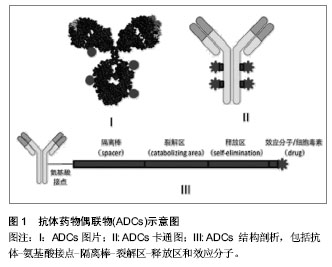
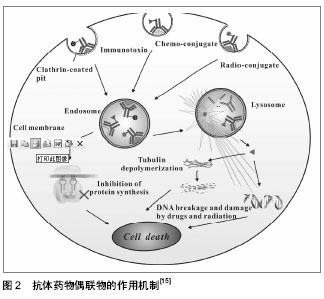
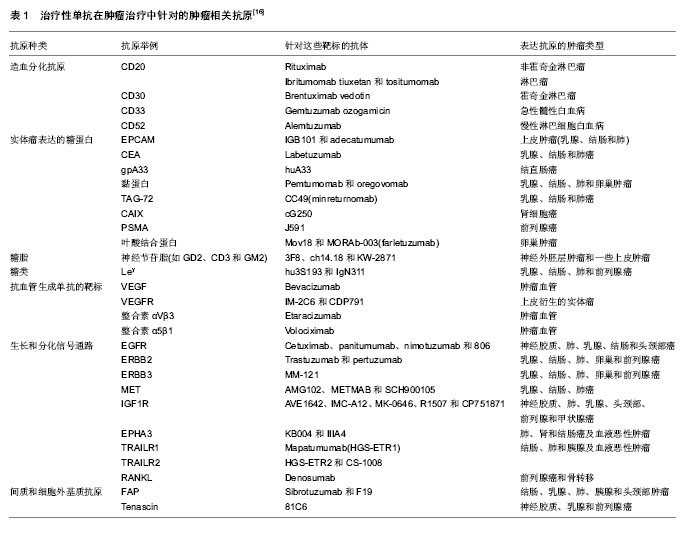
| [1] Dosio F, Brusa P, Cattel L. Immunotoxins and anticancer drug conjugate assemblies: the role of the linkage between components.Toxins (Basel). 2011;3(7):848-883. [2] Polson AG, Calemine-Fenaux J, Chan P,et al. Antibody-drug conjugates for the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: target and linker-drug selection. Cancer Res. 2009;69(6):2358-2364. [3] Zhu GD, Fu YX. Design of next generation antibody drug conjugates.Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2013;48(7):1053-1070.[4] Thurber GM, Schmidt MM, Wittrup KD. Antibody tumor penetration: transport opposed by systemic and antigen-mediated clearance.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008; 60(12): 1421-1434. [5] Hagenbeek A, Gadeberg O, Johnson P,et al. First clinical use of ofatumumab, a novel fully human anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody in relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma: results of a phase 1/2 trial.Blood. 2008;111(12):5486-5495. [6] Miao QF, Shao RG, Zhen YS. An overview of antibody-based cancer therapy.Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012; 47(10):1261-1268.[7] Watanabe TS, Ohtori S, Koda M, et al. Adenoviral gene transfer in the peripheral nervous system.J Orthop Sci. 2006; 11(1):64-69.[8] 甄永苏.抗体药物与肿瘤靶向治疗[J].医学研究杂志, 2007,36(2): 1-2.[9] Pastan I, Hassan R, FitzGerald DJ,et al. Immunotoxin treatment of cancer.Annu Rev Med. 2007;58:221-237.[10] Laske DW, Muraszko KM, Oldfield EH,et al.Intraventricular immunotoxin therapy for leptomeningeal neoplasia. Neurosurgery. 1997;41(5):1039-1049. [11] Weaver M, Laske DW.Transferrin receptor ligand-targeted toxin conjugate (Tf-CRM107) for therapy of malignant gliomas. J Neurooncol. 2003;65(1):3-13.[12] Sun Y, Yu F, Sun BW. Antibody-drug conjugates as targeted cancer therapeutics.Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2009;44(9):943-952.[13] 詹金彪,郑树.天然蛋白毒素的研究和临床应用展望[J].浙江大学学报:医学版,2005,34(3):197-200.[14] Shenoi J, Gopal AK, Press OW, et al. Recent advances in novel radioimmunotherapeutic approaches for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation.Curr Opin Oncol. 2010; 22(2):143-149. [15] Lin L, Ding Q, Tang Q,et al. Antibody-drug conjugates and their application in the treatment of hematological malignancies.Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012;47(10):1287-1296.[16] Scott AM,Wolchok JD,Old LJ. Antibody therapy of cancer.Nat Rev Cancer.2012;12:278-287.[17] Govindan SV, Goldenberg DM. Designing immunoconjugates for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(7): 873-890. [18] Saini KS, Azim HA Jr, Metzger-Filho O,et al. Beyond trastuzumab: new treatment options for HER2-positive breast cancer.Breast. 2011;20 Suppl 3:S20-27.[19] Lewis Phillips GD, Li G, Dugger DL,et al. Targeting HER2-positive breast cancer with trastuzumab-DM1, an antibody-cytotoxic drug conjugate.Cancer Res. 2008;68(22): 9280-9290.[20] Amadori S, Stasi R. Monoclonal antibodies and immunoconjugates in acute myeloid leukemia.Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2006;19(4):715-736.[21] 张敏,朱虹光.抗HER2单克隆抗体研究新进展[J].国外医学:生理、病理科学与临床分册, 2003,23(3):257-259.[22] Shak S.Overview of the trastuzumab (Herceptin) anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody clinical program in HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. Herceptin Multinational Investigator Study Group.Semin Oncol. 1999;26(4 Suppl 12):71-77.[23] Pegram MD, Slamon DJ.Combination therapy with trastuzumab (Herceptin) and cisplatin for chemoresistant metastatic breast cancer: evidence for receptor-enhanced chemosensitivity.Semin Oncol. 1999;26(4 Suppl 12):89-95.[24] Cirstoiu-Hapca A, Buchegger F, Lange N,et al. Benefit of anti-HER2-coated paclitaxel-loaded immuno-nanoparticles in the treatment of disseminated ovarian cancer: Therapeutic efficacy and biodistribution in mice.J Control Release. 2010; 144(3):324-331.[25] 张雷,Gregg Hadley.CD103免疫毒素在同种胰岛移植中的应用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2011,28(2):194-196.[26] Oflazoglu E, Stone IJ, Gordon K,et al. Potent anticarcinoma activity of the humanized anti-CD70 antibody h1F6 conjugated to the tubulin inhibitor auristatin via an uncleavable linker.Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(19):6171-6180.[27] Junutula JR, Flagella KM, Graham RA,et al. Engineered thio- trastuzumab-DM1 conjugate with an improved therapeutic index to target human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(19):4769-4778. [28] Hamblett KJ, Senter PD, Chace DF,et al. Effects of drug loading on the antitumor activity of a monoclonal antibody drug conjugate.Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(20):7063-7070.[29] Lewis Phillips GD, Li G, Dugger DL, et al.Targeting HER2-positive breast cancer with trastuzumab-DM1, an antibody-cytotoxic drug conjugate.Cancer Res. 2008;68(22): 9280-9290. [30] Riley JL, June CH, Blazar BR. Human T regulatory cell therapy: take a billion or so and call me in the morning. Immunity. 2009;30(5):656-665. [31] Mori M, Muroi K, Matsuyama T,et al. Benefits of mycophenolate mofetil for refractory graft-versus-host disease. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2007;48(8):624-631.[32] 郭怡,蔡常洁.CTLA4Ig诱导免疫耐受作用的研究进展[J].国际内科学杂志,2007,34(7):427-431.[33] 金海龙,石炳毅. CTLA-4相关药物与移植免疫研究进展[J].西南国防医药, 2011, 21(12):1410-1412.[34] 罗良生,黄强.基因重组免疫毒素研究进展[J].国外医学:肿瘤学分册,2000,27(5):269-273.[35] 卢丽琨,田利源,汪莉.人源化免疫毒素的研究进展[J].国际药学研究杂志,2009,36(6): 426-430.[36] Tazzari PL, Polito L, Bolognesi A,et al. Immunotoxins containing recombinant anti-CTLA-4 single-chain fragment variable antibodies and saporin: in vitro results and in vivo effects in an acute rejection model.J Immunol. 2001;167(8):4222-4229.[37] Feng Y, Wang D, Yuan R,et al. CD103 expression is required for destruction of pancreatic islet allografts by CD8(+) T cells. J Exp Med. 2002;196(7):877-886.[38] 张雷,Gregg Hadley.CD103分子介导CD8+T淋巴细胞对同种胰岛移植物的损伤[J].中华器官移植杂志,2011,32(2):91-94.[39] Zhang L, Hadley GA. Application of anti-CD103 immunotoxin for saving islet allograft in context of transplantation.Chin Med J (Engl). 2010;123(24):3644-3651.[40] Zhang L, Moffatt-Bruce SD, Gaughan AA,et al. An anti-CD103 immunotoxin promotes long-term survival of pancreatic islet allografts.Am J Transplant. 2009;9(9):2012-2023. [41] Zeng L, Wan L, Chen L,et al. Selective depletion of activated T cells by recombinant immunotoxin containing anti-CTLA-4 single-chain fragment of variable antibody and N-terminal fragment of perforin.Transplant Proc. 2006;38(7):2151-2153.[42] You S, Zuber J, Kuhn C,et al. Induction of allograft tolerance by monoclonal CD3 antibodies: a matter of timing.Am J Transplant. 2012;12(11):2909-2919. [43] 王宗凯,刘煜.抗体偶联药物的有关进展[J].药物生物技术,2011, 18(4): 359-363. |