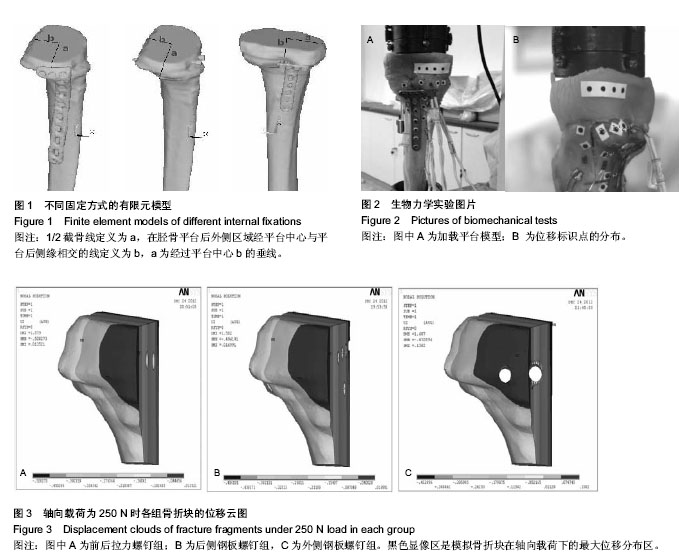
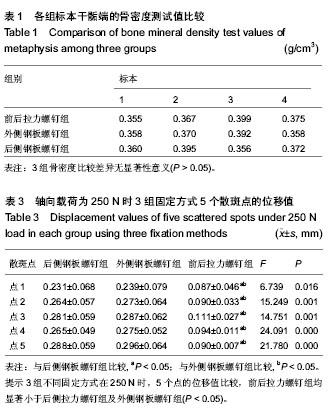
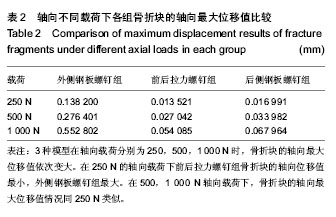
| [1] Piposar J, Fowler JR, Gaughan JP, et al. Race may not affect [correct] outcomes in operatively treated tibia fractures.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(5):1513-1517.
[2] Babis GC, Evangelopoulos DS, Kontovazenitis P, et al. High energy tibial plateau fractures treated with hybrid external fixation. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011;(14):35.
[3] Zura RD, Browne JM, Black MD,et al.Current management of high-energy tibial plateau fractures. Curr Orthop. 2007;21(3): 229-235.
[4] Papagelopoulos PJ, Partsinevelos AA, Themistocleous GS, et al. Complications after tibia plateau fracture surgery. Injury. 2006;37(6):475-484.
[5] Stauffer KD, Tuttle TA, Elkins AD, et al. Complications associated with 696 tibial plateau leveling osteotomies (2001-2003). J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 2006;42(1):44-50.
[6] Cross WW 3rd, Levy BA, Morgan JA, et al. Periarticular raft constructs and fracture stability in split-depression tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2013;44(6):796-801.
[7] Heikkilä JT, Kukkonen J, Aho AJ, et al. Bioactive glass granules: a suitable bone substitute material in the operative treatment of depressed lateral tibialplateau fractures: a prospective, randomized 1 year follow-up study. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22(4):1073-1080.
[8] Hsieh CH, Huang HT, Liu PC,et al. Anterior approach for posteromedial tibial plateau fractures. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2010;26(3):130-135.
[9] Luo CF, Hu CF, Gao H, et al. Three-column classification for tibial plateau fractures. Chin J Orthop Trauma 2009;11(3): 201-205.
[10] Luo CF, Sun H, Zhang B. Three-column fixation for complex tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2010;24(11): 683-692.
[11] Cooper HJ, Kummer FJ, Egol KA, et al.The effect of screw type on the fixation of depressed fragments in tibial plateau fractures. Bull Hosp Jt Dis. 2002;60:72-75.
[12] Ali AM, Yang L, Hashmi M, et al. Bicondylar tibial plateau fractures managed with the Sheffield Hybrid Fixator. Biomechanicalstudy and operative technique. Injury. 2001;32 Suppl 4:SD86-91.
[13] Ali AM, Saleh M, Bolongaro S, et al. The strength of different fixation techniques forbicondylar tibial plateau fractures-abiomechanical study. Clin Biomech. 2003; 18: 864-870.
[14] Yushkevich PA,Piven J, Hazlett HC,et al.User- guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency andreliabiity. Neurolmage. 2006;3:1116-1128.
[15] Sonoda N, Chosa E, Totoribe K,et al. Biomechanical analysis for stress fractures of the anterior middle third of the tibia in athletes:nonlinear analysis using a three-dimensional finite element method. J Orthop Sci. 2003;4:505-513.
[16] Lacroix D, Prendergast PJ. Three-dimensional simulation of fracture repair in the human tibia. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2002;5: 369-376.
[17] 龚璐璐,杨铁毅,张岩,等.LISS钢板治疗胫骨远端骨折有限元建模及分析[J].生物医学工程进展,2010, 31(1):12-17.
[18] 孙江波,廖怀章,蒋勇,等.胫骨平台后柱骨折钢板固定的三维有限元分析[J].临床医学研究,2012, 29(5):813-817.
[19] Sonoda N, Chosa E, Totoribe K,et al. Biomechanical analysis for stress fractures of the anterior middle third of the tibia in athletes:nonlinear analysis using a three-dimensional finite element method. J Orthop Sci. 2003;8:505-513.
[20] Meng L, Zhang Y, Lu Y. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of mini-external fixation and Kirschner wire internal fixation in Bennettfracture treatment. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013;99(1):21-29,
[21] Kantardzi? I, Vasiljevi? D, Blazi? L,et al. Influence of cavity design preparation on stress values in maxillary premolar: a finite element analysis. Croat Med J. 2012;53(6):568-576.
[22] Herrera A, Ibarz E, Cegoñino J, et al. Applications of finite element simulation in orthopedic and trauma surgery. World J Orthop. 2012; 3(4): 25-41.
[23] Liu XS, Wang J, Zhou B,et al. Fast trabecular bone strength predictions of HR-pQCT and individual trabeculae segmentation-based plate and rod finite element model discriminate postmenopausal vertebral fractures. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(7):1666-1678.
[24] Varga P, Schefzig P, Unger E, et al. Finite element based estimation of contact areas and pressures of the human scaphoid in various functional positions of the hand. J Biomech. 2013;46(5):984-990.
[25] Nishiyama KK, Macdonald HM, Hanley DA, et al. Women with previous fragility fractures can be classified based on bone microarchitecture and finite element analysis measured with HR-pQCT. Osteoporos Int. 2013;24(5):1733-1740.
[26] Miranda MA. Locking plate technology and its role in osteoporotic fractures. Injury.2007;38(9):Suppl 3:S35-39.
[27] Will R, Englund R, Lubahn J, et al. Locking plates have increased torsionalstiffness compared to standard plates in a segmental defect model of claviclefracture. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011;131(6):841–847.
[28] Jia YW, Cheng LM, Yu GR, et al. A finite element analysis of the pelvic reconstruction using fibular transplantation fixed with four different rod-screw systems after type I resection. Chin Med J. 2008;121(4):321-326.
[29] Graeff C, Marin F, Petto H,et al. High resolution quantitative computed tomography-based assessment of trabecular microstructure and strength estimates by finite-element analysis of the spine, but not DXA, reflects vertebral fracture status in men with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Bone. 2013;52(2):568-577.
[30] 张国柱,蒋协远,王满宜.CT扫描对胫骨平台骨折分型及治疗的影响[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2006,8(4):326-329.
[31] 谢祖宏,吕亮,胡汉敏,等.胫骨平台骨折后需早期康复锻炼但不宜过早负重锻炼[J].中国临床康复, 2002, 6(2): 238-239.
[32] Howard NE, Phaff M, Aird J,et al. Does human immunodeficiency virus status affect early wound healing in open surgically stabilised tibial fractures?: A prospective study. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(12):1703-1707.
[33] Uchiyama S, Itsubo T, Nakamura K,et al. Effect of early administration of alendronate after surgery for distal radial fragility fracture on radiological fracture healing time.Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(11):1544-1550.
[34] Matsunaga FT, Tamaoki MJ, Matsumoto MH, et al. Treatment of the humeral shaft fractures--minimally invasive osteosynthesis with bridge plate versus conservative treatment with functional brace: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2013;14:246.
[35] Urita A, Iwasaki N, Kondo M, et al. Effect of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on bone healing at osteotomy sites after forearm bone shortening. J Hand Surg Am. 2013;38(3): 498-503.
[36] Epari DR, Kassi JP, Schell H., et al. Timely fracture-healing requires optimization of axial fixation stability. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007:89(7):1575-1585.
[37] Guo LX,Teo EC,Qiu TX.Prediction of biomechanical characteristics of intact and injured lower thoracic spine segment under different loads. J Musculoskel Res. 2004;8: 87-99.
[38] 巴雪峰,孙改生,凯瑟尔.等. 胫骨平台骨折的治疗新进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(12):1104-1107.
[39] 冯卫,郝廷,郝增涛,等.3种股骨近端髓内钉固定股骨转子间骨折的有限元分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(8):730-733. |