| [1]Ma PX.Biomimetic materials for tissue engineering.Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2008;60(2):184-198.
[2]Metcalfe AD,Ferguson MWJ.Bioengineering skin using mechanisms of regeneration and repair. Biomaterials. 2007; 28(34):5100-5113.
[3]Luangbudnark W,Viyoch J,Laupattarakasem W,et al. Properties and biocompatibility of chitosan and silk fibroin blend films for application in skin tissue engineering.Scientific World J.2012;2012:697201.
[4]Locke M,Windsor J,Dunbar PR.Human adipose‐derived stem cells: isolation, characterization and applications in surgery.ANZ J Surg.2009;79(4):235-244.
[5]Shiffman MA,Mirrafatti S.Fat transfer techniques: the effect of harvest and transfer methods on adipocyte viability and review of the literature. Dermatol Surg.2001;27(9):819-862.
[6]Itoi Y,Takatori M,Hyakusoku H,et al.Comparison of readily available scaffolds for adipose tissue engineering using adipose-derived stem cells. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010;63(5):858-864.
[7]Kim EH,Heo CY.Current applications of adipose-derived stem cells and their future perspectives.World J Stem Cells. 2014; 6:65-68.
[8]Mizuno H,Tobita M,Uysal AC.Adipose-Derived Stem Cells as a Novel Tool for Future Regenerative Medicine.Stem Cells. 2014;12:165-174.
[9]陶忠芬,蔡永国,杨仕明,等.树突状细胞扫描电镜样本制备方法[J].第三军医大学学报,2005,27(12):1299-1300.
[10]朱晓琳,徐丽丽,杨乃龙.尿酸抑制人骨髓间充质干细胞的成脂分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(36):6669-6673.
[11]唐军,刘毅,徐斌.胰岛素基因转染的人脐带间充质干细胞与丝素蛋白支架构建组织工程脂肪的研究[J].中华医学美学美容杂志, 2012,18(4):277-281.
[12]邢昕,吕蓉,李素萍,等.体外分离培养人源性脂肪间充质干细胞及其鉴定[J].中国输血杂志,2013,26(8):708-712.
[13]Dyakonov T,Yang CH,Bush D,et al.Design and characterization of a silk-fibroin-based drug delivery platform using naproxen as a model drug.J Drug Deliv. 2012;2012: 490514.
[14]Cao Y,Wang B.Biodegradation of silk biomaterials.Int J Mol Sci. 2009;10(4):1514-1224.
[15]Ju HW,Sheikh FA,Moon BM,et al.Fabrication of poly (lactic-co-glycolic acid) scaffolds containing silk fibroin scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2013 Sep 11. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.34947. [Epub ahead of print]
[16]王宏昕,李敏.丝素蛋白作为组织工程生物材料的研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2008,28(2):192-194.
[17]Li SL,Liu Y,Hui L.Construction of engineering adipose‐like tissue in vivo utilizing human insulin gene‐modified umbilical cord mesenchymal stromal cells with silk fibroin 3D scaffolds. J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2013 Mar 19. doi: 10.1002/term. 1695. [Epub ahead of print]
[18]Bhardwaj N,Kundu SC.Silk fibroin protein and chitosan polyelectrolyte complex porous scaffolds for tissue engineering applications.Carbohydr Polym. 2011;85(2): 325-333.
[19]Bhardwaj N,Nguyen QT,Chen AC,et al.Potential of 3-D tissue constructs engineered from bovine chondrocytes/silk fibroin-chitosan for in vitro cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials.2011;32(25):5773-5781.
[20]杨久林,谢红国,于炜婷,等.组织工程用壳聚糖研究进展[J].功能材料,2013,44(11):1521-1525.
[21]Denga JH,Zhonga DC,Luoa XZ,et al.Syntheses, crystal structures and luminescent investigations of cobalt(II) and zinc(II) complexes with 2-propyl-4,5-dicarboxylate-imidazole (H3PIDC).Inorg Chem Commun.2013;36:249-252.
[22]Wei Y,Gong K,Zheng Z,et al.Chitosan/silk fibroin-based tissue-engineered graft seeded with adipose-derived stem cells enhances nerve regeneration in a rat model.J Mater Sci Mater Med.2011;22(8):1947-1964.
[23]Kim UJ,Park J,Kim HJ,et al.Three-dimensional aqueous-derived biomaterial scaffolds from silk fibroin. Biomaterials.2005;26(15):2775-2785.
[24]Lu Q,Huang Y,Li M,et al.Silk fibroin electrogelation mechanisms.Acta Biomater.2011;7(6):2394-2400.
[25]Tiyaboonchai W.Chitosan nanoparticles: a promising system for drug delivery.Naresuan Univ J.2013;11(3):51-66.
[26]Croisier F,Jérôme C.Chitosan-based biomaterials for tissue engineering. Eur Polym J.2013;49(4):780-792.
[27]Mauney JR,Nguyen T,Gillen K,et al.Engineering adipose-like tissue in vitro and in vivo utilizing human bone marrow and adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells with silk fibroin 3D scaffolds. Biomaterials.2007;28(35):5280-5290.
[28]Sterodimas A,de Faria J,Nicaretta B,et al.Tissue engineering with adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs): current and future applications.J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2010;63(11): 1886-1892. |

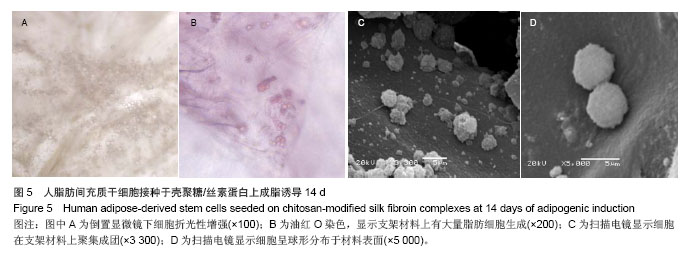
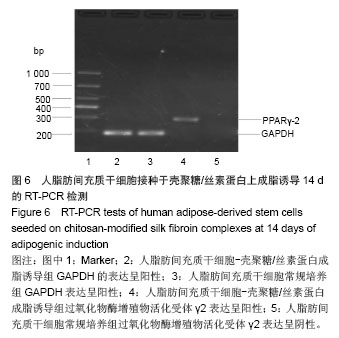
.jpg)