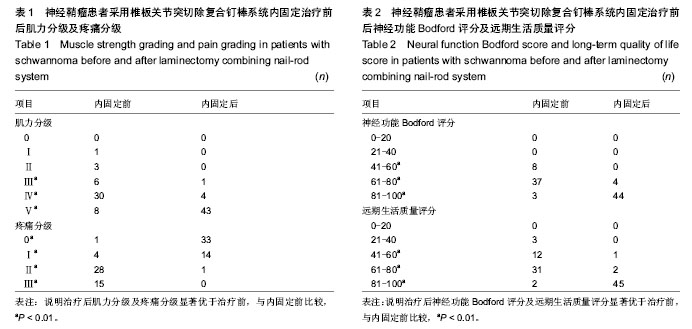
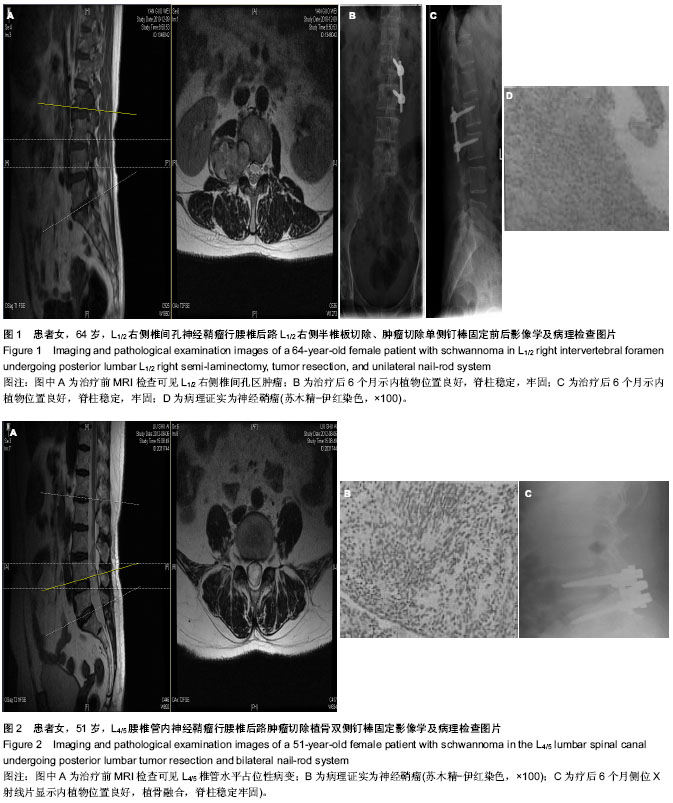
| [1] Seppala MT,Haltia MJ,Sankila RJ,et al.Long-term outcome after removal of spinal schwannoma: a clinicopathological study of 187 cases.J Neurosurg.1995;83(4):621-630.[2] 王书中.椎管内神经鞘瘤的MRI诊断[J]. 实用医学杂志,2006,18 (22):2149-2150.[3] 汤永祥,张金平,王成道.椎管内神经鞘瘤的MRI诊断[J].上海医学影像,2001,10(4):254-257.[4] 田锦林,王宁,张林医,等.MRI增强对椎管内神经鞘瘤的诊断价值[J].医学影像学杂志,2004,14(5):354-356.[5] Slin’ko EI,Al-Qashqish II.Intradural ventral and ventrolateral tumors of the spnial cord:surgical treatment and results. Neurosurg Focus.2004;7(1):ECP2.[6] 贾连顺.现代脊柱外科学[M].人民军医出版社,2007:489.[7] 冯正仪.内科护理学[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2001:272. [8] 谭冠先.疼痛诊疗学[M].北京:人民卫生出版社,2001.[9] Crooks V, Waller S, Smith T, et al. The use of the Karnofsky Performance Scale in determining outcomes and risk in geriatric outpatients. J Gerontol.1991;46(4):M139-44.[10] Hussein AA,E1-Karef E,Hafez M.Reconstruction Surgery In Spinal Tumors.EurJ Surg Oncol.2001;27(2):196-199.[11] 张小卫,尹战海,李萌,等.颈椎恶性肿瘤的手术治疗分析[J].现代肿瘤医学,2010,18(12) : 2459-2460. [12] 任斌,蔡林,王建平,等.后路椎板切除入路手术治疗椎管内神经鞘瘤的疗效.[J].中国脊柱肿瘤杂志,2012,22(8):688-692.[13] 马乐群,徐亮,王多,等.显微手术治疗脊椎管硬膜内肿瘤[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2004,9(7):298-299.[14] 谢京城,王振宇,马长城.改良椎板成形术在颈椎管内肿瘤切除术中的应用[J].中华外科杂志,2008,24(2):117.[15] Lida Y.Postoperation lumbar spinal instability occurring on progressing secondary to laminectomy.Spine. 1990; 15(11):1186-1189.[16] Denis.The three coloumn spine and its significance in the classification of acute thoracolumbar spinal injuries.Spine. 1983;8(8):817-831.[17] Gihara S,seichiA,IwasakiM,et al.Concurrent spinal Schwannomas and meningiamas Case illastration. Neurosurg. 2003;98(3):300-306.[18] O’Toole JE,McCormick PC.midline wentral intradural schwannnoma of the cervical Spinal cord resected via anterior corpectomy with reconstruction:technical case report and review of the literature.Neurosurgery.2003;52(6): 1482-1486.[19] 龙厚清,刘少喻,陈坚,等.良性椎管内肿瘤的诊断和手术治疗[J].中国骨肿瘤骨病,2005,4(2):79-83.[20] 赵学凌,王兵,黄河,等.颈椎侧块钢板在颈椎管内外肿瘤手术中的应用[J].中华神经医学杂志,2005,4(5):500-502.[21] Kawahara N,Tomita K,Shinya Y.et al.Recapping T-saw lamioplasty for spinal cord tumors.Spine.1999;24:1363-1370.[22] McCullen GM,Garfin SR.Spine update:cervical spine internal fixtion using screw and screw-plate constucts.Spine. 2000;25: 643-652.[23] Sridhar K,Ramamurthi R,Vasudevan MC,et al. Giant invasive spinal schWannomas: definition and surgical management. J Neurosurg.2001;94(2 Supple):210.[24] 谭颖,刘少喻,李浩淼,等.胸椎椎弓根钉内固定治疗胸椎管内髓外62例体会[J],脊柱外科杂志,2012,10(4):251-252.[25] 蒋兵.钉棒内固定系统在椎管内肿瘤切除术的应用[J].健康必读, 2013,12(10):239-240.[26] 祝斌,刘晓光,姜亮.脊柱哑铃型肿瘤的分型与治疗进展[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(8):696-699.[27] Schuhheiss R,Gullotta G.Resection of relevant nerve roots in surgery of spinal neurinomas without persisting neurological deficit.Acta Neurochir(Wien).1993;122(1-2):91-96.[28] Hussein AA,EL-Karef E,Hafez M.Reconstructive surgery in spinal tumors.Eur J Surg Oncol.2001;27(2):196-199.[29] 朱若夫.颈椎椎弓根内固定术的基础和临床研究[D].苏州大学, 2008.[30] 朱江,季烈峰,曹浙标.Ⅰ期经后路椎板切除治疗上颈椎椎管内肿瘤[J].浙江创伤外科,2012,17(6):795-797.[31] 高方友,王曲,刘窗溪,等.颈段椎管内外“哑铃”形肿瘤的Ⅰ期显微手术疗效初步探讨[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志,2013,13(7): 636-640.[32] 陈永杰,陈赞,菅凤增.脊髓功能区神经鞘瘤手术治疗[J].中国现代神经疾病杂志,2013,13(11):931-935[33] 杨兴海,肖建如,吴志鹏,等.上颈段哑铃形肿瘤的外科治疗策略[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2010,2(3):186-190.[34] 郭卫,汤小东,李大森,等.全骶骨切除术治疗骶骨多节段恶性肿瘤[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010,20(6):472-476.[35] 秦晓平.腰椎管内神经鞘膜瘤1例分析[J].中国误诊学杂志,2011, 11(23):5669-5669.[36] 谢京城,王振宇,林国中,等.经后路一期手术切除腰椎管哑铃型肿瘤[J].中华神经外科杂志,2012,28(6):572-576.[37] 杨强,李建民,杨志平,等.全脊椎整块切除术治疗胸腰椎肿瘤及稳定性重建结果[J].中华肿瘤杂志,2013,35(3):225-230.[38] 陈赞,菅凤增,叶明,等.一期显微手术切除椎管内外沟通性哑铃型肿瘤(附13例分析)[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2007,12(11): 491-493.[39] 李强,李如求,王建波.椎管内神经鞘瘤的诊断和手术治疗分析[J].中国现代手术学杂志,2009,13(4):284-285.[40] 肖建如,杨兴海,陈华江,等.颈椎管哑铃形肿瘤的外科分期及手术策略[J].中华骨科杂志,2006,26(12):798-802.[41] 周政,杨辉,安宁,等.颈椎肿瘤的诊断及显微外科治疗[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2004,9(7):298-299. |