中国组织工程研究 ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (44): 7681-7686.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.44.004
• 肾移植 kidney transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
亲属活体肾移植后供者安全性评价
陆瀚澜,陈 瑜,傅尚希,周梅生,朱有华,郑鳕洋
- 解放军第二军医大学长征医院器官移植研究所,上海市 200003
Safety of kidney donors after living-related kidney transplantation
Lu Han-lan, Chen Yu, Fu Shang-xi, Zhou Mei-sheng, Zhu You-hua, Zheng Xue-yang
- Department of Organ Transplantation, Changzheng Hospital, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200003, China
摘要:
背景:随访研究表明,肾移植对供肾者的安全影响较正常人群无统计学差异,甚至有更高的生活质量。
目的:评价亲属活体肾移植对供者的安全性影响。
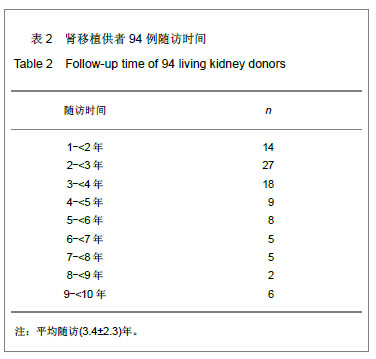
方法:通过门诊定期随访、配合电话随访以及定期举办肾友会的方式对94例亲属活体肾移植后供者随访1-10年,比较肾移植供者供肾前后血清肌酐、血尿和尿蛋白以及血压和血脂的变化情况。
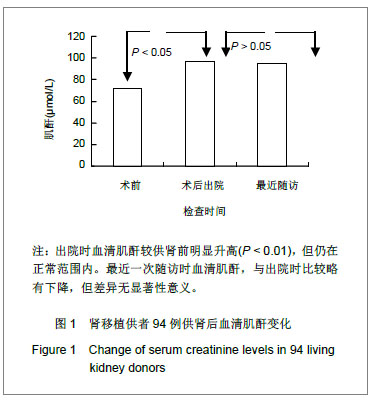
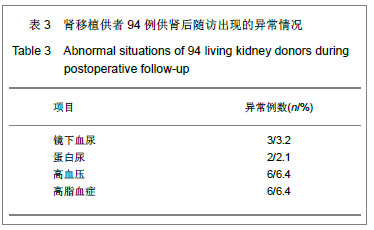
结果与结论:供者供肾后出院时血清肌酐较供肾前明显升高(P < 0.01),但仍在正常范围内,且保持在稳定水平,最近一次随访时血清肌酐与出院时差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。供者供肾后镜下血尿3例(3.2%)、蛋白尿2例(2.1%),经休息后可好转;高血压6例(6.4%);高脂血症6例(6.4%);无一例供者死亡。说明对于健康供者而言,供肾是安全可行的,供肾前全面评估和供肾后长期随访对保障供者的安全有十分重要的意义。
中图分类号:
.jpg)