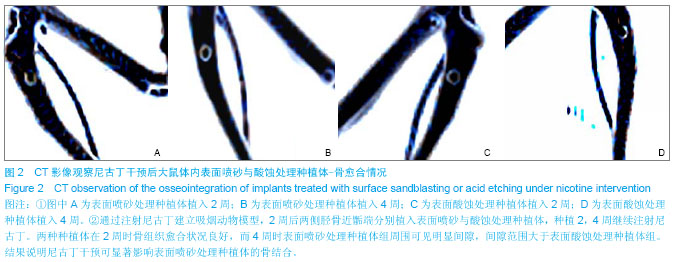
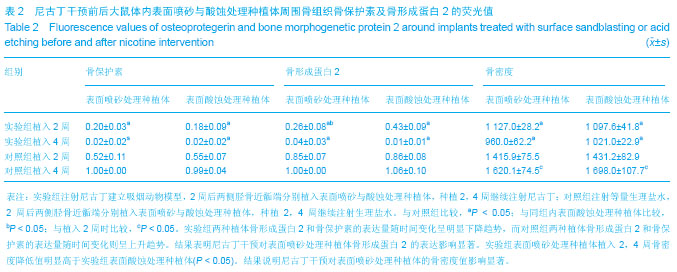
| [1] Wu K,Song W,Zhao L,et al.MicroRNA Functionalized Microporous Titanium Oxide Surface by Lyophilization with Enhanced Osteogenic Activity.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(7):2733-2744. [2] Akin H,Guney U.Effect of various surface treatments on the retention properties of titanium to implant restorative cement.Lasers Med Sci.2012;27(6):1183-1187. [3] Aparicio C,Manero JM,Conde F,et al.Acceleration of apatite nucleation on microrough bioactive titanium for bone-replacing implants.J Biomed Mater Res. 2007;82: 521-529. [4] Prodanov L,Lamers E,Domanski M,et al.The effect of nanometric surface texture on bone contact to titanium implants in rabbit tibia. Biomaterials. 2013;34(12):2920- 2927. [5] Zhang F,Zhang CF,Yin MN,et al.Effect of heat treatment on H2O2/HCl etched pure titanium dental implant:an in vitro study.Med Sci Monit.2012;18(7):265-272. [6] Yamada M,Ueno T,Minamikawa H,et al.Early-stage osseointegration capability of a submicrofeatured titanium surface created by microroughening and anodic oxidation. Clin Oral Implants Res.2013;24(9):991-1001. [7] Akhter MP,Lund AD,Gairola CG.Bone biomechanical property deterioration due to tobacco smoke exposure.J Bone Miner Res.2005;77(5):319-326. [8] Korpelainen R,Korpelainen J,Heikkinen J,et al.Lifelong risk factors for osteoporosis and fractures in elderly women with low body mass index-A population-based study.Bone.2006; 39(2): 385-391. [9] Silcox D, Daftari KT,Bodden MK,et al.The effect of nicotine on spine fusion.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).1995;20:1594-1553. [10] Sherwin M,Gastwirth C.Detrimental effects of cigarette smoking on lower extremity wound healing.J Foot Surg.1990;29:84-87. [11] Raikin SM,Landsman JC,Alexander VA,et al.Effect of nicotine on the rate and strength of long bone fracture healing. Clin Orthop Relat Res.1998;353:231-237. [12] Alzoubi KH,Srivareerat M,Tran TT,et al.Role of α7- and α4β2-nAChRs in the neuroprotective effect of nicotine in stress-induced impairment of hippocampus-dependent memory.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol.2013;16(5):1105-1113. [13] Berley J,Yamano S,Sukotjo C.The effect of systemic nicotine on osseointegration of titanium implants in the rat femur.J Oral Implantol. 2010;36(3):185-193.[14] 刘献文,逯素芬,于爱兰,等.改良尼古丁依赖_戒断大鼠模型的建立与疼痛敏感性观察[J].国际麻醉学与复苏学杂志,2013,34(7):591-640.[15] Malin DH,Lake JR,Newlin-Maultsby P,et al.Rodent model of nicotine abstinence syndrome.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1992;43(3):779-784.[16] Duarte PM,de Mendonga AC,Maximo MB,et al.Differential cytokine expressions affect the severity of peri-implant disease. J Clin Oral Implants Res.2009;20(5):514-520. [17] Hofbauer LC,Khosla S,Dunstan CR,et al.The roles of osteoprotegerin and osteoprotegerin ligand in the paracrine regulation of bone resorption.J Bone Miner Res.2000;15(1): 2-12.[18] Derynck R,Zhang Y.Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways in TGF-beta family signaling.Nature. 2003;425(6958):577-584. [19] Schmierer B,Hill CS.TGF beta-SMAD signal transduction: molecular specificity and functional flexibility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.2007;8(12):970-982.[20] Akin H,Guney U.Effect of various surface treatments on the retention properties of titanium to implant restorative cement.Lasers Med Sci.2012;27(6):1183-1187. [21] 孙轲,侯玉东.烟草浸提液对牙龈成纤维细胞在钛板上粘附增殖的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2009,25(1):80-83. [22] 侯玉东,沈建英,王桂龙,等.烟草浸提液对大鼠成骨细胞在钛板上附着和增殖的影响[J].实用口腔医学杂志, 2011,27(1):17-20.[23] Egger P,Duggleby S,Hobbs R,et al.Cigarette smoking and bone mineral density in the elderly.J Epidemiol Community Health.1996;50:47-50.[24] Lemons JE,Laskin DM,Roberts WE,et al.Changes in patient screening for a clinical study of dental implants after increased awareness of tobacco use as a risk factor.J Oral Maxillofac Surg.1997;55:72-75. [25] Yamano S,Berley JA,Kuo WP,et al.Effects of nicotine on gene expression and osseointegration in rats.Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21(12):1353-1359. [26] Pereira ML,Carvalho JC,Peres F,et al.Simultaneous effects of nicotine, acrolein, and acetaldehyde on osteogenic-induced bone marrow cells cultured on plasma-sprayed titanium implants.Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants.2010;25(1):112-122. [27] Hoffmann D,Hoffmann I.The musculoskeletal effects of smoking.J Am Acad Orthop Surg.2001;9:9-17. |