| [1] Freemont AJ. Review The cellular pathobiology of the degenerate intervertebral disc and discogenic back pain. Rheumatology (Oxford).2009;48(1):5-10.
[2] Videman T, Gibbons LE, Battié MC.Age- and pathology-specific measures of disc degeneration.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2008;33(25):2781-2788.
[3] Hadjipavlou AG, Tzermiadianos MN, Bogduk N,et al.The pathophysiology of disc degeneration: a critical review. J Bone Joint Surg Br.2008; 90(10):1261-1270.
[4] Costi JJ, Stokes IA, Gardner-Morse MG,et al. Frequency-dependent behavior of the intervertebral disc in response to each of six degree of freedom dynamic loading: solid phase and fluid phase contributions. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2008; 33(16):1731-1738.
[5] O'Connell GD, Guerin HL, Elliott DM.Theoretical and uniaxial experimental evaluation of human annulus fibrosus degeneration. J Biomech Eng.2009; 131(11):111007.
[6] Stokes IA,Iatridis JC.Review Mechanical conditions that accelerate intervertebral disc degeneration: overload versus immobilization. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(23): 2724-2732.
[7] Shirazi-Adl A,Taheri M,Urban JP.Analysis of cell viability in intervertebral disc: Effect of endplate permeability on cell population. J Biomech.2010; 43(7):1330-1336.
[8] Eskola PJ,Lemmelä S,Kjaer P,et al.Genetic association studies in lumbar disc degeneration: a systematic review. PLoS One.2012;7(11):e49995.
[9] Smith LJ, Kurmis AP, Slavotinek JP, et al.In vitro evaluation of a manganese chloride phantom-based MRI technique for quantitative determination of lumbar intervertebral disc composition and condition. Eur Spine J.2011; 20(3):434-439.
[10] Kettler A, Wilke H. Review of existing grading systems for cervical or lumbar disc and facet joint degeneration.Eur Spine J.2006;15(6):705-718.
[11] Antoniou J, Demers CN, Beaudoin G,et al.Apparent diffusion coefficient of intervertebral discs related to matrix composition and integrity.Magn Reson Imaging.2004;22(7): 963-972.
[12] Williams JR.The Declaration of Helsinki and public health. Bull World Health Organ.2008;86(8):650-652.
[13] Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, et al. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine.2001;26(17):1873-1878.
[14] Campana S,Charpail E, Guise J,et al.Relationships between viscoelastic properties of lumbar intervertebral disc and degeneration grade assessed by MRI.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater.2011;4(4):593-599.
[15] Sharp CA, Roberts S, Evans H, et al.Disc cell clusters in pathological human intervertebral discs are associated with increased stress protein immunostaining. Eur Spine J.2009; 18(11):1587-1594.
[16] Setton L, Chen J. Mechanobiology of the intervertebral disc and relevance to disc degeneration.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88(Suppl 2):52-57.
[17] Haefeli M, Kalberer F, Saegesser D, et al.The course of macroscopic degeneration in the human lumbar intervertebral disc. Spine.2006;31(14):1522-1531.
[18] Rajasekaran S, Babu JN, Arun R, et al. ISSLS prize winner: a study of diffusion in human lumbar discs: a serial magnetic resonance imaging study documenting the influence of the endplate on diffusion in normal and degenerate discs. Spine. 2004;29(23):2654-2667.
[19] Beattie PF, Morgan PS, Peters D. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of normal and degenerative lumbar intervertebral discs: a new method to potentially quantify the physiologic effect of physical therapy intervention. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther.2008;38(2):42-49.
[20] Antoniou J, Demers CN, Beaudoin G, et al.Apparent diffusion coefficient of intervertebral discs related to matrix composition and integ-rity. Magn Reson Imaging.2004; 22(7):963-972.
[21] Kealey SM, Aho T, Delong D, et al. Assessment of apparent diffusion coefficient in normal and degenerated intervertebral lumbar disks: initial experience. Radiology.2005; 235(2): 569-574.
[22] Anderson DG, Tannoury C.Molecular pathogenic factors in symptomatic disc degeneration.Spine J.2005;5(6):260-266.
[23] Roughley PJ.Biology of intervertebral disc aging and degeneration: involvement of the extracellular matrix. Spine.2004;29(23):2691-2699.
[24] Roberts S, Evans H, Trivedi J.Histology and pathology of the human intervertebral disc. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2006; 88(2):10-14.
[25] Urban JP, Winlove CP.Pathophysiology of the intervertebral disc and the challenges for MRI.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;25(2):419-432.
[26] Adams MA, McNally DS, Dolan P.‘Stress’ distributions inside intervertebral discs: the effects of age and degeneration. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1996;78(6):965-972.
[27] Brown MF, Hukkanen MV, McCarthy ID, et al.Sensory and sympathetic innervation of the vertebral endplate in patients with degenerative disc disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1997; 79(1):147-153.
[28] Ohtori S,Inoue G,Ito T,et al.Tumor necrosis factor-immunoreactive cells and PGP 9.5-immunoreactive nerve fibers in vertebral endplates of patients with discogenic low back pain and Modic type 1 or type 2 changes on MRI. Spine.2006; 31(9): 1026-1031.
[29] Ren J,Huan Y, Wang H,et al. Dynamic contrast -enhanced MR imaging of benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostatic carcinoma: correlation with angiogenesis. Clin Radiol.2008; 63(2): 153-159.
[30] Siemionow K, An H, Masuda K.The effects of age, sex, ethnicity, and spinal level on the rate of intervertebral disc degeneration: a review of 1712 intervertebral discs. Spine. 2011;8(17): 1333-1339.
[31] Boos N, Weissbach S, Rohrbach H, et al.Classification of age-related changes in lumbar intervertebral discs: 2002 Volvo Award in basic science. Spine. 2002;27(23):2631-2644.
[32] 徐宝山,杨强,夏群.腰椎间盘退变的分子病理学变化及发病机制[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复.2011,15(2):335-338.
[33] 王娟,周义成,夏黎明,等.使用ADC值评估正常及退变腰椎间盘的初步研究[J].医学影像学杂志. 2006,16 (10): 1093-1096.
[34] 郭家川,杨汉丰,杜勇,等. ADC值在腰椎间盘退行性变诊断中价值的初步研究[J].临床放射学杂志,2011, 30(2): 239-242.
[35] 常英娟,颜蕾,任静等,正常和变性腰椎间盘ADC值定量研究[J].国际医学放射杂志, 2011, 34(3):211-214.
[36] Keller TS, Colloca CJ,Harrison DD, et al.Influence of spine morphology on intervertebral disc loads and stresses in asymptomatic adults: implications for the ideal spine. Spine. 2005;5(3):297-309.
[37] Takatalo J,Karppinen J,Niinimäki J ,et al. Prevalence of degenerative imaging findings in lumbar magnetic resonance imaging among young adults. Spine. 2009; 34(16): 1716- 1721.
[38] Takatalo J, Karppinen J, Niinimäki J, et al.Association of modic changes, Schmorl's nodes, spondylolytic defects, high-intensity zone lesions, disc herniations, and radial tears with low back symptom severity among young Finnish adults. Spine.2012;37(14):1231-1239.
[39] Wang YX, Griffith JF, Ma HT. Relationship between gender, bone mineral density, and disc degeneration in the lumbar spine: a study in elderly subjects using an eight-level MRI-based disc degeneration grading system. Osteoporosis Int. 2011;22(1):91-96.
[40] Wang YX, Griffith JF.Effect of menopause on lumbar disk degeneration: potential etiology. Radiology. 2010; 257(2): 318-320. |
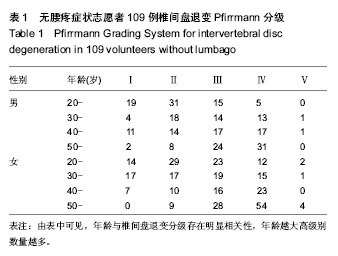
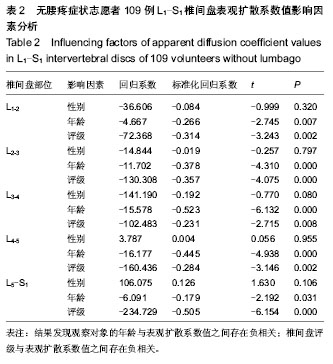
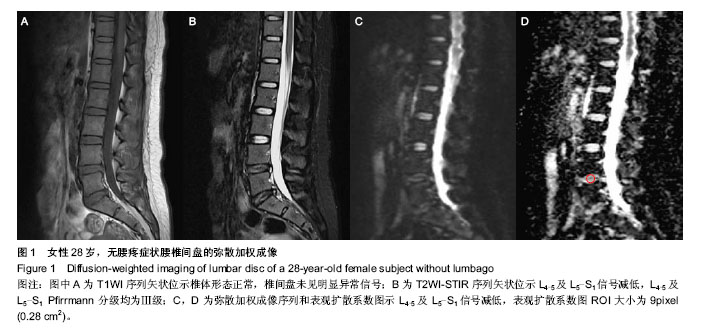
.jpg)