| [1]Hetdecke V,Ramov NG,Marx T,et al.Outcome in cloward anterior fusion for degenerative cervical spinal disease.Acta Neurochir. 2000;142(3):283-291.
[2]Sampath P,Bendebba M,Davis JD,et al.Outcome in patients with cervical radiculopathy,prospective multicenter study with indepentent clinical review.Spine.1999;24(6):591-597.
[3]Yonenobu K,Wada E,Tanaka T,et al.Japanese orthopaedic association cervical myelopathy evaluation questionnaire (JOACMEQ):Part 2.Endorsement of the alternative item.J Orthop Sci.2007;12(3):241-248.
[4]Vernon H,Mior S.The Neck Disability Index:A study of reliability and validity.J Manipulative Physiol Ther.1991;14(7): 409-415.
[5]Quan GM,Vital JM, Hansen S,et al.Eight-year clinical and radiological follow-up of the Bryan cervical disc arthroplasty. Spine.2011;36(8):639-646.
[6]Ikenaga M, Shikata J, Tanaka C.Long-term results over 10 years of anterior corpectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical myelopathySpine.2006;31(14):1568-1575.
[7]Papadopoulos EC, Huang RC, Girardi FP, et al.Three-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with plate fixation:radiographic and clinical results.Spine.2006;31(8):897-902.
[8]Kaiser MG, Haid RW, Subach BR, et al.Anterior cervical plating enhances arthrodesis after discectomvy and fusion with cortical allograft.Neurosurgery.2002;50(2):229-238.
[9]Joseph T, King J, John JM, et al.Muhimodal assessment after surgery for cervical spondylotic myelopathy.J Neurosurgery. 2005;2(5):526-534.
[10]Kim SW, Limson MA, Kim SB, et al.Comparison of radiographic changes after ACDF versus bryan disc athroplasty in sigle and bi-level cases.J Eur Spine. 2009; 18(2):218-231.
[11]Goffin J,Geusens E,Vantomme N,et al.Long-term follow-up after interbody fusion of the cervical spine.J Spinal Disord Tech.2004;17:79-85.
[12]Azmi H, Schlenk RP.Surgery for postarthrodesis adjacent-cervical segment degeneration.Neurosurg Focus. 2003;15:E6.
[13]Taha JM ,ZuccarelloM.Orion anterior cervical plate system. Neurosurgery.1996;38:607-610.
[14]Kansziora F,Pflugmacher R,Schafer J,et al.Biomechanical comparison of cercical spine interbody fusion cages.Spine. 2001;26:1850-1857.
[15]Kettler A, Wilke HJ,Dietl R,et al.Stabilizing effect of posterior lumbar interbody fusion cage befor and after cyclie lording.J Neurosurg.2000;92:87-92.
[16]Do Koh Y, Lim TH, Won You J, et al.A biomenchanical comparison of mosern anterior and posterior plate fixation of the cervial spine.Spine.2001;26:15-21.
[17]Lee KY, Siff TE, Heggeness MH,et al.Anterior locking screw plate fixtion for cervical spondylosis.Am J Orthop.2002;31: 27-30.
[18]Anderson PA, Saseo BC, Riew KD.Comparison of adverse events between the Bryan artificial cervical disc and anterior cervical artllrodesis.Spine.2008;33:1305-1312.
[19]王岩,肖嵩华,陆宁,等.颈人工椎间盘假体置换术的临床应用[J].中华外科杂志,2004,42(21):1333-1337.
[20]Hu N, Cunningharn BW, MeAfee PC, et al.Porous coated motion cervical disc replacement:a biomechanical,histomorphometric,and biologic wear analysis in a caprine model.Spine(phila pa1976).2006;31(15):1666-1673.
[21]Lehman R, Bevevino AJ, Brewer DD, et al.A systematic review of cervical artificial disc replacement wear characteristics and durability.Evid Based Spine Care J. 2012; 3(S1):31-38.
[22]Daniels AH, Riew KD, Yoo JU,et al.Adverse events associated with anterior cervical spine surgery.J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2008;16(12):729-738.
[23]Chin KR, Seale J, Butron V, et al.Postoperative cervical haematoma complicated by ipsilateral carotid thrombosis and aphasia after anterior cervical fusion: a case report. Case Rep Med. 2013; 2013:590639.
[24]王岩,白一冰,肖嵩华,等.颈椎病前路择期手术术后早期并发症分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2004,24(9):538-542.
[25]Thongtrangan I,Balabhadra RS,Kim DH.Management of strut graft failure in anterior cervical spine surgery. Neurosurg Focus. 2003;15(3):E4.
[26]陈雄生,贾连顺,曹师锋,等.颈椎前路手术的并发症[J].中华骨科杂志,2003,23(11):644-649.
[27]Koller H, Hempfing A, Acosta F, et al.Cervical anterior transpedicular screw fixation. Part I: Study on morphological feasibility, indications, and technical prerequisites.Eur Spine J. 2008; 17(4):523-538.
[28]夏展,赵兴,范顺武.颈椎前路手术并发食管瘘的诊治进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2011,31(4):384-386.
[29]Ardon H, Van Calenbergh F, Van Raemdonck D, et al.Oesophageal perforation after anterior cervical surgery:management in four patients.Acta Neurochir.2009; 151(4):297-302.
[30]Cannada LK, Scherping SC, Yoo JU, et al.Pseudarthrosis of the cervical spine:a comparison of radiographic diagnostic measures.Spine.2003;28:46-51.
[31]Gok B, Sciubba DM, McLoughlin GS, et al.Revision surgery for cervical spondylotic myelopathy:surgical results and outcome.Neurosurgery.2008;63:292-298.
[32]蒋富贵,瞿东滨,朱志刚,等.颈椎前路减压及内固定的解剖学问题[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2000,18(4):314-315. |
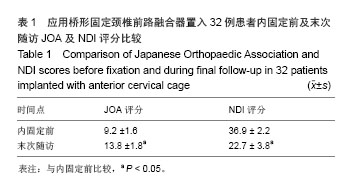
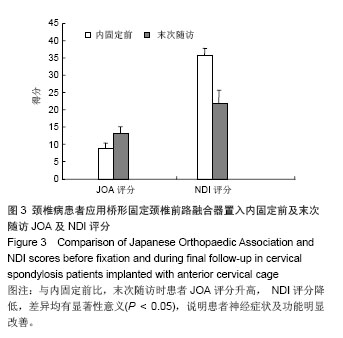
.jpg)
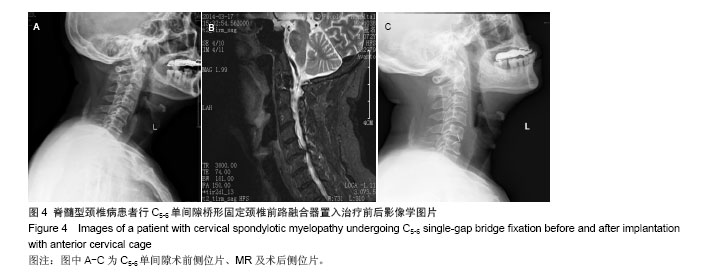
.jpg)