中国组织工程研究 ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (7): 1003-1008.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.07.004
• 软骨组织构建 cartilage tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
不同分期骨关节炎滑膜细胞中COX-2 mRNA表达的差异
曾明珠1,段 戡2,袁长深2,梅其杰2,秦 凯3
- 1广西自治区骨伤医院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530012
2广西中医药大学第一附属医院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530023
3广西中医药大学研究生学院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530001
COX-2 mRNA expression at different stages of osteoarthritis synoviocytes
Zeng Ming-zhu1, Duan Kan2, Yuan Chang-shen2, Mei Qi-jie2, Qin Kai3
- 1Orthopedics Hospital of Guangxi Autonomous Region, Nanning 530012, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
2The First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
3Graduate School, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:
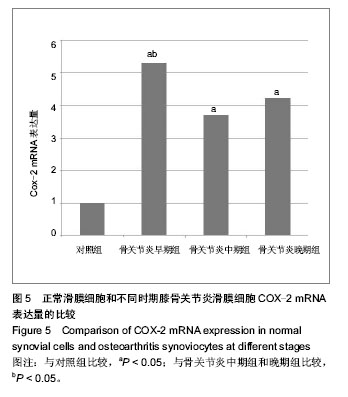
背景:COX-2基因实际存在于关节成纤维样滑膜细胞里,影响骨关节炎症的发生、发展。阐明不同分期骨关节炎滑膜细胞中COX-2基因表达量的差异对进一步深入了解骨关节炎的发生与发展,以及滑膜细胞在这一过程中的作用,具有重要的理论意义。 目的:分析COX-2 mRNA在不同分期骨关节炎成纤维样滑膜细胞中表达的差异。 方法:收集膝骨关节炎病变滑膜44例及正常滑膜12例,经原代细胞培养生长至4代的成纤维样滑膜细胞用于实验,应用实时荧光定量RT-PCR检测骨关节炎和正常成纤维样滑膜细胞中COX-2 mRNA的表达情况,最后使用2-ΔΔCt方法进行相对定量分析。 结果与结论:COX-2 mRNA在骨关节炎的成纤维样滑膜细胞中的表达明显高于正常成纤维样滑膜细胞 (P < 0.05),其中骨关节炎早期组表达最高,与骨关节炎中期组、晚期组比较差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05),骨关节炎中期组与晚期组中表达量差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。结果说明COX-2mRNA可能是骨关节炎症病变过程中的重要生物学指标,且主要起作用于骨关节炎病变早期。
中图分类号:
.jpg)