 deaf brothers. Otol Neurotol. 2013; 34(9):1590-1594.
[22] Guo L, Lee AA, Rizvi TA, et al. The protein kinase A regulatory subunit R1A (Prkar1a) plays critical roles in peripheral nervedevelopment. J Neurosci. 2013;33(46):17967-17975.
[23] Liu K, Zhu W, Shi J, et al. Foot drop caused by lumbar degenerative disease: clinical features, prognostic factors of surgical outcome and clinical stage. PLoS One. 2013;8(11): e80375.
[24] Burke RM, Norman TA, Haydar TF, et al. BMP9 ameliorates amyloidosis and the cholinergic defect in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110 (48):19567-19572.
[25] Kim DW, Kim US. Isolated complete bitemporal hemianopia in traumatic chiasmal syndrome.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2013; 61(12):759-760.
[26] Lv L, Wang Y, Zhang J, et al. Healing of periodontal defects and calcitonin gene related peptide expression following inferior alveolar nerve transection in rats. J Mol Histol. 2014; 45(3):311-320.
[27] Sahakyants T, Lee JY, Friedrich PF, et al. Return of motor function after repair of a 3-cm gap in a rabbit peroneal nerve: a comparison of autograft, collagen conduit, and conduit filled with collagen-GAG matrix.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013;95(21): 1952-1958.
[28] Van Dine SE, Salem E, George E, et al. Cellular and axonal diversity in molecular layer heterotopia of the rat cerebellar vermis.Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:805467.
[29] Hazer DB, Bal E, Nurlu G, et al.In vivo application of poly-3-hydroxyoctanoate as peripheral nerve graft. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2013;14(11):993-1003.
[30] Kim JM, Park KH, Kim SJ, et al. Comparison of localized retinal nerve fiber layer defects in highly myopic, myopic, and non-myopic patients with normal-tension glaucoma: a retrospective cross-sectional study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2013; 13:67.
[31] Chowdhury S, Wang S, Patterson BW, et al.The combination of GIP plus xenin-25 indirectly increases pancreatic polypeptide release in humans with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. Regul Pept. 2013;187:42-50.
[32] Darcy MJ, Trouche S, Jin SX, et al. Age-dependent role for Ras-GRF1 in the late stages of adult neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus.Hippocampus. 2014;24(3):315-325.
[33] Marinescu SA, Z?rnescu O, Mihai IR, et al. An animal model of peripheral nerve regeneration after the application of a collagen-polyvinyl alcohol scaffold and mesenchymal stem cells. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2014;55(3):891-903.
[34] Huang L, Li R, Liu W, et al. Dynamic culture of a thermosensitive collagen hydrogel as an extracellular matrix improves the construction of tissue-engineered peripheral nerve. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(14):1371-1378.
[35] Liu H, Wen W, Hu M, et al. Chitosan conduits combined with nerve growth factor microspheres repair facial nerve defects. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(33):3139-3147.
[36] Biazar E, Keshel SH, Pouya M. Efficacy of nanofibrous conduits in repair of long-segment sciatic nerve defects. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(27):2501-2509.
[37] Biazar E, Keshel SH, Pouya M, et al. Nanofibrous nerve conduits for repair of 30-mm-long sciatic nerve defects. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(24):2266-2274.
[38] Zhang L, Zhang J, Li B, et al. Transplanted epidermal neural crest stem cell in a peripheral nerve gap. Sheng Wu Gong Cheng Xue Bao. 2014;30(4):605-614.
[39] Riccio M, Pangrazi PP, Parodi PC, et al. The amnion muscle combined graft (AMCG) conduits: a new alternative in the repair of wide substance loss of peripheral nerves. Microsurgery. 2014;34(8):616-622.
[40] Wu MC, Yuan H, Li KJ, et al. Cellular Transplantation-Based Evolving Treatment Options in Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014 [Epub ahead of print].
[41] Rochkind S, Nevo Z. Recovery of peripheral nerve with massive loss defect by tissue engineered guiding regenerative gel. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:327578.
[42] Cirillo V, Clements BA, Guarino V, et al. A comparison of the performance of mono- and bi-component electrospun conduits in a rat sciatic model. Biomaterials. 2014;35(32): 8970-8982. |
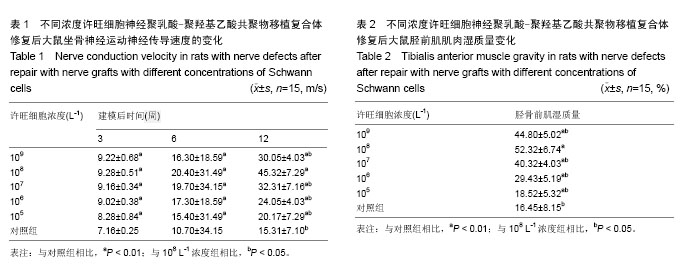
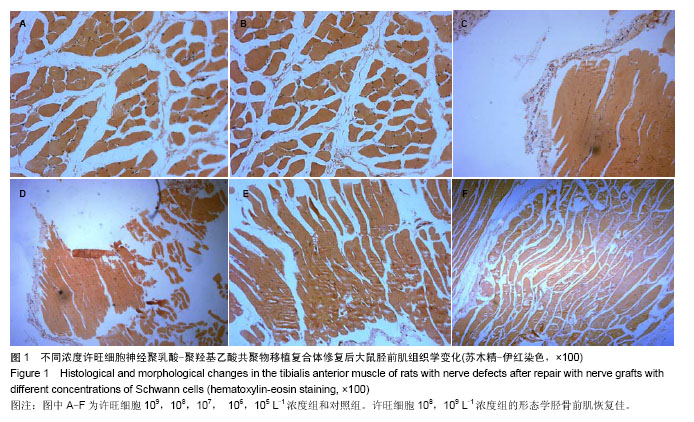
.jpg)