| [1]Kucia M, Reca R, Campbell FR, et al. A population of very small embryonic-like (VSEL) CXCR4(+)SSEA-1(+)Oct-4+ stem cells identified in adult bone marrow.Leukemia. 2006; 20(5):857-869.
[2]Wojakowski W, Tendera M, Kucia M, et al. Mobilization of bone marrow-derived Oct-4+ SSEA-4+ very small embryonic-like stem cells in patients with acute myocardial infarction.J Am Coll Cardiol.2009;53(1):1-9.
[3]Kucia M , Wysoczynski M, Wu W, et al. Evidence that very small embryonic-like stem cells are mobilized into peripheral blood. Stem Cells. 2008;26(8):2083-2092.
[4]Halasa M, Baskiewicz-Masiuk M, Dabkowska E, et al. An efficient two-step method to purify very small embryonic-like(VSEL) stem cells from umbilical cord blood (UCB). Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 2008;46(2):239-243.
[5]Zuba-Surma EK, Kucia M, Dawn B,et al. Bone marrow-derived pluripotent very small embryonic-like stem cells (VSELs) are mobilized after acute myocardial infarction. J Mol Cell Cardiol.2008;44(5):865-873.
[6]Kucia M, Halasa M,Wysoczynski M, et al.Morphological and molecular characterization of novel population of CXCR4+ SSEA-4+ Oct-4+ very small embryonic-like cells purified from human cord blood: preliminary report.Leukemia. 2007;21(2): 297-303
[7]Paczkowska E, Kucia M, Koziarska D, et al. Clinical evidence that very small embryonic-like stem cells are mobilized into peripheral blood in patients after stroke. Stroke. 2009;40(4): 1237-1244
[8]Ratajczak MZ, Kucia M, Ratajczak J, et al. A multi- instrumental approach to identify and purify very small embryonic like stem cells (VSELs) from adult tissues. Micron. 2009;40(3):386-393.
[9]Zuba-Surma EK, Guo Y, Taher H,et al.Transplantation of expanded bone marrow-derived very small embryonic-like stem cells (VSEL-SCs) improves left ventricular function andremodeling after myocardial infarction. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(6):1319-1328.
[10]Wu JH, Wang HJ, Tan YZ, et al.Characterization of Rat Very Small Embryonic-Like Stem Cells and Cardiac Repair After Cell Transplantation for Myocardial Infarction. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(8):1367-1379.
[11]Zhang Q, Yang YJ, Qian HY, et al.Very small embryonic-like stem cells (VSELs)-a new promising candidate for use in cardiac regeneration. Ageing Res Rev. 2011;10:173-177.
[12]Pang R, Zhang Y, Pan X, et al. Embryonic-like stem cell derived from adult bone marrow: immature morphology, cell surface markers, ultramicrostructure and differentiation into multinucleated fibers in vitro. Cell Mol Biol. 2010;56: 1276-1285.
[13]Bhartiya D, Shaikh A, Nagvenkar P, et al. Very small embryonic-like stem cells with maximum regenerative potential get discarded during cord blood banking and bone marrow processing for autologous stem cell therapy. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21:1-6.
[14]Abdel-Latif A, Zuba-Surma EK, Ziada KM, et al.Evidence of Mobilization of Pluripotent Stem Cells into Peripheral Blood of Patients with Myocardial Ischemia.Exp Hematol.2010; 38: 1131-1142.
[15]郭慧娟,王健,张兴秀,等. 粒细胞集落刺激因子对骨髓极小胚胎样干细胞的动员和募集[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 15(14):2530-2534.
[16]Kucia M, Wysoczynski M, Ratajczak J, et al. Identification of very small embryonic like (VSEL) stem cells in bone marrow. Cell Tissue Res.2008;331(1):125-134.
[17]Shin DM, Zuba-Surma EK, Wu W, et al. Novel epigenetic mechanisms that control pluripotency and quiescence of adult bone marrow-derived Oct4(+) very small embryonic-like stem cells. Leukemia. 2009;23:2042-2051.
[18]杨跃进,王红.一种分选人骨髓极小胚胎样干细胞的方法. 中国 201110132905.0[P].2011-11-02.
[19]Lee JB,Song JM,Lee JE , et al.Available human feeder cells for the maintenance of human embryonic stem cells. Reproduction. 2004;128(6):727-735.
[20]Li F,Liu Y, Chen D,et al. Leukemia inhibitory factor-expressing human embryonic lung fibroblasts as feeder cells for human embryonic germ cells.Cells Tissues Organs. 2007;186 (4): 221-228
[21]Sidhu KS , Lie KH, Tueh BE.Transgenic human fetal fibroblasts as feeder layer for human embryonic stem cell lineage selection. Stem Cells Dev. 2006;15(5):741-747
[22]Kibschull M, Mileikovsky M, Michael IP, et al. Human embryonic fibroblasts support single cell enzymatic expansion of human embryonic stem cells in xeno-free cultures. Stem Cell Res. 2011; 6(1):70-82.
[23]中华人民共和国国务院.医疗机构管理条例. 1994-2-26.
[24]Wang YB, Chen B, Wang YC, et al. The feeder layer of human embryonic fibroblasts supports the growth of human spermatogonial stem cells. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2008; 14(12):1063-1068.
[25]Lapan AD, Gussoni E. Isolation and characterization of human fetal myoblasts. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;798:3-19.
[26]常志存,窦忠英,高志敏.人胚胎成纤维细胞的冷冻保存[J].西北农业学报,2000,9(1):6-9.
[27]Na RS, Zhao QJ, Jin da P, et al. Establishment and biological characteristics of Ujumqin sheep fibroblast line. Cytotechnology. 2010;62(1):43-52.
[28]余树民,王晗,窦忠英. 丝裂霉素C处理后鼠胚成纤维细胞活力分析[J].西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版, 2007,35(5):1-5.
[29]Paczkowska E,Dabkowska E,Nowacki P,et al. Stem cell-based therapy in central nervous system diseases. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2009;43(6):550-558.
[30]Paczkowska E,Kucia M,Koziarska D, et al. Clinical evidence that very small embryonic-like stem cells are mobilized into peripheral blood in patients after stroke. Stroke. 2009;(4): 1237-1244.
[31]Huang Y,Kucia M,Hussain LR,et al. Bone marrow transplantation temporarily improves pancreatic function in streptozotocin-induced diabetes: potential involvement of very small embryonic-like cells. Transplantation. 2010;89(6): 677-685.
[32]Liu Y,Gao L,Zuba-Surma EK, et al. Identification of small Sca-1(+), Lin(-), CD45(-) multipotential cells in the neonatal murine retina. Exp Hematol.2009;(9):1096-1107.
[33]Havens AM, Shiozawa Y, Jung Y, et al. Human very small embryonic-like cells generate skeletal structures, in vivo. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(4):622-630.
[34]陈永珍,李芳,陈谦,等.人胚胎成纤维细胞对人胚胎生殖细胞生长的作用[J].解剖学杂志,2005,28(6):625-628.
[35]王英, 何津, 李玉林.人胚胎成纤维细胞的分离、培养和鉴定及人胚胎生殖细胞体外生长所需细胞因子的表达[J].吉林大学学报: 医学版, 2007,33(2):245-248.
[36]Nieto A, Cabrera CM, Catalina P, et al. Effect of mitomycin-C on human foreskin fibroblasts used as feeders in human embryonic stem cells: immunocytochemistry MIB1 score and DNA ploidy and apoptosis evaluated by flow cytometry. Cell Biol Int. 2007;31(3):269-278. |
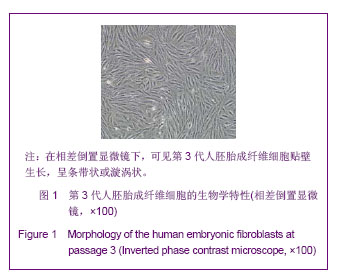
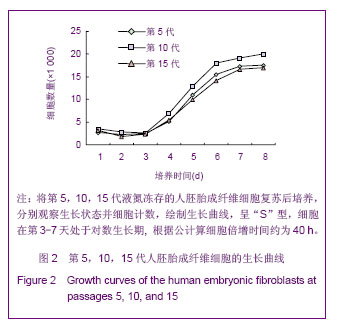
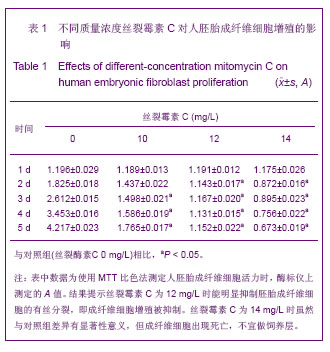
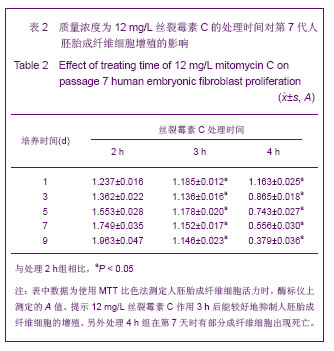
.jpg)