中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (27): 4271-4276.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.27.002
• 器官移植动物模型 organ transplantation and animal model • 上一篇 下一篇
去卵巢骨质疏松模型大鼠小肠钙结合蛋白mRNA表达与菟丝子黄酮的干预
李小林1,武密山2,朱紫薇3,邓勇存3,叶圆圆3,赵素芝4,任立中5,李 彬6
- 1河北医科大学第二医院,河北省石家庄市 050000; 2河北中医学院基础医学院方剂学教研室,河北省石家庄市 050200;3河北中医学院2011级中医学专业,河北省石家庄市 050091; 4石家庄市桥东区胜北社区卫生服务中心,河北省石家庄市 050041;5河北医科大学第一医院骨科,河北省石家庄市 050031;6河北医科大学生物化学教研室,河北省石家庄市 050017
Effects of flavonoids from Cuscuta chinensis on intestinal calcium-binding protein mRNA expression in ovariectomized osteoporosis model rats
Li Xiao-lin1, Wu Mi-shan2, Zhu Zi-wei3, Deng Yong-cun3, Ye Yuan-yuan3, Zhao Su-zhi4, Ren Li-zhong5, Li Bin6
- 1 Second Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China; 2 Department of Prescriptions, Basic Medicine College, Hebei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050200, Hebei Province, China; 3 Department of 2011 Grade of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hebei University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shijiazhuang 050091, Hebei Province, China; 4 Qiaodong District Shengbei Community Health Center of Shijiazhuang, Shijiazhuang 050041, Hebei Province, China; 5 Department of Orthopedics, First Hospital, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050031, Hebei Province, China; 6 Department of Biochemistry, Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang 050017, Hebei Province, China
摘要:
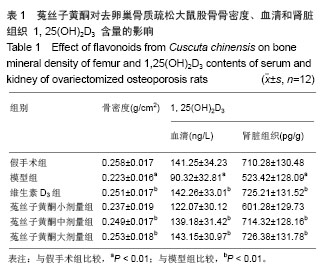
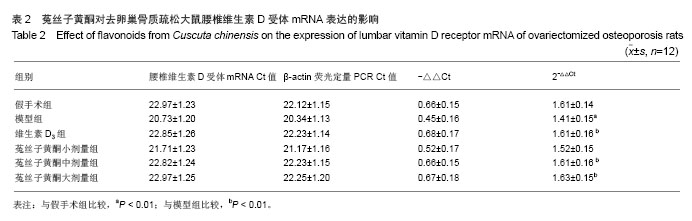
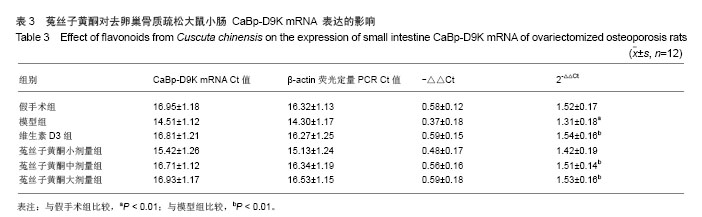
背景:菟丝子是旋花科植物菟丝子Cuscutachinensis Lam.的成熟种子,为温补肾阳的要药,前期研究表明,由菟丝子组成的补肾复方在抑制骨量丢失,改善骨密度方面有明显疗效。 目的:探讨菟丝子黄酮对去卵巢骨质疏松模型大鼠股骨骨密度、血清和肾脏1,25-二羟基维生素D3(1,25(OH)2 D3)含量、小肠钙结合蛋白(CaBp-D9K)mRNA表达的影响。 方法:72只SD雌性大鼠,随机数字表法均分为6组(n=12):假手术组、模型组、维生素 D3组和菟丝子黄酮小、中、大剂量组。假手术组仅行假手术,其余5组分别行卵巢切除,1周后分别灌胃给予维生素D3 (2 mg/kg)以及小、中、大剂量菟丝子黄酮连续给药3个月。腹主动脉取血,分离血清,取出肾脏,采用酶联免疫吸附法检测 1,25(OH)2 D3含量。之后处死动物,取出股骨,测定骨密度;取出第2腰椎,采用实时荧光反转录聚合酶链反应(real-time RT-PCR)测定腰椎和肾脏组织维生素D受体mRNA表达。取出小肠,采用RT-PCR测定小肠CaBp-D9K mRNA表达。 结果与结论:与假手术组相比,模型组股骨骨密度、血清和肾脏 1,25(OH)2 D3、腰椎组织维生素D受体mRNA、小肠CaBp-D9K mRNA表达均下降。与模型组比较,菟丝子黄酮中、大剂量组和维生素D3组均可使股骨骨密度、血清和肾脏1,25(OH)2 D3、腰椎组织维生素D受体mRNA、小肠CaBp-D9K mRNA表达增加。菟丝子黄酮能够显著提高去卵巢大鼠股骨骨密度、血清和肾脏1,25(OH)2 D3、腰椎组织维生素D受体mRNA、小肠CaBp-D9K mRNA表达,促进肠钙吸收与成骨细胞活性,增强骨质量。
中图分类号:
.jpg)