| [1] Owtad P, Potres Z, Shen G,et al.A histochemical study on condylar cartilage and glenoid fossa during mandibular advancement.Angle Orthod. 2011;81(2):270-276.[2] Barnouti ZP, Owtad P, Shen G,et al.The biological mechanisms of PCNA and BMP in TMJ adaptive remodeling. Angle Orthod. 2011;81(1):91-99. [3] 王昕,罗颂椒,周秀坤,等.功能矫形前伸下颌后幼年大鼠下颌前伸肌的组织化学研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,1992,10(3):220-223. [4] Yagci A, Uysal T, Kara S,et al.The effects of myofunctional appliance treatment on the perioral and masticatory muscles in Class II, Division 1 patients.World J Orthod. 2010;11(2): 117-122.[5] Erdem A, Kilic N, Eröz B.Changes in soft tissue profile and electromyographic activity after activator treatment.Aust Orthod J. 2009;25(2):116-122.[6] 倪琳,刘洪臣,徐娟,等. 功能矫形前伸青春期大鼠下颌对翼外肌Na+/K+-ATPase功能活性的影响[J]. 口腔颌面修复学杂志,2009,10(6):324-326.[7] 黄宁,陈开云,罗颂椒. 青春期大鼠前伸下颌后浅层嚼肌细胞膜乙酰胆碱受体研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2008,26(4): 365-367.[8] Cucina A, Fuso A, Coluccia P,et al. Nicotine inhibits apoptosis and stimulates proliferation in aortic smooth muscle cells through a functional nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.J Surg Res. 2008;150(2):227-235.[9] 赵云罡,徐建兴.线粒体,活性氧和细胞凋亡[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2001,28(2):168-171.[10] Hikim AP, Lue Y, Swerdloff RS.Separation of germ cell apoptosis from toxin-induced cell death by necrosis using in situ end-labeling histochemistry after glutaraldehyde fixation. Tissue Cell. 1997;29(4):487-493.[11] Strasser A, Huang DC, Vaux DL.The role of the bcl-2/ced-9 gene family in cancer and general implications of defects in cell death control for tumourigenesis and resistance to chemotherapy.Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1333(2):F151- F178.[12] Liu J, Liu J, Mao J,et al.Caspase-3-mediated cyclic stretch-induced myoblast apoptosis via a Fas/FasL- independent signaling pathway during myogenesis.J Cell Biochem. 2009;107(4):834-844.[13] So J, Warsh JJ, Li PP.Impaired endoplasmic reticulum stress response in B-lymphoblasts from patients with bipolar-I disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2007;62(2):141-147. [14] Wei J, Rahman S, Ayaub EA,et al.Protein misfolding and endoplasmic reticulum stress in chronic lung disease.Chest. 2013;143(4):1098-1105.[15] Wang Q, He Z, Zhang J,et al.Overexpression of endoplasmic reticulum molecular chaperone GRP94 and GRP78 in human lung cancer tissues and its significance.Cancer Detect Prev. 2005;29(6):544-551.[16] Matsumoto H, Miyazaki S, Matsuyama S,et al.Selection of autophagy or apoptosis in cells exposed to ER-stress depends on ATF4 expression pattern with or without CHOP expression.Biol Open. 2013;2(10):1084-1090. [17] Yoshida H, Okada T, Haze K,et al.ATF6 activated by proteolysis binds in the presence of NF-Y (CBF) directly to the cis-acting element responsible for the mammalian unfolded protein response.Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20(18):6755-6767.[18] Safra M, Ben-Hamo S, Kenyon C,et al.The ire-1 ER stress-response pathway is required for normal secretory-protein metabolism in C. elegans.J Cell Sci. 2013; 126(Pt 18):4136-4146. [19] Jaasma MJ, Jackson WM, Tang RY,et al.Adaptation of cellular mechanical behavior to mechanical loading for osteoblastic cells.J Biomech. 2007;40(9):1938-1945. [20] Brunig M.Numerical simulation of the large elastic-plastic deformation behavior of hydrostatic stress-sensitive solids. International Journal of Plasticity,1999;15(11):1237-1264.[21] Liu J, Wang Y, Yuan X,et al.Cyclic-stretch induces the apoptosis of myoblast by activation of Caspase-3 protease in a magnitude-dependent manner.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2010; 42(12):2004-2011.[22] Tetsunaga T, Furumatsu T, Abe N,et al.Mechanical stretch stimulates integrin alphaVbeta3-mediated collagen expression in human anterior cruciate ligament cells.J Biomech. 2009;42(13):2097-2103. [23] Brink NG, Spragg JH, Roberts DB.The binding of antibodies to Drosophila embryonic cells and their effect on in vitro cell differentiation.Cell Differentiation.1981;10(3):183-191.[24] Du J, Zhou L, Chen X,et al.IFN-γ-primed human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induce tumor cell apoptosis in vitro via tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012;44(8):1305-1314. [25] Yasuharu Yamazaki,Koichi Nakakuki, Masahiko Ozeki,et al. Multidisciplinary Treatment for Correction of Malocclusion due to Maxillofacial Deformity from Fractures: a Report of 2 Patients.Asian Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2009; 21(3-4):114-119.[26] Chen Y, Liu CP, Xu KF,et al.Effect of taurine-conjugated ursodeoxycholic acid on endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis induced by advanced glycation end products in cultured mouse podocytes.Am J Nephrol. 2008;28(6): 1014-1022.[27] 谭家莉.应力条件下成肌细胞增殖、分化和凋亡的调控及其分子机制的探讨[D].西安:第四军医大学, 2010.[28] Hiyama S, Ono PT, Ishiwata Y,et al.Neuromuscular and skeletal adaptations following mandibular forward positioning induced by the Herbst appliance.Angle Orthod. 2000;70(6): 442-453.[29] 阎潇,李菲菲,刘丽娟,等. 核转录因子κB信号通路在应力调控成肌细胞分化中的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(24): 4441-4446.[30] Yoshida H.ER stress and diseases.FEBS J. 2007;274(3): 630-658.[31] Daugaard M, Rohde M, Jäättelä M.The heat shock protein 70 family: Highly homologous proteins with overlapping and distinct functions.FEBS Lett. 2007;581(19):3702-3710.[32] Yu F, Feng J, Harada JN,et al.B cell terminal differentiation factor XBP-1 induces reactivation of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus.FEBS Lett. 2007;581(18): 3485-3488. [33] Okamoto A, Koike M, Yasuda K,et al.Maintaining ATP levels via the suppression of PERK-mediated rRNA synthesis at ER stress.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;394(1):42-47. [34] Chen WT, Zhu G, Pfaffenbach K,et al. GRP78 as a regulator of liver steatosis and cancer progression mediated by loss of the tumor suppressor PTEN.Oncogene. 2013. doi: 10.1038/onc.2013.437. [Epub ahead of print][35] Roller C, Maddalo D.The Molecular Chaperone GRP78/BiP in the Development of Chemoresistance: Mechanism and Possible Treatment.Front Pharmacol. 2013;4:10.[36] Brewer JW.Regulatory crosstalk within the mammalian unfolded protein response.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. [Epub ahead of print][37] Duan X, Zhou Y, Teng X,et al.Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis is activated in vascular calcification.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;387(4): 694-699. [38] Friedman AD.GADD153/CHOP, a DNA damage-inducible protein, reduced CAAT/enhancer binding protein activities and increased apoptosis in 32D c13 myeloid cells.Cancer Res. 1996;56(14):3250-3256.[39] Chen YY, Sun LQ, Wang BA,et al.Palmitate induces autophagy in pancreatic β-cells via endoplasmic reticulum stress and its downstream JNK pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2013; 32(6):1401-1406. [40] Lien YC, Kung HN, Lu KS,et al.Involvement of endoplasmic reticulum stress and activation of MAP kinases in beta-lapachone-induced human prostate cancer cell apoptosis.Histol Histopathol. 2008;23(11):1299-1308.[41] Schroder M, Kaufman RJ.The mammalian unfolded protein response.Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:739-789.[42] Ohyama H, Yamada T, Ohkawa A,et al.Radiation-induced formation of apoptotic bodies in rat thymus.Radiat Res. 1985; 101(1):123-130. |
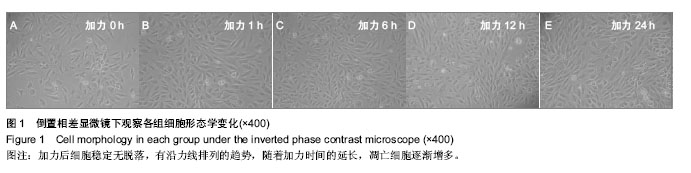
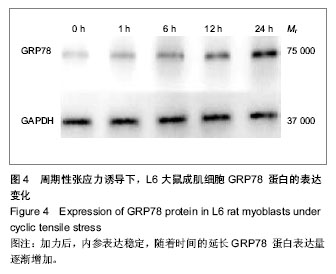
.jpg)