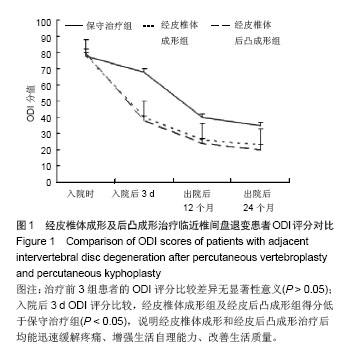
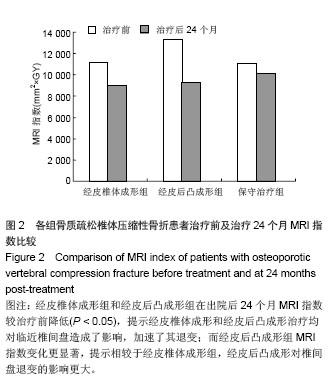
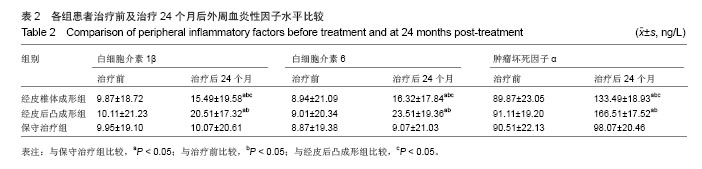
| [1]Campbell PG,Harrop JS. Incidence of fracture in adjacent levels in patients treated with balloon kyphoplasty: a review of the literature. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med.2008;1(1): 61-64.
[2]杨惠林.科学认识椎体成形术与椎体后凸成形术的临床价值[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010, 20(6):441-443.
[3]Weiler C, Nerlich AG, Bachmeier BE, et al. Expression and distribution of tumor necrosis factor alpha in human lumbar intervertebral discs:a study in surgical specimen and autopsy controls. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1):44-53.
[4]Hiyama A, Mochida J, Sakai D. Stem cellapplications in intervertebral disc repair. Cell Mol Biol;2008, 54:24-32.
[5]Le Maitre CL, Hoyland JA, Freemont AJ.Catabolic cytokine expression in degenerate and herniated human intervertebral discs: IL-1beta and TNFalpha expression profile.Arthritis Res Ther. 2007;9(4):R77.
[6]Steiner G, Studnicka-Benke A, Witzmann G, et al.Soluble receptors for tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-2 in serum and synovial fluid of patients with rheumatoid arthritis, reactive arthritis and osteoarthritis.J Rheumatol. 1995;22(3): 406-412.
[7]Séguin CA, Pilliar RM, Roughley PJ, et al. Tumor necrosis fac-tor-alpha modulates matrix production and catabolism in nucleuspulposus tissue. Spine ( Phila Pa 1976 ). 2005;30 (17): 1940-1948.
[8]Holm S,Mackiewicz Z,Holm AK, et al. Pro-inflammatory, pleiotropic, and anti- inflammatory TNF-a, IL-6,and IL-10 in experimental porcine intervertebral disk degeneration. Vet Pathol.2009;6: 1292-1300.
[9]Wu CL, Lin LY, Yang JS, et al. Attenuation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by treatment with IL-10. Respirology.2009; 4: 511-521.
[10]Takahashi H. A meckenism for sciatic pain causrd by lumbar disk herniation involvement of inflammation cytokins with sciatic pain. Nippon Seikeigeka Gakkai Zasshi. 1995; 69(1): 17- 29.
[11]Sobajima S, Kompel JF, Kim JS, et al. A slowly progressive and reproducible animal model of intervertebral disc degeneration characterized by MRI, X-ray, and histology. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30 (1): 15-24.
[12]Galibert P, Deramond H, Rosat P, et al. Preliminary note on the treatment of vertebral angioma by percutaneous acrylic vcrtebroplasty. Ncurochirurgie.1987;33(2):166-168.
[13]Pitton MB, Herber S, Bletz C, et al. CT-guided vertebroplasty in osteoproticvertebral fractures; incidence of secondary fractures and inpact of intradisal cement leakages during follow up. Eur Radiol. 2008;18:43-50.
[14]Qian J, Yang HL, Jing JH, et al. The Early Stage Adjacent Disc Degeneration afterPercutaneous Vertebroplasty and Kyphoplasty in The Trcatment of Osteoporotic VCFs. Plos ONE.2012;7(10): c46323.
[15]Fan SW, Zhou ZJ, Hu ZJ, et al. Quantitative MRI analysis of the surface area, signal intensity and MRI index of the central bright area for the evaluation of early adjacent disc degeneration after lumbar fusion. Eur Spine.2012; 21(9): 1709-1715.
[16]Berlemann U, Ferguson SJ, Nohe LP, et al. Adjacent vertebral failure after vertebroplasty:a biomechanical investigation . J Bone Joint Surg Br.2002; 84(5):748-752.
[17]Polikeit A,Nolte LP,Ferguson SJ. The effect of cement augmentation on the load transfer in an osteoporotic functional spinal unit:finite-element analysis.Spine. 2003; 28(10):991-996.
[18]李志远,申勇,王林峰,等,椎体成形术治疗老年骨质疏松椎体压缩骨折对邻近节段生物力学的影响[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志, 2009, 19(5): 388-391.
[19]Ogata K, Whiteside LA.An experimental study using hydrogen washout technique.Spine.1981; 6:211-216.
[20]Sato M, Asazuma T, Ishihara M, et al.An experimental study of the regeneration of the intervertebral disc with an allograft of cultured annulus fibrosus cells using a tissue-engineering method.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003 Mar 15; 28(6):548-553.
[21]Nerlich AG, Schleicher ED, Boos N. Immunohistologic markers for age-related changes of human lumbar intervertebral discs. Spine.1997;22: 2781-2795.
[22]Weiler C, Nerlich AG, Bachmeier BE, et al.Expression and distribution of tumor necrosis factor alpha in human lumbar intervertebral discs: a study in surgical specimen and autopsy controls.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(1):44-53; discussion 54.
[23]Liu GZ, Ishihara H, Osada R, et al. Nitric oxide mediates the Change of proteoglycan synthesis in the human lumbar intervertebral disc in response to hydrostatic pressure. Spine; 2001; 26:134-141.
[24]Genevay S, Finkh A, Mezin F, et al. Influence of cytokine inhibitors on concentration and active of MMP-1 and MMP-3 in disc herniation. Arthritis Res Ther, 2009, 11: R169.
[25]Sadowski T, Steinmeyer J.Effects of non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs and dexamethasone on the activity and expression of matrix metalloproteinase-1, matrix metalloproteinase-3 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 by bovine articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001; 9(5):407-415.
[26]Elfervig MK, Minchew JT, Francke E, et al. IL-1β Sensitizes Intervertebral Disc Annulus Cells to Fluid-Induced Shear Stress. J Cell Biochem.2001;82:290-298.
[27]Keller TS, Kosmopoulos V, Lieberman IH.Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty affect vertebral motion segment stiffness and stress distributions: a microstructural finite-element study.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(11):1258-1265.
[28]Kim JM, Shin DA, Byun DH, et al. Effect of bone cement volume and stiffness on occurrences of adjacent vertebral fractures after vertebroplasty. J Korean Neurosurg Soc.2012; 52 (5): 435-440. |