中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (44): 7111-7116.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.44.011
• 脊柱植入物 spinal implant • 上一篇 下一篇
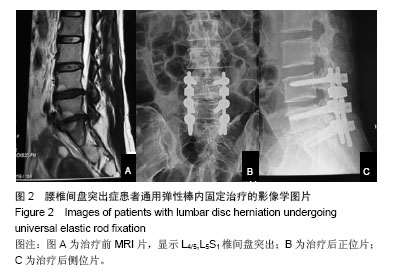
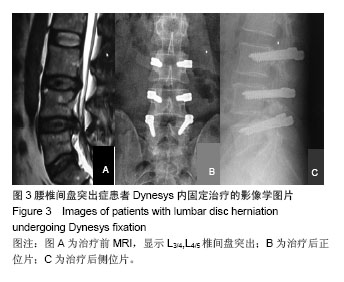
腰椎椎弓根动态内固定修复腰椎退行性疾病:K-Rod弹性棒、通用弹性棒及Dynesys系统比较
刘 涛,王振江,陈 凡,张大鹏,郭宁国,马方南,冯纪川,强晓军
- 濮阳市油田总院骨科,河南省濮阳市 457001
Dynamic lumbar pedicle fixation in repair of lumbar degenerative disease: K-Rod elastic rod, universal elastic rod and Dynesys system
Liu Tao, Wang Zhen-jiang, Chen Fan, Zhang Da-peng, Guo Ning-guo, Ma Fang-nan, Feng Ji-chuan, Qiang Xiao-jun
- Department of Orthopedics, Puyang Municipal Oil Field General Hospital, Puyang 457001, Henan Province, China
摘要:
背景:椎间盘摘除椎弓根内固定融合是修复腰椎退变疾病的金标准,但在治疗疾病的同时可引出来其他并发症,如邻近节段的退行性变或加剧已存在的脊柱退行性变等问题。针对腰椎融合固定的问题,近年来腰椎弹性固定成为一个热点。
目的:探讨腰椎椎弓根动态内固定修复腰椎管狭窄症和腰椎间盘突出症的近期疗效。
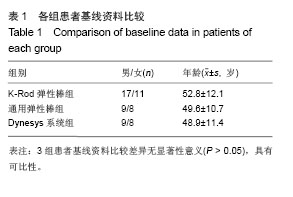
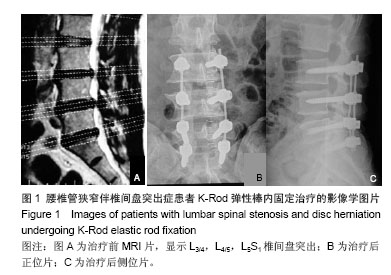
方法:2010年12月至2012年12月采用腰椎动态内固定系统共治疗腰椎管狭窄症和腰椎间盘突出症患者62例。L3,4节段5例;L4,5节段20例;L5S1节段20例;L3,4,L4,5双节段6例;L4,5,L5S1双节段8例,L3,4,5 S1三节段患者3例。男34例,女28例;年龄32-72岁,平均50.8岁。根据使用不同内固定系统分为3组,使用通用动态腰椎固定系统17例,K-Rod后路动态稳定系统28例,Dynesys系统17例。随访24-48个月,评价指标包括目测类比评分、Oswestry功能障碍指数、影像学分析及疗效优良率。
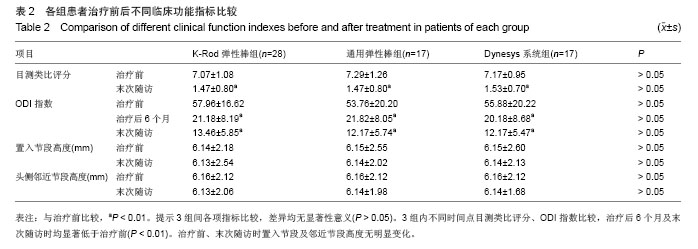
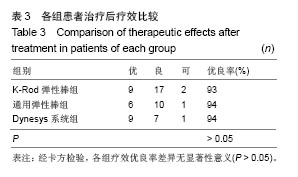
结果与结论:结果显示,与治疗前相比,治疗后6个月及末次随访时各组患者目测类比评分、Oswestry功能障碍指数均获得显著改善(P < 0.01)。治疗前、末次随访时置入节段及邻近节段高度无明显变化。治疗后各组疗效优良率差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。提示腰椎动态内固定系统是修复腰椎管狭窄症和腰椎间盘突出症的一种有效方法,3种弹性固定虽然存在结构的不同,但是早期治疗效果上无明显区别,远期效果有待进一步观察。
中图分类号: