3.1 非类固醇抗炎药及其对骨质疏松性骨折愈合的影响 非类固醇抗炎药从1860年的乙酰水杨酸到2000年的罗非昔布,经历了一个由发展到再认识的过程。非类固醇抗炎药其重要的药理作用特征是抗炎、镇痛和不同程度的退热效应,虽然非类固醇抗炎药的化学结构各不相同,但有相似的作用机制:主要通过抑制环氧化酶使前列腺素合成减少而产生镇痛作用。非类固醇抗炎药的作用一般在外周,主要治疗轻度至中度疼痛。20世纪90年代,经研究证实环氧化酶有2种同工酶(环氧化酶1和环氧化酶2),它们在结构和功能上具有重要差别。非类固醇抗炎药对环氧化酶1和环氧化酶2的不同抑制作用,既可产生类似的治疗效应,但又存在不同的安全特性。1971年John Vane用环氧化酶理论解释了非类固醇抗炎药的作用机制:“阿司匹林样药物”(Aspirin-like drugs)的作用机制是抑制前列腺素的合成;而非类固醇抗炎药治疗作用及其主要副作用都是阻碍前列腺素合成的结果
[18-22]。
起初人们以为环氧化酶1是生理性酶,维持生理平衡,全是良性作用;而环氧化酶2是病理性酶或诱导酶,参与炎症反应,全是恶性作用。由此期望研制新型的“选择性环氧化酶2抑制剂”,在完全抑制环氧化酶2作用的同时,不影响环氧化酶1作用。1999年昔布类药物(选择性环氧化酶2抑制剂)上市,经过几年的临床实践发现,昔布类药物又引起了一些新的临床问题,其中包括心血管、肾脏等不良反应。因此,一些学者提出应该对环氧化酶理论进行再认识:一方面只抑制环氧化酶2、不抑制环氧化酶1并不合适;另一方面,环氧化酶2也有其重要的生理功能,抑制了环氧化酶2同样可产生相应不良作用。其中,环氧化酶1以消化道不良反应为主,环氧化酶2则以心血管不良反应为主。研究还发现:非类固醇抗炎药具有确切的最高限度效应,即在一个特定点上增加药物的剂量水平,不但不能增加镇痛作用,反而增加副作用。因此,临床上要注意避免两种或两种以上非类固醇抗炎药同时使用,只有在一种非类固醇抗炎药足量使用一两周无效后才考虑改为另一种。
目前非类固醇抗炎药在骨关节疾病和创伤骨科方面的应用相当普遍。然而近期研究发现,非类固醇抗炎药可能是导致骨折延迟愈合,甚至骨折不愈合的原因之一。Nwadinigwe等[21]进行了一项回顾性研究,分析其作用的可能机制为:①非类固醇抗炎药可以可逆或不可逆的阻断环氧化酶途径抑制前列腺素的合成,而前列腺素不单单是极为重要的炎症递质,同时也是强有力的骨吸收刺激剂。前列腺素通过增强破骨细胞的活性,从而加快骨折断端坏死骨以及机化组织的吸收,有利于新生血管的长入;此外前列腺素还能刺激血管及成骨细胞增殖。②进一步研究发现,环氧化酶2的转录调节是骨代谢强有力的调节因子,针对环氧化酶2的特异性抑制剂可以同时影响成骨作用和骨吸收过程而阻断骨形成。 因此环氧化酶2在骨折愈合的过程中起重要作用,它可以促进软骨内骨化过程,从而促进骨折愈合[23-26]。
研究发现非类固醇抗炎药主要通过抑制环氧化酶2的生物活性,主要影响骨折愈合的早期,表现为软骨痂期的延长,骨折端软骨细胞和间充质细胞残留,成骨活动减少。而骨质疏松性骨折愈合过程分为纤维骨痂期、软骨骨痂期和骨性骨痂期。骨质疏松性骨折愈合的组织细胞学观察表明:纤维骨痂期主要是成纤维细胞合成的Ⅲ型胶原;软骨骨痂期主要是成软骨细胞合成、分泌的Ⅱ型胶原;骨性骨痂期主要为软骨内成骨的出现和发展,Ⅱ型胶原逐渐消失,被抗张力性能较强的Ⅰ型胶原所取代[27-29]。
一般来说,实验性骨质疏松性骨折的愈合方式与一般骨折愈合过程基本相似,膜内成骨及软骨内成骨共同参与了骨质疏松性骨折的修复,但以软骨内成骨为主。软骨内成骨迟缓,骨性骨痂改造加速(骨吸收大于骨形成),骨痂内胶原纤维疏松、排列紊乱且与主应力方向不一致,导致骨折愈合质量降低。因而使用非类固醇抗炎药可能会进一步影响骨质疏松性骨折的愈合。
3.2 中枢性镇痛药及其对骨质疏松性骨折愈合的影响 中枢性镇痛药是一类作用于中枢神经系统,能消除或抑制疼痛、改变对疼痛情绪反应的药物。中枢性镇痛药按强度分为弱阿片药(与受体不饱和结合)和强阿片药;按受体激动类型分为激动药、部分激动药、激动拮抗剂和拮抗药。最早使用的镇痛药是来自于罂粟蒴果浆汁的干燥物——阿片及其提纯品吗啡;第二次世界大战前后合成了哌替啶、美沙酮等一系列具有吗啡样作用的药物,具有强大的镇痛作用,可用于各种原因引起的急慢性疼痛。中枢性镇痛药与非类固醇抗炎药相比,具有明显呼吸抑制、镇静或欣快等中枢作用;长期使用易致耐受性、依赖性和成瘾性,造成用药者精神变态而出现药物滥用及停药戒断症状,因此,在获得镇痛作用的同时,应当积极预防中枢性镇痛药的相关不良反应。中枢性镇痛药的镇痛机制在于:①与位于脊髓背角胶状质感觉神经元上的阿片类受体结合,抑制P物质的释放,从而阻止疼痛传入脑内。②作用于大脑疼痛中枢,发挥下行的疼痛抑制作用。阿片类受体主要有μ、κ、δ 3种,从功能上还可能存在ε、σ等。中枢性镇痛药是目前发现镇痛作用最强的药物,并且没有“天花板”效应,镇痛作用随剂量的增加而增加。
实验应用的盐酸曲马多是一种弱中枢性镇痛药,它与阿片类受体具有较低的亲和力,镇痛效果可达吗啡的1/10-1/6,能满足大部分临床镇痛的需要。盐酸曲马多具有弱阿片类和非阿片类二者的性质。其阿片类性质与μ阿片受体激动有关;非阿片类性质是抑制了突触前膜对去甲肾上腺素和5-羟色胺的再摄取。盐酸曲马多的依赖性较低,常规剂量下不会产生呼吸抑制及平滑肌痉挛,对血液动力学亦无显著影响;此外盐酸曲马多不易产生依赖性,是一种较为安全有效的药物。
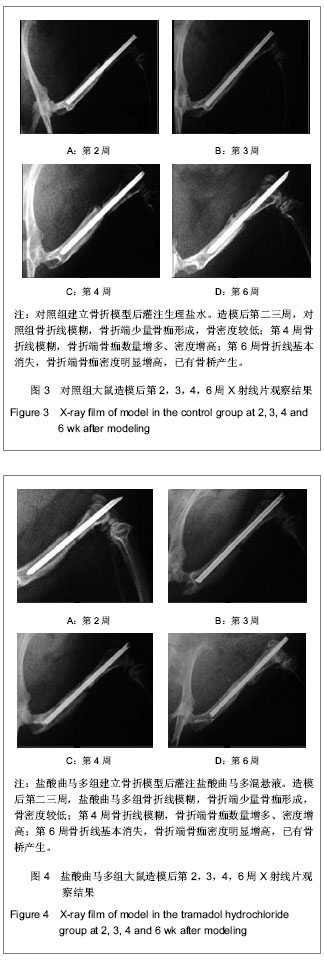
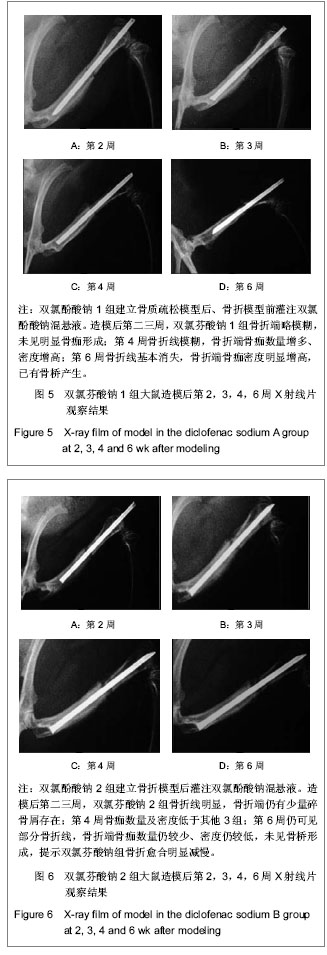
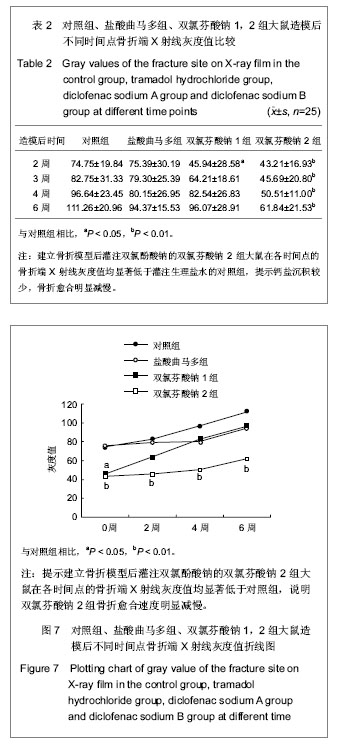
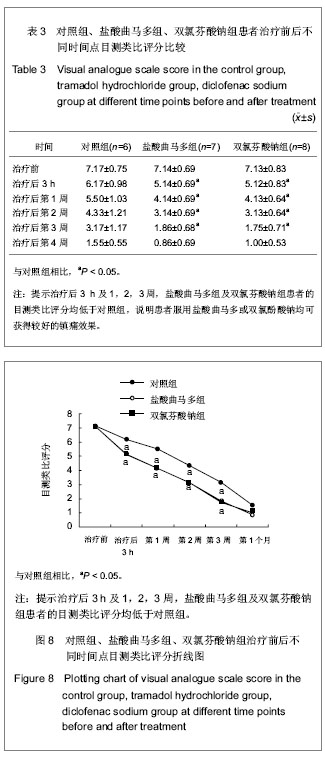
3.3 动物实验检测指标及其意义 实验影像学观察发现,对照组、盐酸曲马多组在术后第2-4周骨折线逐渐模糊消失,骨折端有骨桥产生,开始改造塑形;术后第6周骨折线基本消失,新生骨痂量较多。双氯芬酸钠1组在术后第二三周骨折线仍明显存在,新生骨痂量少,没有骨桥产生;在术后第4周骨折线逐渐模糊消失,骨折端有骨桥产生,开始改造塑形;术后第6周骨折线基本消失。双氯芬酸钠2组在术后第二三周骨折线也仍然明显存在,新生骨痂量少,没有骨桥产生。与双氯芬酸钠1组不同的是,双氯芬酸钠2组的骨折线在术后第4周时依旧明显,新生骨痂量少,没有骨桥产生。双氯芬酸钠2组在术后第6周时骨折线仍然模糊可见,且新生骨痂量仍然较少,骨痂密度低。
实验通过测定灰度值定量地评价了骨折愈合程度,原理在于:骨组织中钙盐沉积的多少可以通过X射线穿透量(即灰度)的多少来体现。在设定相同曝光参数摄片后,通过计算机图像分析系统可以测定骨折端的X射线灰度值,定量地反映新生骨中钙盐的沉积情况。灰度值高则钙盐沉积多,灰度值低则相反。术后第2,3,4,6周,各组X射线的灰度值随着时间推移逐渐增加,符合一般骨折愈合过程。但是双氯芬酸钠2组的骨折愈合时间明显延长,可见双氯酚酸钠影响了骨质疏松性骨折的愈合。
有研究采用Wistar大鼠左侧胫骨骨折模型,通过CT扫描、生物力学以及组织学观察,也发现口服双氯酚酸钠会显著延迟骨折愈合。这里需特别指出,本实验中共有2组大鼠灌注了双氯酚酸钠,分别为双氯芬酸钠1组和双氯芬酸钠2组。其中双氯芬酸钠1组为先灌注双氯酚酸钠6周后建立骨折模型,而双氯芬酸钠2组为建立骨折模型后灌注双氯酚酸钠。由于给药时间的不同,双氯芬酸钠1组和双氯芬酸钠2组相比也得到了不同的结果:双氯芬酸钠1组在术后第2周与对照组相比差异有显著性意义,在术后第3,4,6周差异无显著性意义;双氯芬酸钠2组在术后第2,3,4,6周与对照组相比差异均有显著性意义。
通过对双氯芬酸钠1组和双氯芬酸钠2组结果的分析,得到了这样的结论:①双氯酚酸钠的经短期使用停药后其抑制骨质疏松性骨折愈合的不良效应将会消散,这个结论也和国外文献相同[6]。②双氯酚酸钠可以在早期可逆的阻断环氧化酶途径,停药后或甚至在用药期间环氧化酶途径即可恢复,则双氯酚酸钠对骨折愈合的影响减小。但是双氯酚酸钠的作用时效具体时间段以及环氧化酶途径可逆性恢复的时间,以及其具体影响机制,尚需要进一步的研究得出。
实验中发现部分大鼠发生了内固定物退针现象,其中对照组1例,盐酸曲马多组1例,双氯芬酸钠1组1例,双氯芬酸钠2组5例。其中,对照组和盐酸曲马多组发生在第2周;双氯芬酸钠1组发生在第3周;双氯芬酸钠2组3例发生在第2周,2例发生在第3周。分析原因为:①服用止痛药物后,骨折早期大鼠即可进行大量活动,致使骨折不稳定,内固定脱出。②双氯芬酸钠2组在内固定脱出中占多数,可能与双氯酚酸钠延迟骨质疏松性骨折愈合,再加上大鼠大量活动导致内固定无法有效固定而脱出。发生退针现象的大鼠均剔除出实验,未参加最后的实验结果统计。
实验选择双氯酚酸钠和盐酸曲马多作为实验对象,原因在于:双氯酚酸钠是国内外研究非类固醇抗炎药的典型代表,它非选择性抑制环氧化酶1和环氧化酶2,广泛应用于临床镇痛。盐酸曲马多是一种临床常用的弱阿片类镇痛药,镇痛效果显著,且成瘾性小,使用安全。
本实验结果证实:双氯酚酸钠能减缓骨质疏松性SD大鼠股骨干骨折愈合的速度,同时降低骨折愈合的强度,与国外文献的报告基本一致,而盐酸曲马多对骨质疏松性SD大鼠股骨干骨折愈合并无明显不利影响。因为其独特的作用机理,不参与骨折局部的炎症反应,因此对骨折端微环境影响甚少,不会减少骨质疏松性骨折愈合所需的细胞因子(如骨形态发生蛋白、白细胞介素6等)和生长因子(胰岛素样生长因子、转化生长因子、血管内皮细胞生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子等)。其次,盐酸曲马多不影响环氧化酶活性,也不参与前列腺素转化过程,因此不会抑制骨折愈合血肿期对死骨及机化组织的吸收,也不会延缓软骨细胞转化为成骨细胞。因此理论上分析,盐酸曲马多对骨质疏松性骨折愈合并无不利影响,但它对骨质疏松性骨折愈合的影响究竟如何,国内外尚未见文献报告。
3.4 临床观察中各检测指标及其意义 根据国际疼痛研究会对疼痛的定义“一种不愉快的感觉和实际的或潜在的组织损伤所引发的情感经历;或者就这一损伤所做的描述”,疼痛是一种不愉快的生理体验;它广泛出现于各种疾病的病程中,是临床最为常见的主诉之一。骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折是老年人最常见的骨折之一,上海市以T2SD为标准,女性发病率约为61.8%。这些患者既要经历骨折时的急性疼痛,还要忍受骨质疏松症本身因骨量丢失引起的全身慢性疼痛以及骨折后残留的慢性疼痛。
按照现代脊柱力学理论,椎体压缩性骨折破坏了三柱的结构,影响了脊柱的整体稳定性及负重能力,在条件允许情况下,大多数患者可以手术复位加内固定,以恢复脊柱的正常力学结构,减少后遗症。老年骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折患者,由于骨质疏松较严重、很少引起神经损伤,加上惧怕手术等多种因素,大多数患有骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折腰椎压缩的老年患者,现在仍选择用非手术治疗。而镇痛是非手术治疗先决条件之一。如何规范骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折疼痛的治疗,提高患者生活质量是摆在骨科医生和药师面前的一个难题。
目前药物镇痛依旧是临床上首选急慢性疼痛的治疗方式。主要包括:非类固醇抗炎药、中枢性镇痛药、辅助型镇痛药(这类药主要适应证不是疼痛,但是可以治疗某些疼痛性疾病的药物,如抗抑郁药、抗惊厥药等);还有一些其他类药物,如α2-肾上腺素能受体激动剂、氯胺酮、利多卡因、NMDA受体拮抗剂、降钙素等。其中非类固醇抗炎药和中枢性镇痛药是骨科门急诊中用于治疗骨质疏松性胸腰椎压缩性骨折疼痛的一线药物,疗效肯定。Manuele等[11]在老年严重性骨质疏松症的治疗中偶然发现非类固醇药物对治疗有相反作用,抑制了骨钙沉积;Riew等[30]发现非类固醇抗炎药能降低脊柱融合术后骨融合的速度和强度。但是,非类固醇抗炎药对骨质疏松性骨折愈合是否有影响,国内外相关文献报道较少。
文章中临床观察选择55-70岁的女性作为研究对象,3组患者的年龄及体质量差异无显著性意义。由于骨折愈合受多方面因素影响,如年龄、饮食、生理和心理状况以及是否服用药物等。为了排除干扰,剔除了胸腰椎陈旧性骨折者、大量吸烟饮酒史、长期服用激素史者以及因胃部疾病不能耐受用药者。
实验中用目测类比评分法评定患者的疼痛情况。在首诊日及第1,2,3周复诊日,盐酸曲马多组和双氯芬酸钠组的目测类比评分要低于对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.05)。第4周复诊日,各组的目测类比评分差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。说明患者服用盐酸曲马多或双氯酚酸钠均可获得较好的镇痛效果。
骨折临床愈合标准是临床上判断骨折愈合情况的重要指标。本实验结果提示盐酸曲马多组和双氯酚酸钠组与对照组相比较,平均骨折临床愈合时间差异无显著性意义,可能是:①观察病例数较少。②随访时间跨度较大。
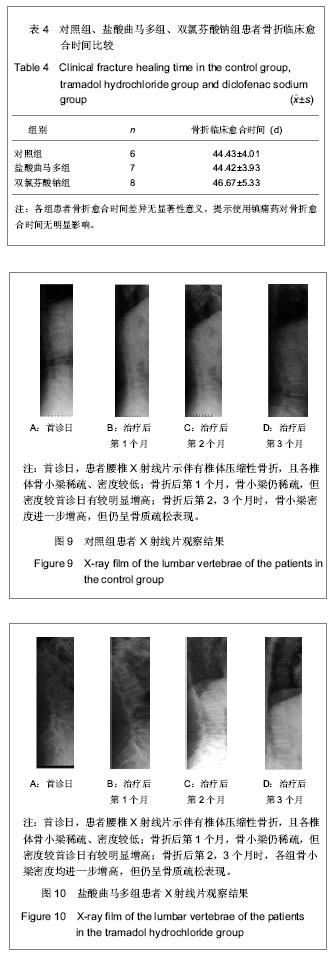
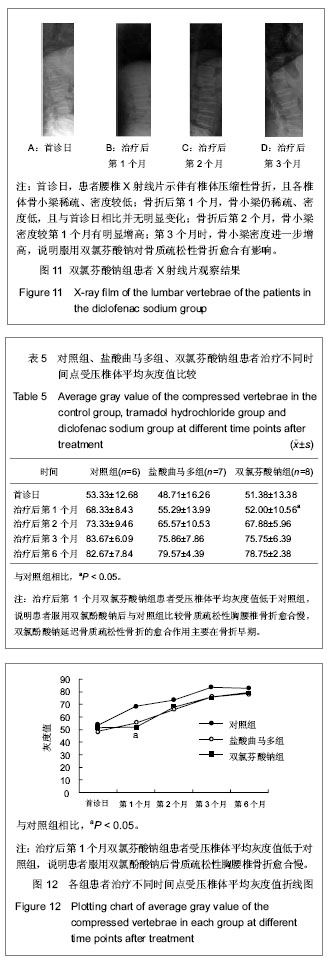
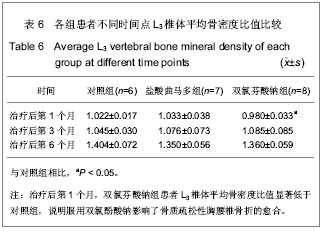
从影像学观察来看,对照组、盐酸曲马多组在首诊日X射线片可见椎体压缩性骨折,各椎体骨小梁稀疏、密度低,在骨折后的第1,2,3,6个月复诊日,X射线各椎体骨小梁密度递增,但仍然符合骨质疏松影像学表现;双氯芬酸钠组在首诊日的X射线片各椎体骨小梁也为稀疏、低密度表现。但与对照组、盐酸曲马多组不同的是,在骨折后第1个月复诊日,其X射线示各椎体骨小梁密度未见明显增多。而在骨折后2,3,6个月复诊日X射线各椎体骨小梁密度递增。比较各组首诊日X射线片和1,2,3,6个月的X射线片可以发现各组的受压椎体的平均骨灰度值呈递增状态,这符合骨折愈合一般过程。由于胸腰椎压缩性骨折的特殊性,无法像管状骨骨折那样测量其骨折端灰度值,而只能测量受压椎体的平均灰度值。各组原始平均灰度值差异无显著性意义,骨折后第1个月双氯芬酸钠组的灰度值较低与对照组比较差异有显著性意义,说明双氯芬酸钠组服用双氯酚酸钠后与对照组比较骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折愈合慢。停药1个月后,各组平均骨灰度值差异无显著性意义,说明双氯酚酸钠延迟骨质疏松性骨折的愈合作用主要在骨折早期。
另外,X射线片观察,双氯酚酸钠组有2例患者的椎体高度在骨折后第1,2个月的复诊日发现进一步压缩,这可能与服用双氯酚酸钠后骨质疏松性骨折愈合过程中软骨内成骨迟缓,骨痂内胶原纤维疏松、排列紊乱且与主应力方向不一致,导致骨折愈合质量降低,椎体高度进一步丢失。为了排除患者没有绝对卧床,经过反复询问,患者坚决否认。
骨密度测量结果,骨折后第1个月时双氯芬酸钠组平均骨密度值较低,与对照组比较差异有显著性意义,这可能是:①骨质疏松症患者虽服用了骨化三醇治疗但治疗早期药物的作用效果尚不明显。②服用双氯酚酸钠影响了骨质疏松性胸腰椎骨折的愈合。骨折后第3,6个月各组患者的骨密度值比较差异无显著性意义,说明停止服用双氯酚酸钠一定时间后,其对骨质疏松性骨折愈合的影响不再明显。
结论:文章中通过动物实验和临床观察结果发现,非类固醇抗炎药会延缓骨质疏松性骨折愈合时间,降低骨质疏松性骨折愈合强度,且主要影响骨质疏松性骨折的早期愈合。因此建议骨质疏松性骨折急性期患者不宜首选非类固醇药物,可选用中枢性镇痛药,如盐酸曲马多等。
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)