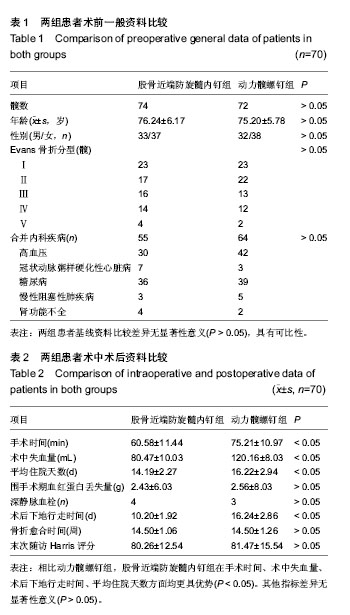
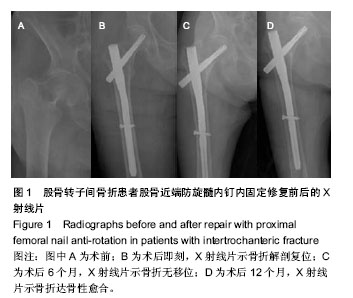
| [1] Zha GC, Chen ZL, Qi XB, et al. Treatment of pertrochanteric fractures with a proximal femur locking compression plate. Injury. 2011;42(11):1294-1299.
[2] 洪磊,吴克俭.手术与非手术治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折的疗效比较[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2013,12(8):605-611.
[3] 陈志军,闫固宁,杨元华,等.不同方法治疗老年股骨粗隆间骨折63例[J].中国老年学杂志,2013,33(23):6035-6036.
[4] 陈兴华,刘涛,黄珍谷,等.长、短股骨近端防旋髓内钉固定股骨转子间骨折的对比[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(4):595-600.
[5] 马洪良,彭军,陈懿,等.解剖型钢板与动力髋螺钉治疗股骨转子间骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(43):7602- 7609.
[6] 周强,陆骅,俞思明,等.动力髋结合转子稳定钢板与Gamma钉内固定治疗股骨转子间骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(9):1441-1452.
[7] 王亚平,路通.人工髋关节置换与股骨近端髓内钉治疗股骨转子间骨折的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(52):8961-8966.
[8] 王奔,葛振新,杨国跃,等.髓内与髓外固定修复股骨转子间骨折的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(4):736-743.
[9] 高延明,张路.防旋髓内钉与动力髋螺钉内固定治疗股骨转子间骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(13):2455-2462.
[10] 梅其伟,唐三元,杨辉.骨生化代谢指标和singh指数预测老年髋部骨折发生的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2013,21(2):140- 142.
[11] 戴克戎,俞昌泰,苑建新.股骨矩的解剖研究及其临床意义.中华骨科杂志,1983,3(2): 111-116.
[12] 朱俊昭,郑洪福,王福贵,等.手术治疗股骨矩碎裂的股骨颈骨折[J].创伤外科杂志,2006,8(2):135-135.
[13] Lin Z.Self-designed concical point contact plate and clinical application. Chin J Tramatol. 2001;4(1):44-47.
[14] 裴国献.任高宏.长管状骨骨折治疗进展[J].中华骨科杂志,2002, 4(1):10-14.
[15] Frigg R.Locking Compression plate(LCP).An osteo-synthesis plate based on the Dynamic Compression Plate and the Point Contact Fixator (PC-Fix). Injury. 2001;32(2):63-66.
[16] 李岩,王东,孙海钰,等.髓内与髓外系统骨钉置入治疗不稳定股骨转子间骨折的综合效果评价[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(35): 6254-6260.
[17] 周世伟,魏亦兵,张志玉,等.Gamma钉与滑动鹅头钉的生物力学测定与比较[J].中华骨科杂志, 1996, 16(4): 257.
[18] Chirodian N, Arch B, Parker MJ. Sliding hip screw fixation of trochanteric hip fractures: outcome of 1024 procedures.Injury. 2005;36(6): 793-800.
[19] 闫洪印, 陈扬.股骨粗隆间骨折早期内固定的手术治疗选择[J]. 骨与关节损伤杂志, 2002,17(2): 148.
[20] 刘奕,朱炯. DHS、PFN治疗高龄股骨粗隆间骨折的比较分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2007,15(12):913-914
[21] Peleg E,Mosheiff R,Liebeqall M. A short plate compression screw with diagonal bolts-a biomechanieal evaluation pedonned experimentally and by numerical computation. Clin Biomech.2006;21(9).963-968.
[22] 钱忠来,徐耀增,王现彬. 动力髋螺钉、股骨近端防旋髓内钉和第3代Gamma钉置入内固定后生物力学性能与临床效果的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(48):8974-8979.
[23] 唐佩福,姚琦,黄鹏.股骨近端髓内钉-螺旋刀片治疗高龄骨质疏松性股骨转子间骨折[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2007,9(7):622-624.
[24] Ho M,Garau G,Walley G. Minimally invasive dynamic hip screw for fixation of hip fractures.Int Orthop. 2009;33(2): 555-560.
[25] Bentler SE,Liu L,Obrizan M. The aftermath of hip fracture:discharge placement,functional status change,and mortality. Am J Epidemiol. 2009;170(10):1290-1299.
[26] Mereddy P, Kamath S, Ramakrishnan M. The AO/ASIF proximal femoral nail anti-rotation(PFNA): a new design for the treatment of unstable proximal femoral fractures. Injury. 2009; 40(4): 428-432.
[27] Pu JS, Liu L,Wang GL,et al.Result of the proximal femoral nail anti-rotation(PFNA) in elderly Chinese patients. Int Orthop. 2009;33(5): 1441. |