中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (15): 2421-2426.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.15.021
• 组织构建基础实验 basic experiments in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
弥散张量成像显示亚急性期脑梗死神经网络损伤及各运动参数分析
肖 湘1,2,李 乐1,吕衍春3,林 强1,黄东锋1
- 1中山大学附属第一医院康复医学科,广东省广州市 510080;2深圳市第五人民医院(罗湖区人民医院)康复医学科,广东省深圳市 518001;3中山大学附属肿瘤防治中心影像与微创介入中心,广东省广州市 510060
-
出版日期:2014-04-09发布日期:2014-04-09 -
通讯作者:黄东锋,教授,博士生导师,中山大学附属第一医院康复医学科,广东省广州市 510080 -
作者简介:肖湘,女,1976年生,湖南省益阳市人,汉族,2012年中山大学毕业,博士,主治医师,主要从事神经康复的研究。
Xiao Xiang 1, 2, Li Le1, Lv Yan-chun3, Lin Qiang1, Huang Dong-feng1
- 1 Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China;
2 Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, the Fifth People’s Hospital of Shenzhen (Shenzhen Luohu People’s Hospital), Shenzhen 518001, Guangdong Province, China; 3 Department of Imaging & Interventional Radiology, Cancer Center, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510060, Guangdong Province, China
-
Online:2014-04-09Published:2014-04-09 -
Contact:Huang Dong-feng, Professor, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Xiao Xiang, M.D., Attending physician, Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510080, Guangdong Province, China; Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, the Fifth People’s Hospital of Shenzhen (People’s Hospital in Luohu District), Shenzhen 518001, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 30973165
摘要:
背景:脑卒中后神经网络与运动功能的相关性尚未明确。 目的:应用磁共振弥散张量成像研究亚急性期脑梗死后神经网络受损情况,并分析其与神经功能缺陷及运动功能障碍的相关性。 方法:将19例亚急性期脑梗死患者和20名正常成人分别进行弥散张量成像检查,分析比较以下参数:各向异性分数、表观扩散系数和各向异性分数指数、表观扩散系数指数。同时对患者进行神经功能缺损和运动功能的各项量表评估,检测10 m步行速度。将脑梗死患者弥散张量成像的各项参数与各项量表及10 m步行速度进行相关性分析。 结果与结论:脑梗死患者各向异性分数指数和双侧内囊后肢的各向异性分数值均小于正常对照,且患侧内囊后肢的各向异性分数值小于健侧内囊后肢的各向异性分数值(P < 0.05)。患侧内囊后肢的表观扩散系数值、表观扩散系数指数大于正常对照内囊后肢的表观扩散系数值和表观扩散系数指数(P < 0.05)。患侧内囊后肢的表观扩散系数值、表观扩散系数指数与下肢Fugl-Meyer评分呈负相关(P < 0.05)。提示弥散张量成像参数与下肢运动功能障碍密切相关。脑卒中后的局灶性病变造成神经网络缺损,是下肢运动功能障碍的主要原因。
中图分类号:
引用本文
肖湘,李乐,吕衍春,林强,黄东锋. 弥散张量成像显示亚急性期脑梗死神经网络损伤及各运动参数分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(15): 2421-2426.
Xiao Xiang, Li Le, Lv Yan-chun, Lin Qiang, Huang Dong-feng. null[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(15): 2421-2426.
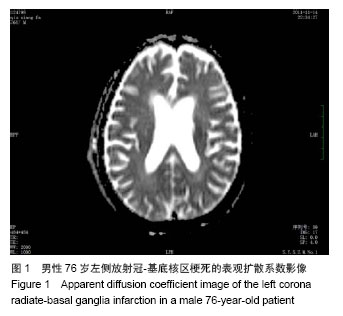
2.3 患者的临床特征 脑梗死患者平均病程(40.89± 15.87) d,左侧偏瘫10例,右侧偏瘫9例,皮质下梗死14例,皮质+皮质下梗死5例(表2);典型病例放射冠-基底核区梗死的表观扩散系数影像见图1。
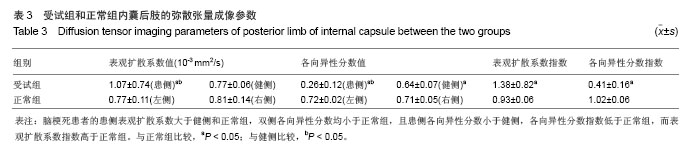
2.4 患者的弥散张量成像数据 正常组双侧内囊后肢的各向异性分数值和表观扩散系数值差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。脑梗死患侧内囊后肢的各向异性分数值小于健侧内囊后肢的各向异性分数值(P < 0.05),且患侧和健侧内囊后肢各向异性分数值均小于正常组双侧内囊后肢的各向异性 分数值(P < 0.05)。患者患侧内囊后肢的表观扩散系数值大于健侧内囊后肢和正常组双侧内囊后肢的表观扩散系数值(P < 0.05)。脑梗死患者的各向异性分数指数低于正常组,而表观扩散系数指数高于正常组(P < 0.05),见表3。
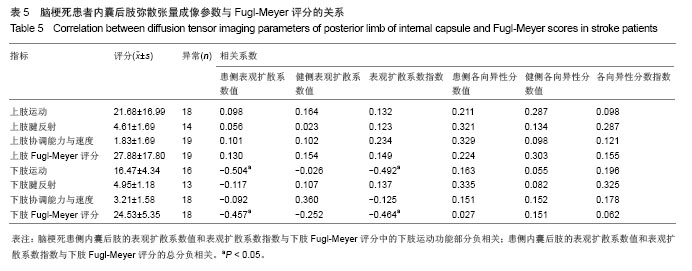
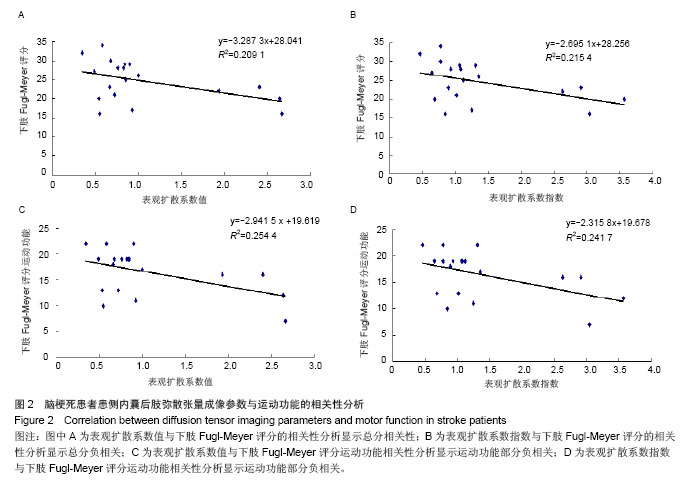
2.5 患者弥散张量成像参数与运动功能的相关性分析 脑梗死患者内囊后肢弥散张量成像参数与神经功能损伤 (NIHSS)无相关性(表4)。脑梗死患侧内囊后肢的表观扩散系数值和表观扩散系数指数与下肢Fugl-Meyer评分的总分负相关(分别为r=-0.457,P=0.049和r=-0.464,P=0.045,表5,图2A,B),而与改良Ashworth评分、Brunel平衡、步行速度、上肢Fugl-Meyer评分无相关性(P > 0.05)。患侧内囊后肢的表观扩散系数值和表观扩散系数指数与下肢Fugl-Meyer评分中的下肢运动功能部分负相关(分别为r=-0.504,P=0.028和r=-0.492,P=0.033,表5,图2C,D),与下肢Fugl-Meyer评分的下肢协调能力与速度、下肢腱反射无相关性。健侧表观扩散系数值、健侧各向异性分数值、患侧各向异性分数值和各向异性分数指数与运动功能的各项参数均无相关性(P > 0.05)。
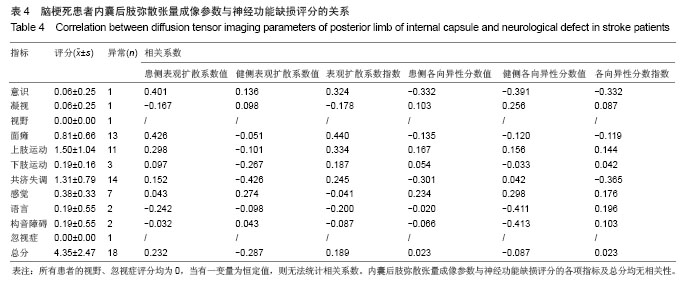
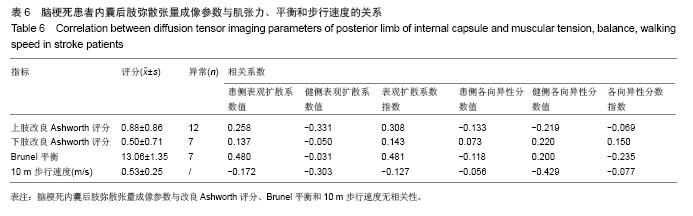
2.6 脑梗死内囊后肢弥散张量成像参数与肌张力、平衡和步行速度的关系 脑梗死内囊后肢弥散张量成像参数与改良Ashworth评分、Brunel平衡和10 m步行速度无相关性(表6)。
| null |
| [1] | 陈子扬, 蒲 锐, 邓 爽, 袁凌燕. 外泌体对运动介导胰岛素抵抗类疾病的调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | 陈 扬, 黄邓高, 高元慧, 王顺兰, 曹 卉, 郑琳麟, 何浩伟, 罗思琴, 肖敬川, 张应爱, 张淑芳. 低强度脉冲场超声促进人脂肪间充质干细胞的增殖和黏附[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [3] | 杨俊辉, 罗金莉, 袁小平. 人生长激素对人牙周膜干细胞增殖及成骨分化的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3956-3961. |
| [4] | 孙建威, 杨新明, 张 瑛. 孟鲁司特联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤模型大鼠[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3962-3969. |
| [5] | 高 珊, 黄东静, 洪海漫, 贾京桥, 孟 斐. 人胎盘间充质干细胞及诱导的胰岛样细胞移植治疗妊娠期糖尿病大鼠效果比较#br#[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [6] | 郝晓娜, 张英杰, 李玉云, 许 涛. 过表达脯氨酰寡肽酶的骨髓间充质干细胞修复肝纤维化模型大鼠[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(25): 3988-3993. |
| [7] | 刘建友, 贾中伟, 牛佳伟, 曹鑫杰, 张 栋, 魏 杰. 构建股骨3D数字化模型提出一种新的股骨颈前倾角测量方法[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3779-3783. |
| [8] | 孟令杰, 钱 辉, 盛晓磊, 陆剑锋, 黄建平, 祁连港, 刘宗宝. 3D打印建模联合骨水泥成形微创治疗塌陷Sanders Ⅲ型跟骨骨折[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [9] | 钱选昆, 黄合飞, 武成聪, 刘克廷, 欧 华, 张金鹏, 任 静, 万建杉. 计算机导航微创经椎间孔腰椎椎间融合治疗腰椎滑脱[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3790-3795. |
| [10] | 胡 靖, 向 阳, 叶 川, 韩子冀. 3D打印辅助与徒手置钉经皮椎弓根钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的1年随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
| [11] | 舒启航, 廖亦佳, 薛静波, 晏怡果, 王 程. 新型颈椎3D打印多孔椎间融合器的三维有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3810-3815. |
| [12] | 王一寒, 李 杨, 张 玲, 张 睿, 徐瑞达, 韩晓峰, 程光齐, 王伟力. 数字骨科三维可视化技术在股骨转子间骨折复位内固定中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3816-3820. |
| [13] | 孙玛骥, 王秋安, 张星晨, 郭 冲, 袁 峰, 郭开今. 新型颈椎前路经椎弓根固定钉板系统的研制及生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3821-3825. |
| [14] | 林 旺, 王盈盈, 郭卫中, 袁翠华, 许胜贵, 张申申, 林成寿. 胫骨平台后外侧柱骨折扩大外侧入路内固定增强力学稳定性及膝关节功能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3826-3827. |
| [15] | 朱 云, 陈 渝, 邱 皓, 刘 盾, 靳国荣, 陈诗谋, 翁 政. 对侧皮质锁定螺钉治疗骨质疏松股骨骨折的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3832-3837. |
设计:病例-对照分析。
脑卒中后神经网络重塑可发生于病灶对侧。动物模型显示脑卒中后健侧皮质脊髓束轴突出芽并投射入失神经支配的脊髓[15] 。DTI研究证实脑卒中后健侧皮质脊髓束纤维数量增多[16] 。有研究显示脑卒中后遗症期患侧内囊后肢的各向异性分数值低于正常对照,健侧内囊后肢的各向异性分数值与正常对照无差异,各向异性分数不对称性高于正常对照[17] ,也有研究显示后遗症期脑卒中患者双侧内囊后肢的各向异性分数值均下降[18] 。健侧各向异性分数值下降预示着较好的功能恢复[19] 。本组中患者双侧内囊后肢的各向异性分数值均低于正常,提示早期脑梗死患者健侧可能存在着代偿性纤维重塑。
脑卒中后病灶累及皮质脊髓束导致患者运动功能障碍在临床上较为常见。病灶的大小、病灶与皮质脊髓束的相对位置及皮质和皮质下的连通性是影响脑卒中功能结局的因素[17,20] 。下肢Fugl-Meyer评分可综合评估下肢的运动控制能力和平衡协调能力。本组结果显示表观扩散系数指数和患侧内囊后肢的表观扩散系数值与下肢Fugl-Meyer评分负相关,且表观扩散系数指数和患侧内囊后肢的表观扩散系数值与Fugl-Meyer评分中的协调能力及腱反射无相关性,与运动功能部分(包括下肢屈肌协同运动、伸肌协同运动、伴有协同运动的活动和脱离协同运动的活动)负相关。表观扩散系数值和表观扩散系数指数增高均与白质缺血导致细胞膜或髓鞘受损有关。而下肢运动功能与表观扩散系数值和表观扩散系数指数负相关提示下肢运动功能障碍可能是神经网络缺损所致,弥散张量成像可协助评估早期脑梗死患者的下肢运动功能。
有研究显示脑部小血管病患侧表观扩散系数值与步行速度负相关,各向异性分数值与步行速度正相关,且表观扩散系数值与步行速度的相关性大于各向异性分数值与步行速度的相关性[21] 。急性期皮质下脑梗死患者的各向异性分数指数与上肢Rivermead运动功能试验评分正相关[5] ,后遗症期性脑卒中患者健侧内囊后肢的各向异性分数值与患者上肢Fugl-Meyer评分正相关[18] ,各向异性分数不对称性与下肢Fugl-Meyer评分和步行速度负相关[22] 。本研究中,各向异性分数值和各向异性分数指数与Fugl-Meyer评分、步行速度无相关性,表观扩散系数值与步行速度也无相关性,可能与研究的对象为亚急性期脑梗死,研究对象的年龄、病情、病变部位与以上研究不同有关。
弥散张量成像可动态观察脑卒中后病灶周围组织的结构重塑以及白质通路连接的恢复[23-25] 。最近有研究发现早期脑卒中患者的各向异性分数值与康复训练前后Fugl-Meyer评分的变化值呈正相关[26] ,训练前病灶中心与健侧对应区的表观扩散系数值接近对称的患者下肢Fugl-Meyer评分改善明显[27] 。皮质脊髓束完整性的损害与脑卒中患者上肢残余运动系统的重组相关[28] 。因此,可进一步利用弥散张量成像追踪患者对康复训练的反应性。
结论:实验显示内囊后肢表观扩散系数值与下肢运动功能有相关性。认为脑梗死后的局灶性病变造成神经网络缺损,可能是下肢运动功能障碍的主要原因。
null
黄东锋2012年应用功能性磁共振研究脑卒中后神经网络受损情况。应用三维运动分析对比下肢步行功能改变结局的关系。11例亚急性期脑梗死患者接受功能性磁共振的弥散张量成像和扩散加权成像,并做三维步态检查,比较中枢神经损伤与肢体运动改变的关系。同时还应用量表对入组患者进行肢体运动功能、平衡及生存质量进行评估。结果:脑卒中患者皮质脊髓束皮质放射纤维部分各向异性(FA)值患侧明显小于健侧(P<0.05),而表观扩散系数两侧差异无显著性。脑卒中患侧各向异性值与患侧步时相关系数为0.615,存在正相关关系。运动功能结局的分析显示各向异性与步时相关。各向异性值与各项量表评分无明显相关性。提示脑卒中后皮质脊髓束的受损可一定程度由各向异性值反映,对监测其病程有一定价值,而表观扩散系数结果则没有显著性意义。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||